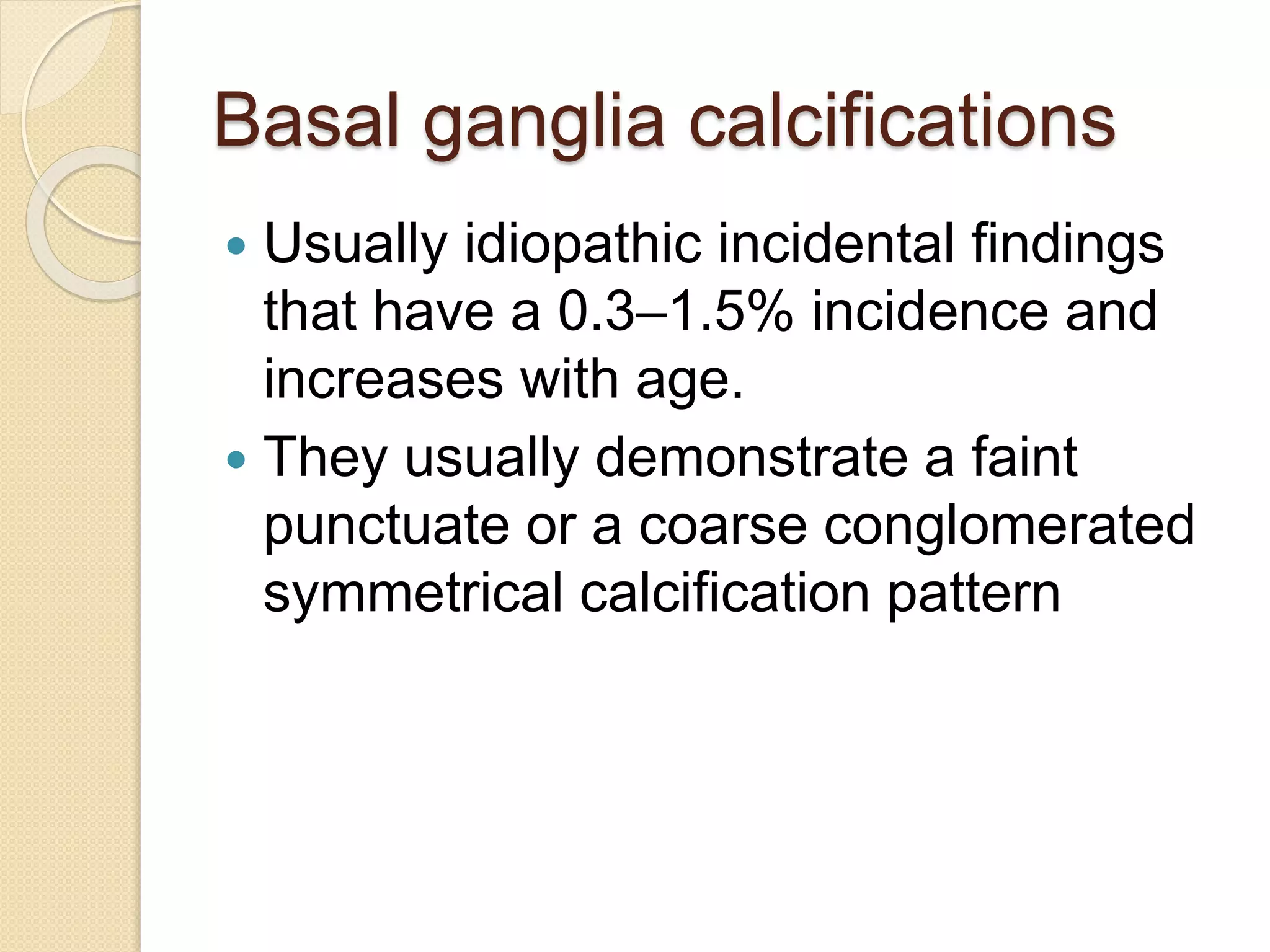
