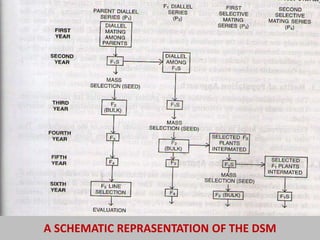
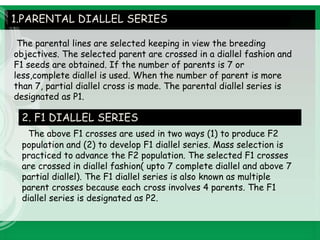
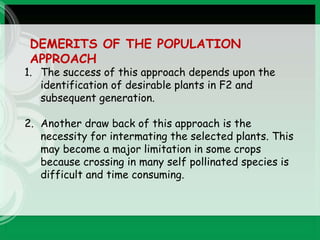
This document discusses the diallel selective mating approach (DSM) for genetic improvement of autogamous crops. DSM involves three steps: 1) a parental diallel series of crosses between multiple parents, 2) F1 diallel series of crosses between F1 plants, and 3) selective mating series where selected F2 plants are intercrossed and selfed in successive generations. The goal is to accumulate desirable genes and increase recombination through restoring heterozygosity via intermating selected plants over multiple cycles. While it broadens the genetic base, DSM is more complex than pedigree methods and success depends on identifying desirable plants in segregating generations.