This document provides an introduction to gene transfer techniques. It discusses:
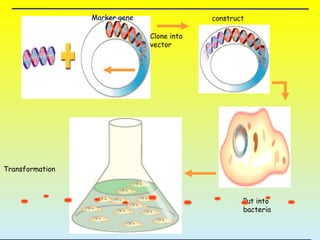
1. The process of gene transfer, which moves a specific piece of DNA into a cell, and genetic transformation, which is the stable integration and expression of a foreign gene into an organism's genome.
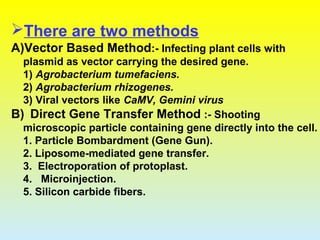
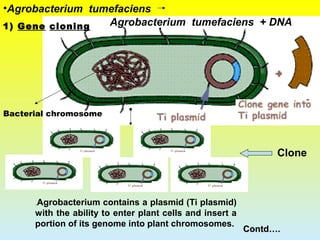
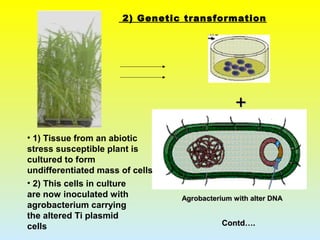
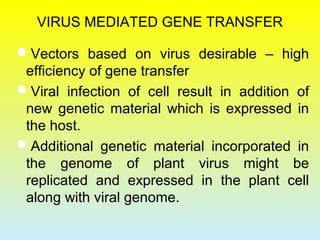
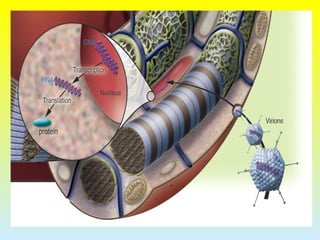
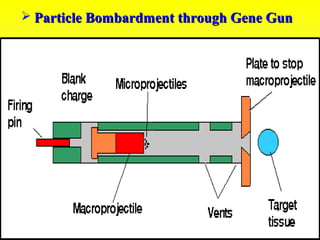
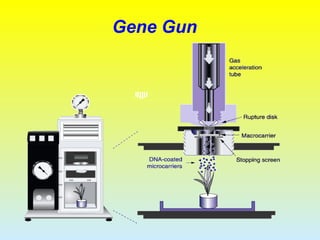
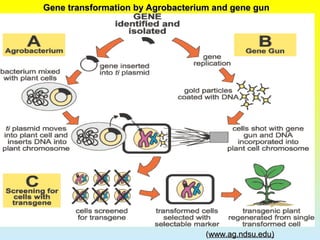
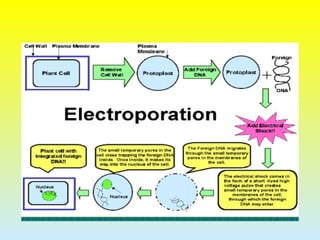
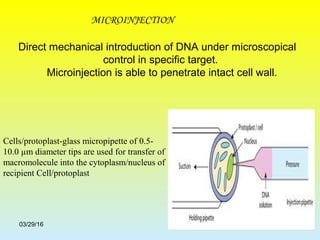
2. The two main methods of gene transfer - vector-based methods using organisms like Agrobacterium tumefaciens and direct gene transfer methods like particle bombardment.
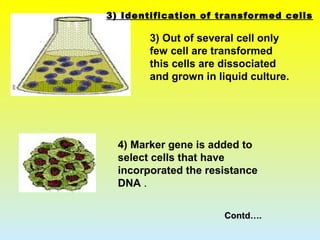
3. The steps involved in transformation which include identifying a desirable gene, designing the gene for insertion, inserting the gene into a target plant, and identifying transformed cells.