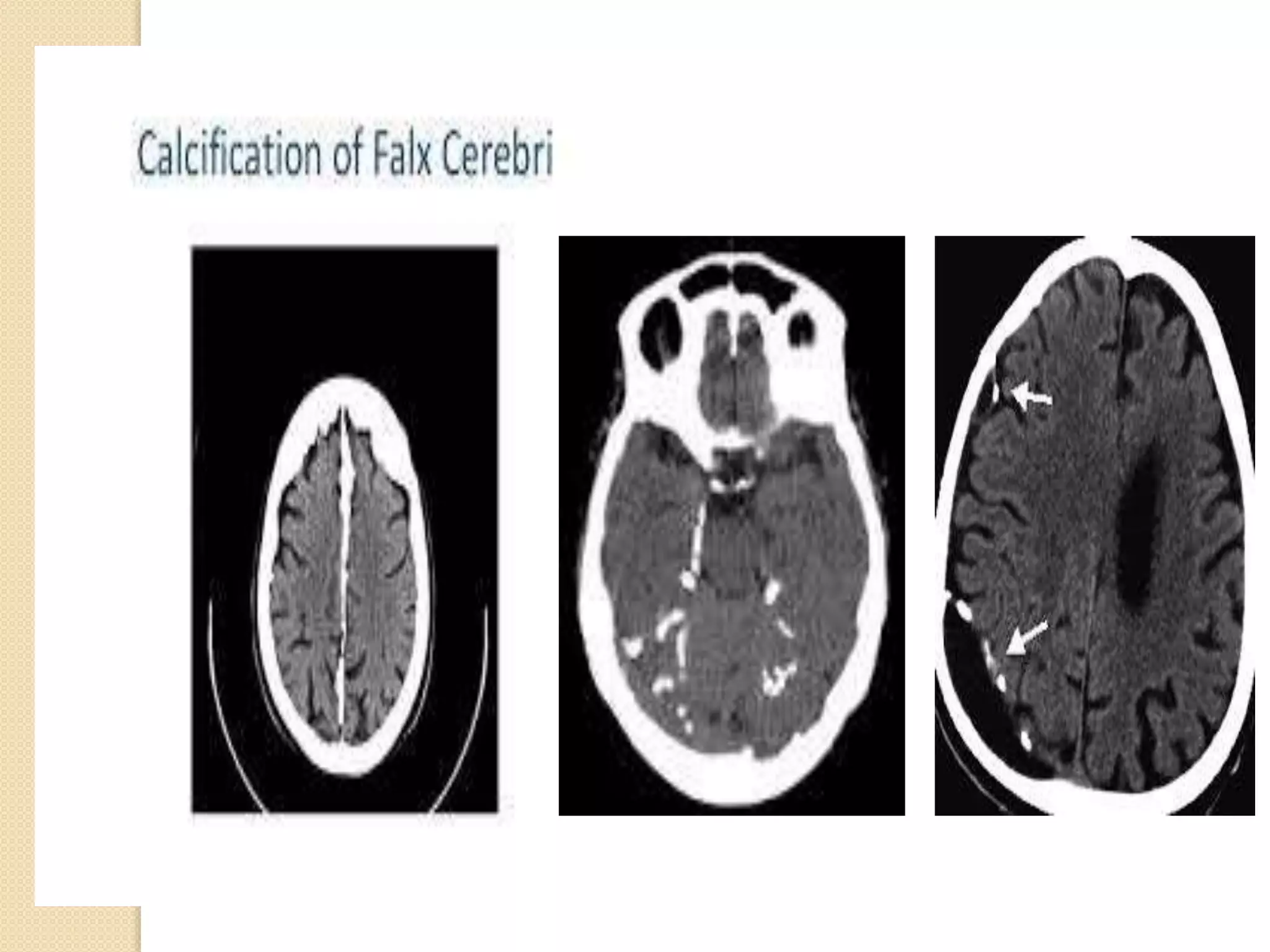
