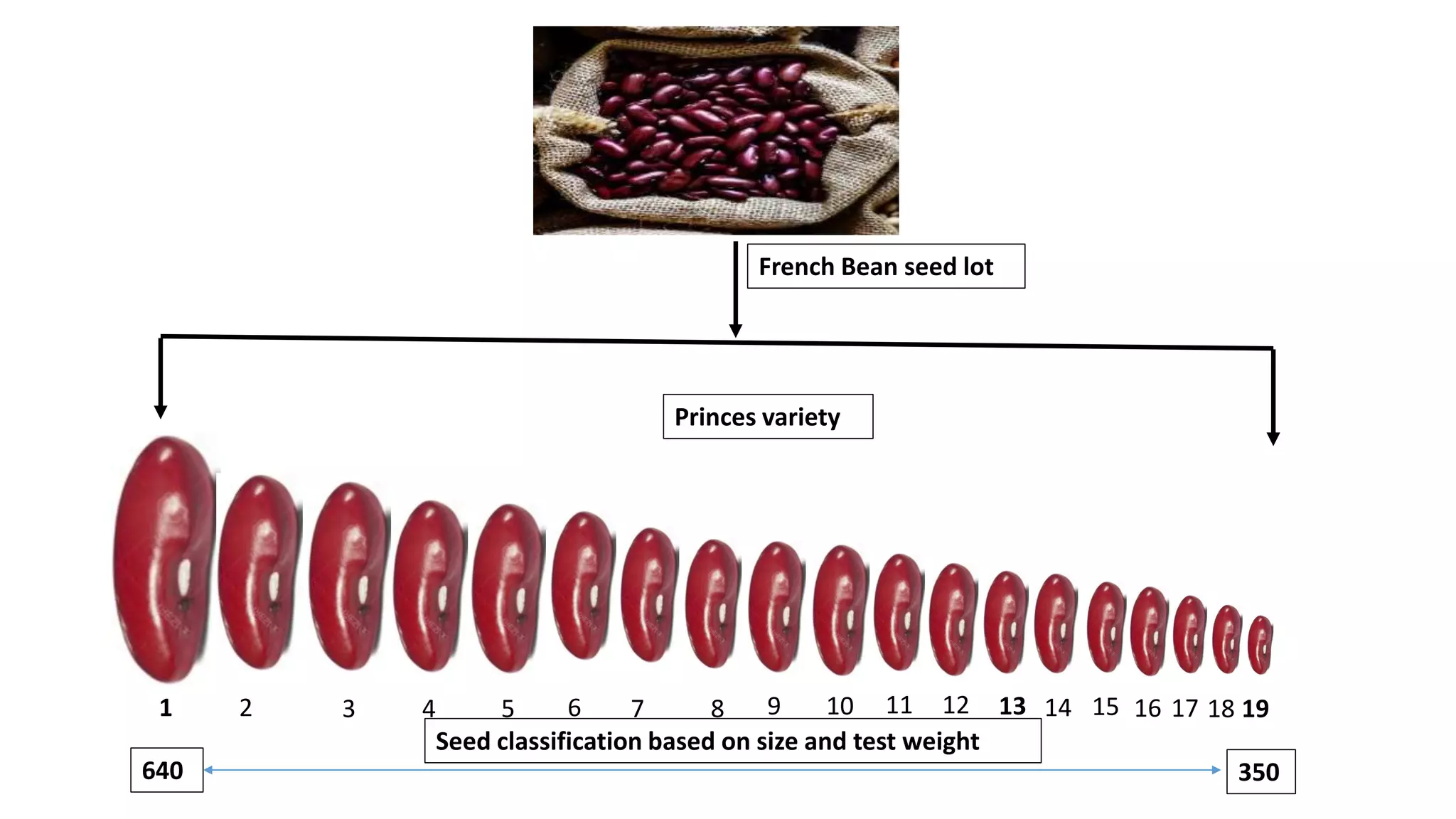
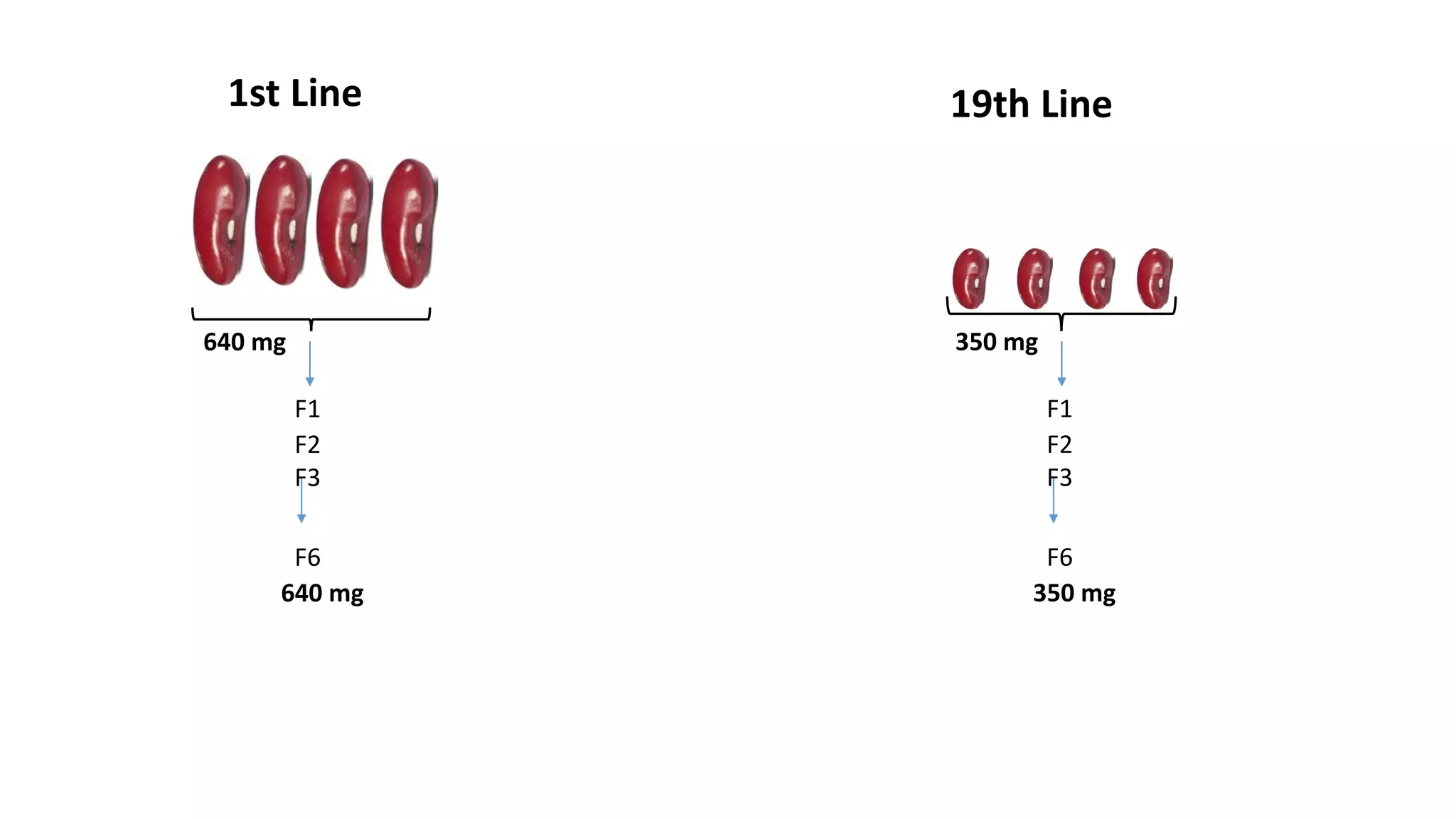
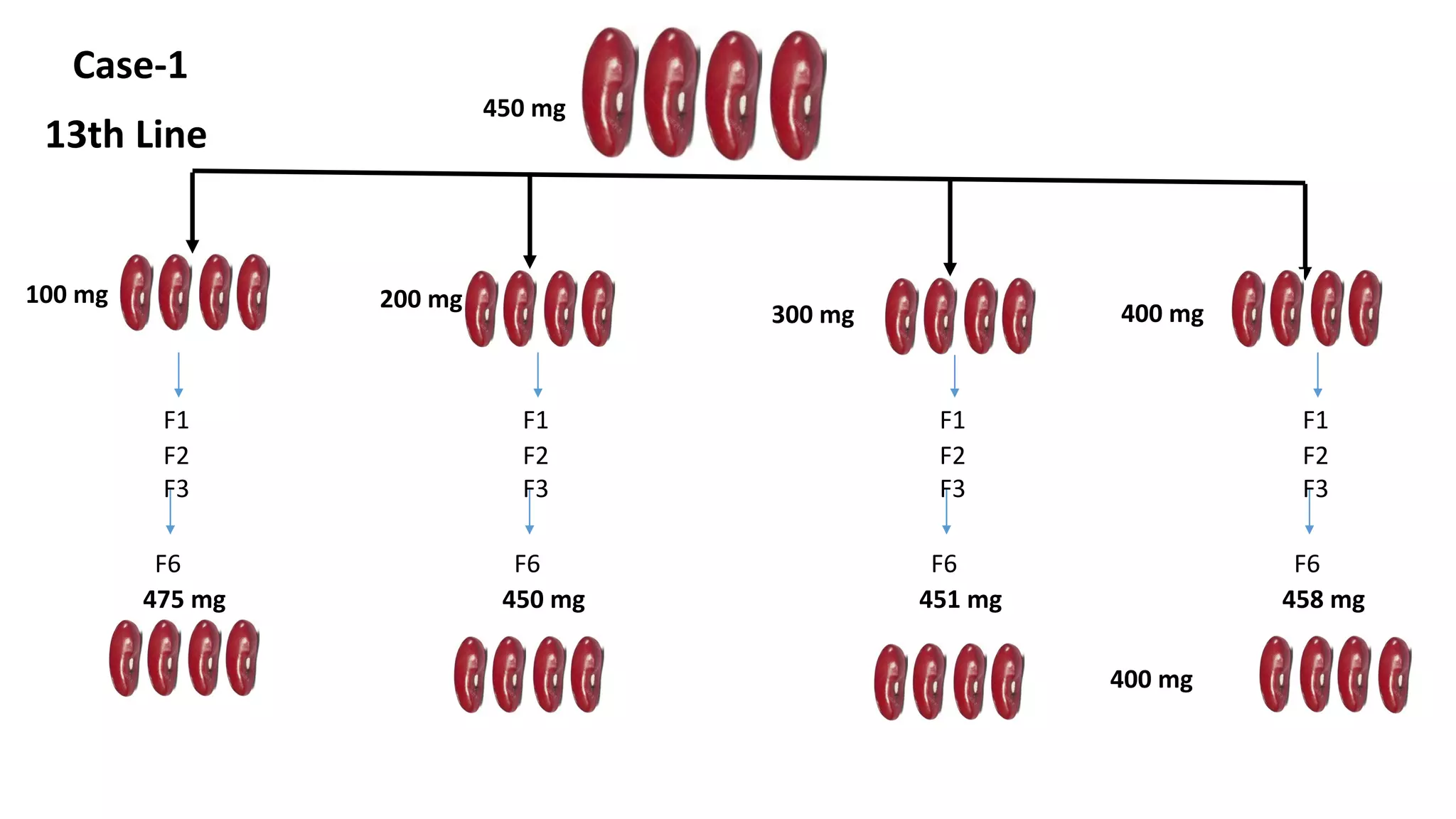
