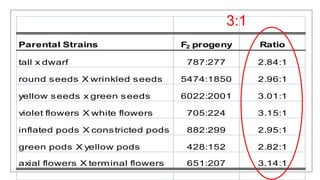
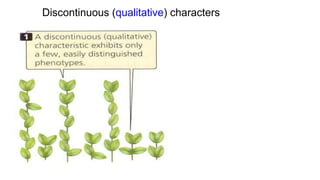
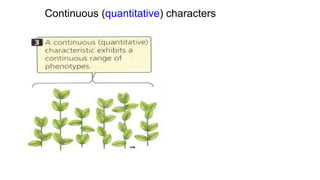
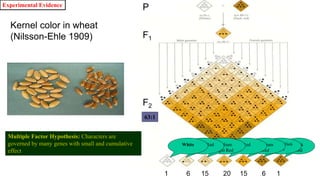
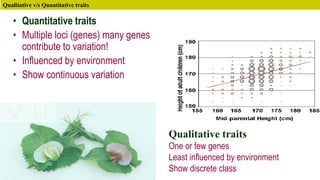
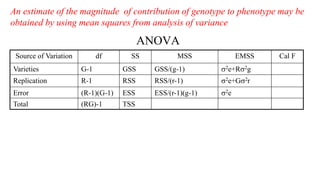
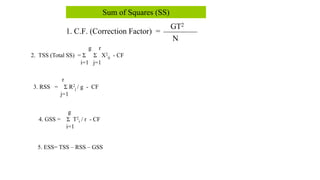
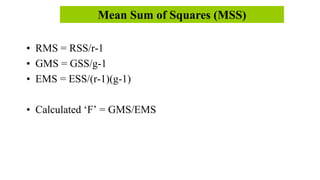
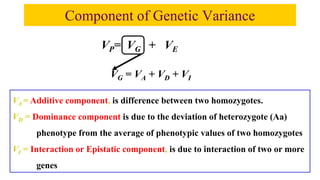
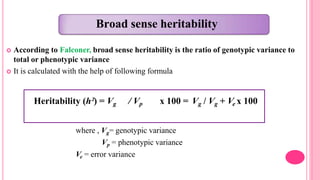
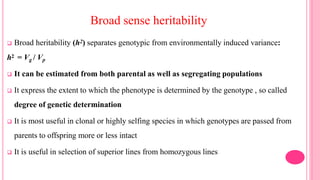
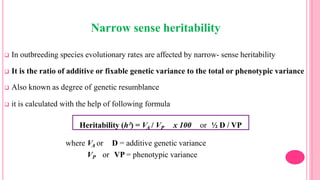
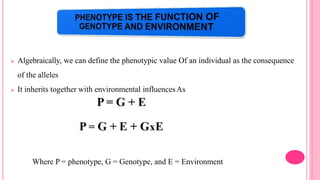
This document discusses components of genetic variation, including heritability and genetic advance. It explains that quantitative traits are influenced by multiple genes and are continuously variable, in contrast to qualitative traits which have discrete classes determined by one or few genes. There are different components of genetic variation, including additive, dominance and epistatic variance. Heritability estimates the proportion of phenotypic variation attributable to genetic factors, and is calculated as the ratio of genetic to phenotypic variance. Broad-sense heritability includes all genetic effects while narrow-sense considers only additive effects. Genetic advance measures the improvement from selection and depends on genetic variation, heritability and selection intensity. The environment also influences quantitative trait expression.