Embed presentation
Downloaded 259 times





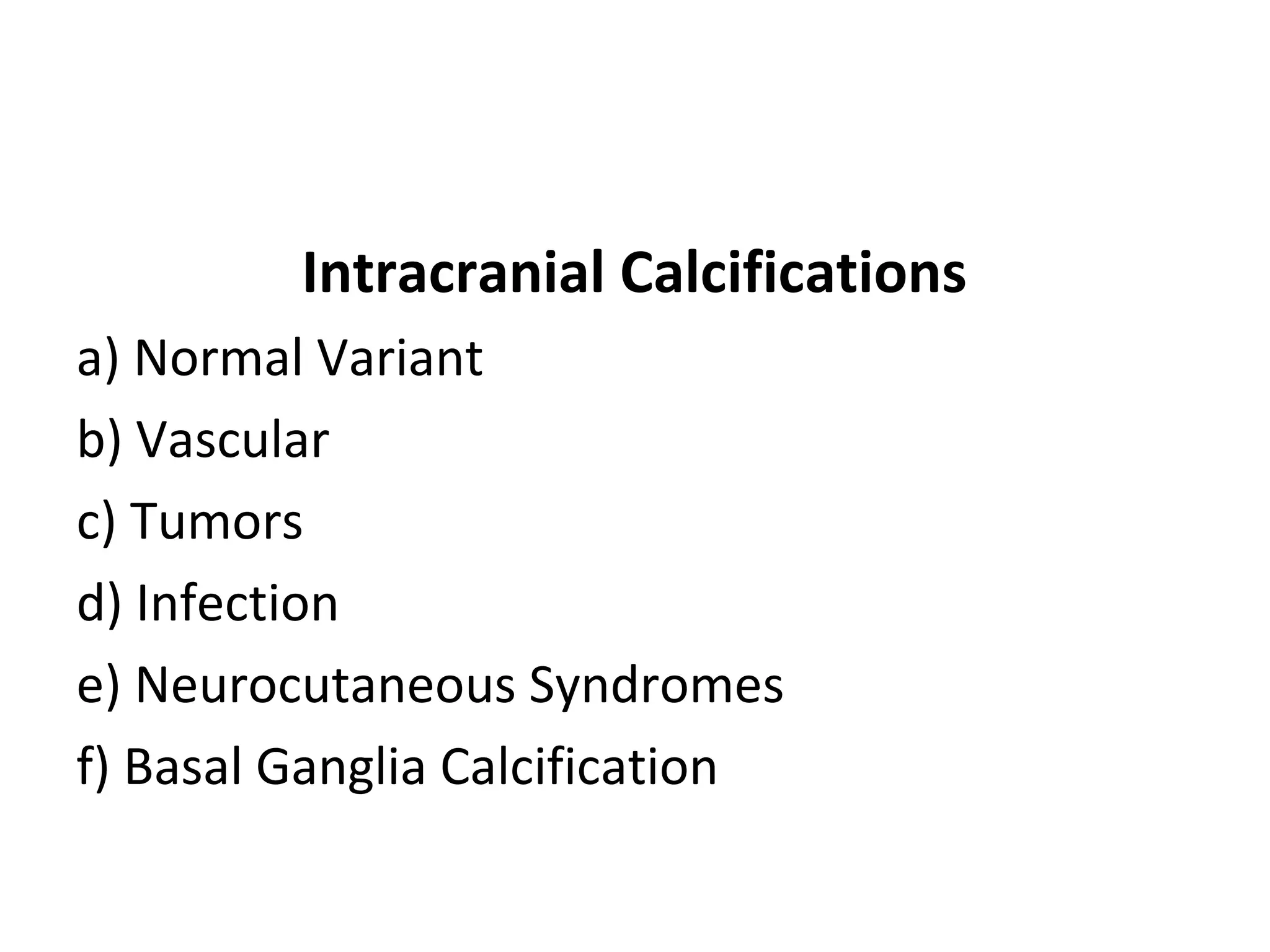











1) The document discusses different types of intracranial calcifications including normal variants, vascular, tumors, infections, neurocutaneous syndromes, and basal ganglia calcification. 2) Specific examples are provided for each category such as pineal calcification as a normal variant, atherosclerosis as a vascular cause, meningioma as a tumor, and cysticercosis as an infectious etiology. 3) Causes of basal ganglia calcification discussed include endocrine disorders, metabolic conditions, toxins, and post-therapeutic mineralizing angiopathy following chemotherapy or radiation.