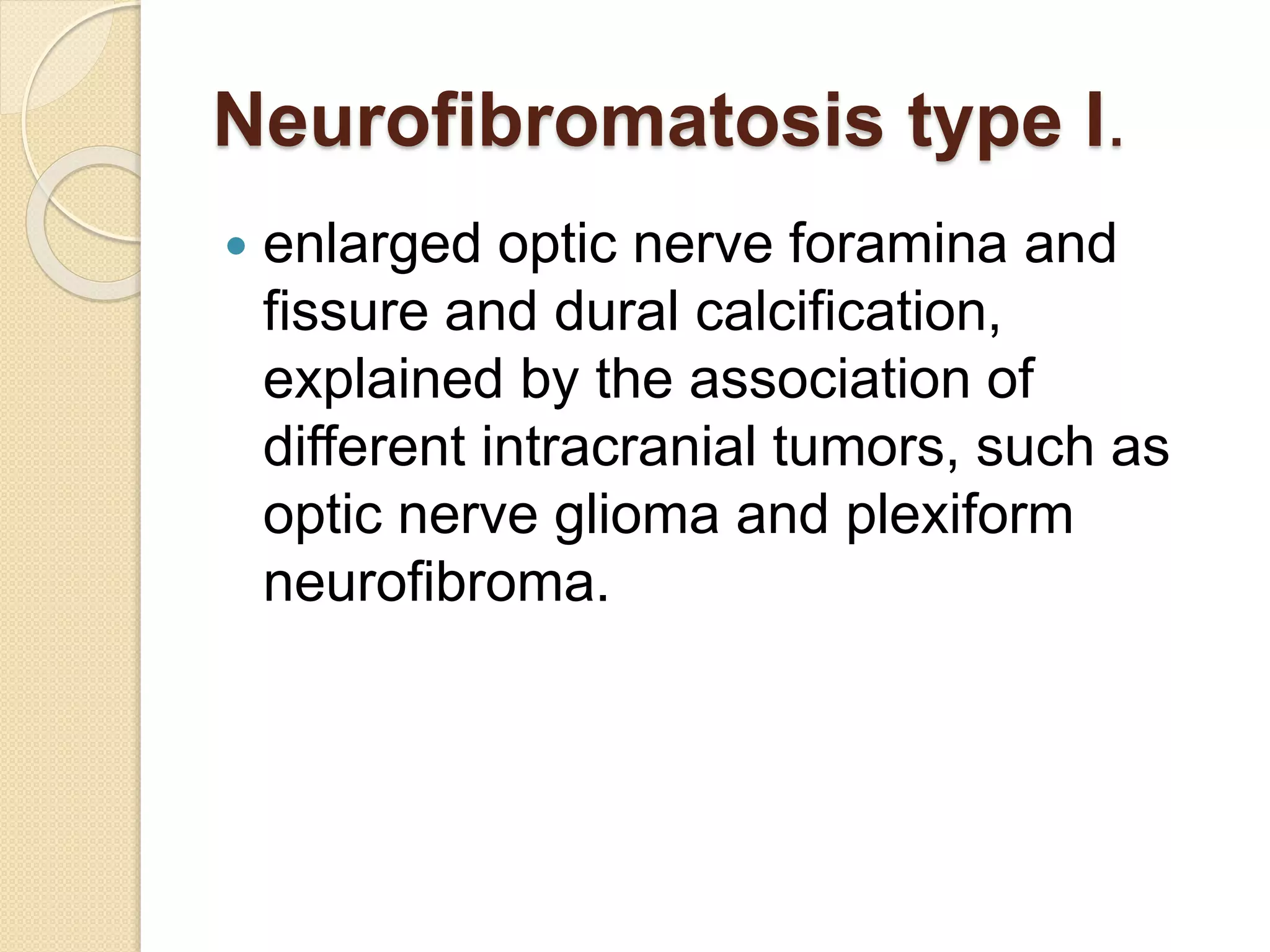