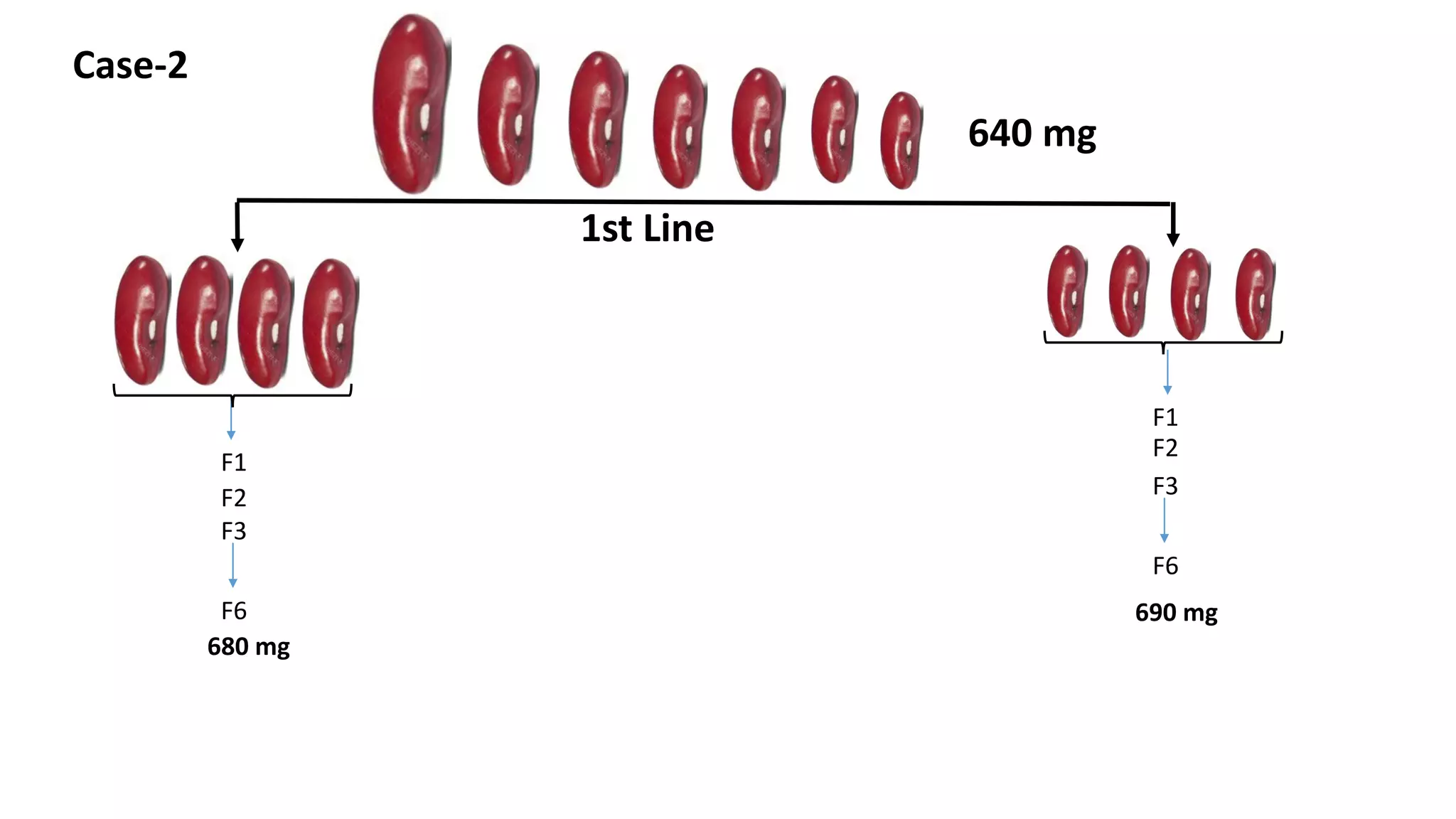
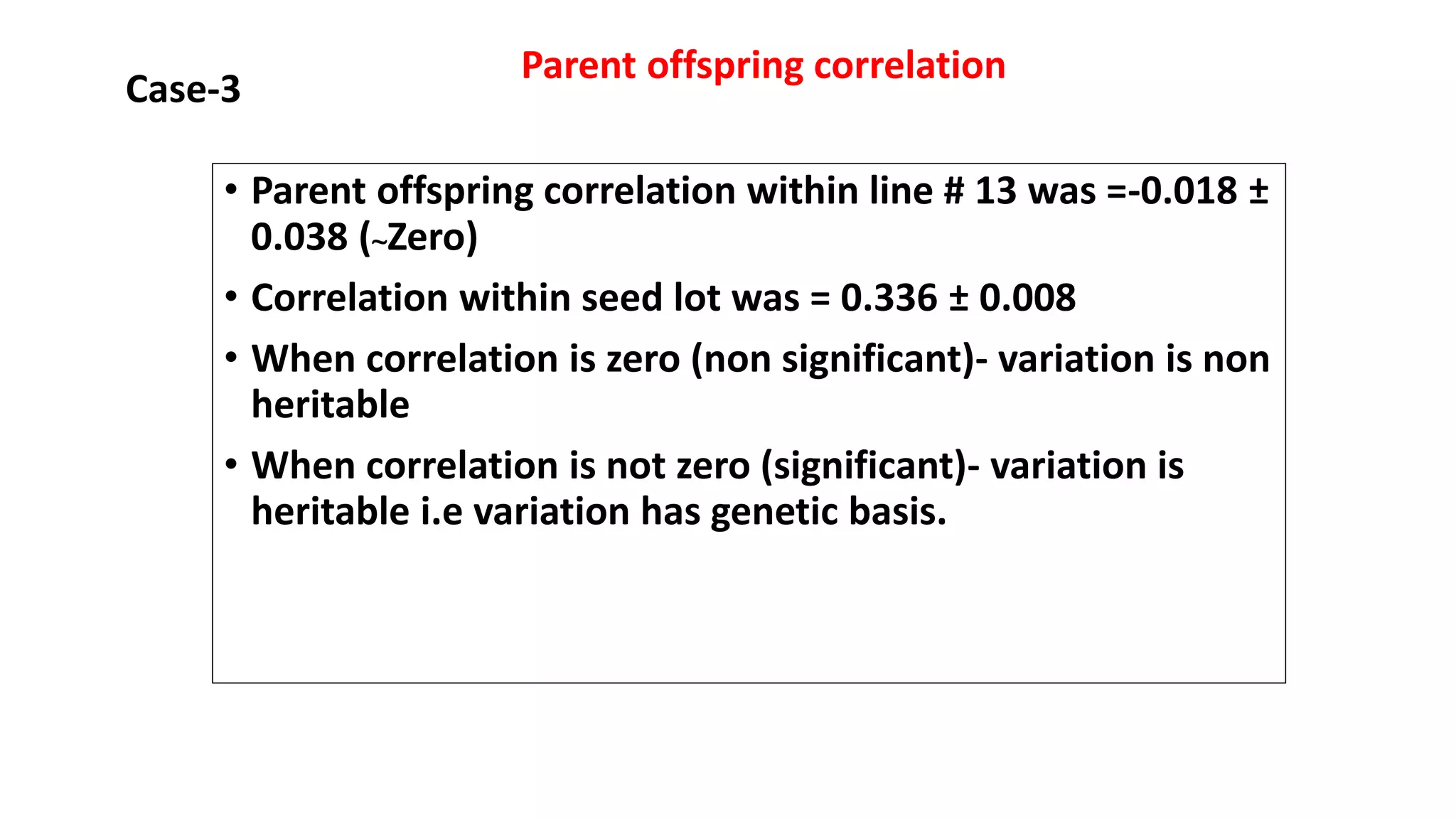
