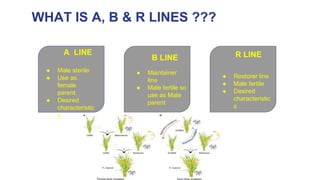
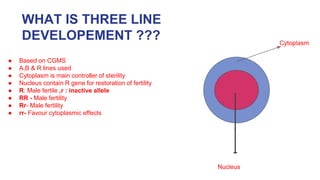
1) There are three main types of lines used in hybrid seed production systems: A lines which are male sterile, B lines which are male fertile maintainers of A lines, and R lines which are male fertile restorers.
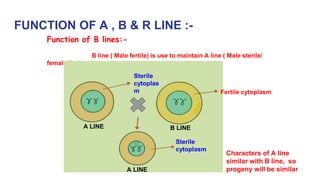
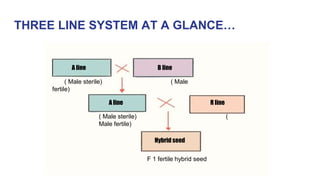
2) The three line system uses A, B, and R lines, where the A line is crossed with the R line to produce hybrid seed. The B line is used to maintain the A line.
3) The two line system does not rely on cytoplasmic male sterility and instead uses environmentally or chemically induced male sterility in the female line, which is crossed with a normal male fertile line to produce hybrid seed. This system is more flexible but requires more treatment and