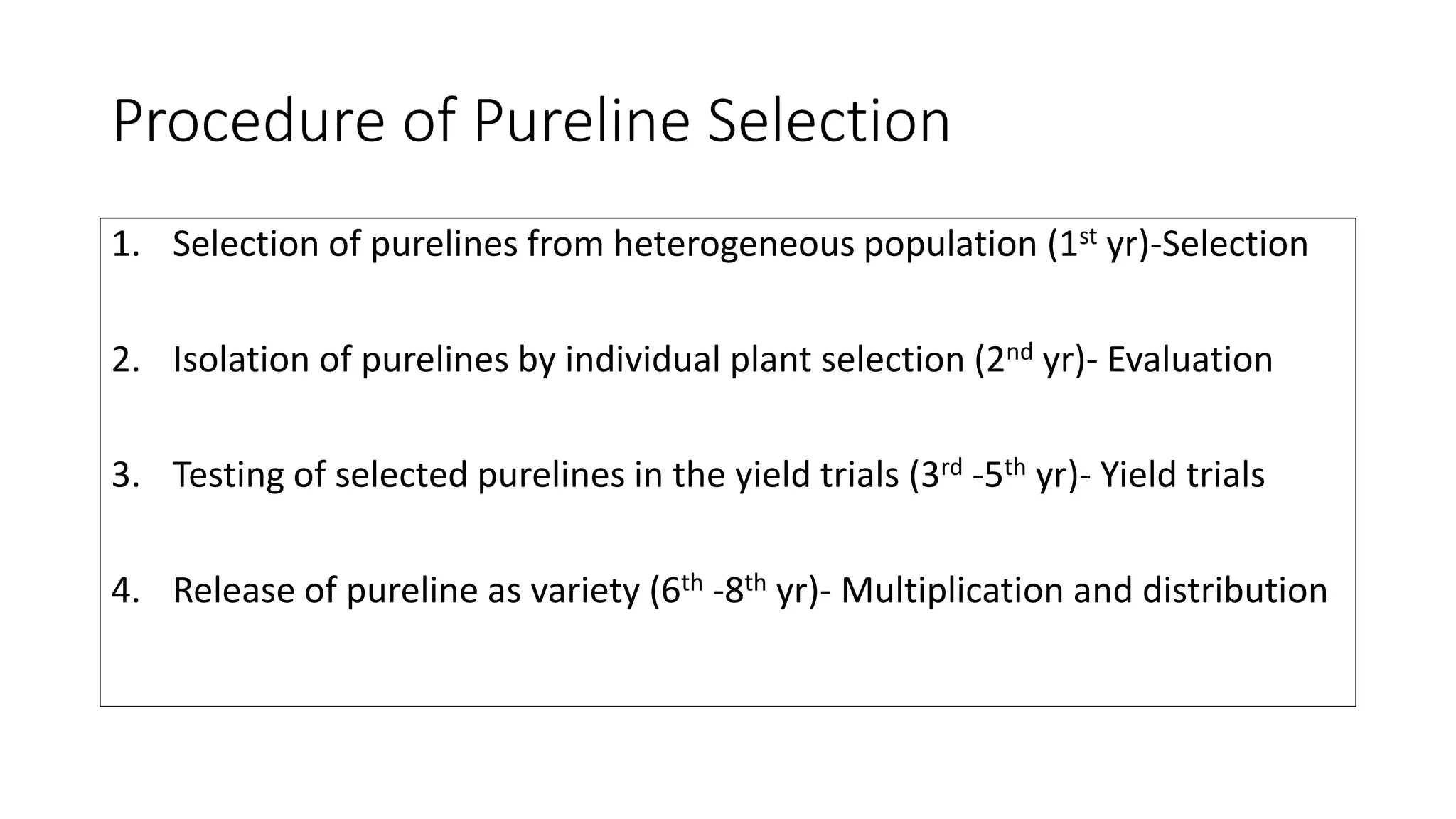
Pureline selection involves the progeny of single homozygous self-pollinated crops, leading to non-heritable variation due to environmental factors. It is primarily used to improve self-pollinated crops, with a systematic process of selection, isolation, testing, and release over several years. The method is advantageous for its efficiency and uniformity but has limitations regarding adaptability and genetic diversity.