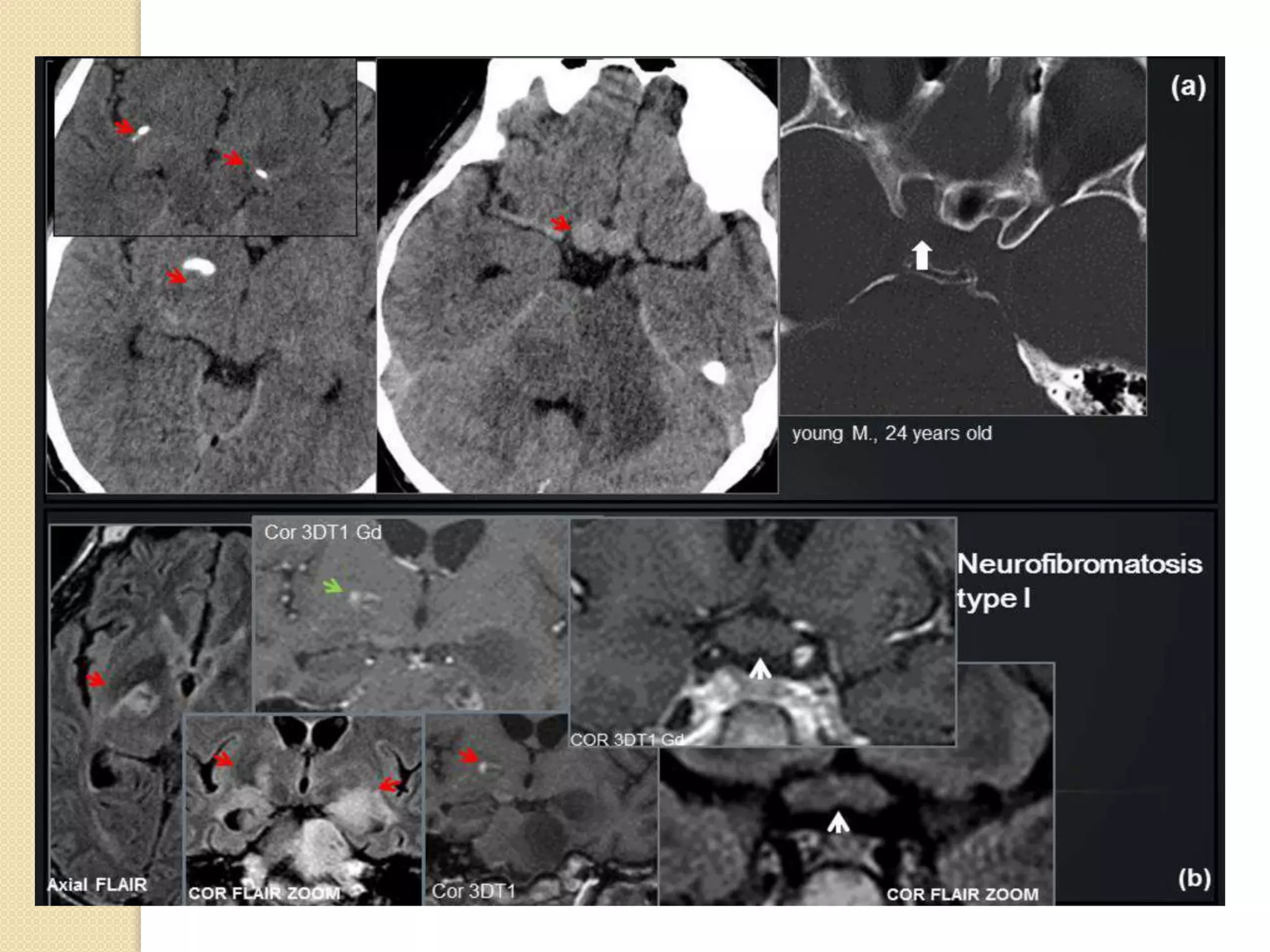
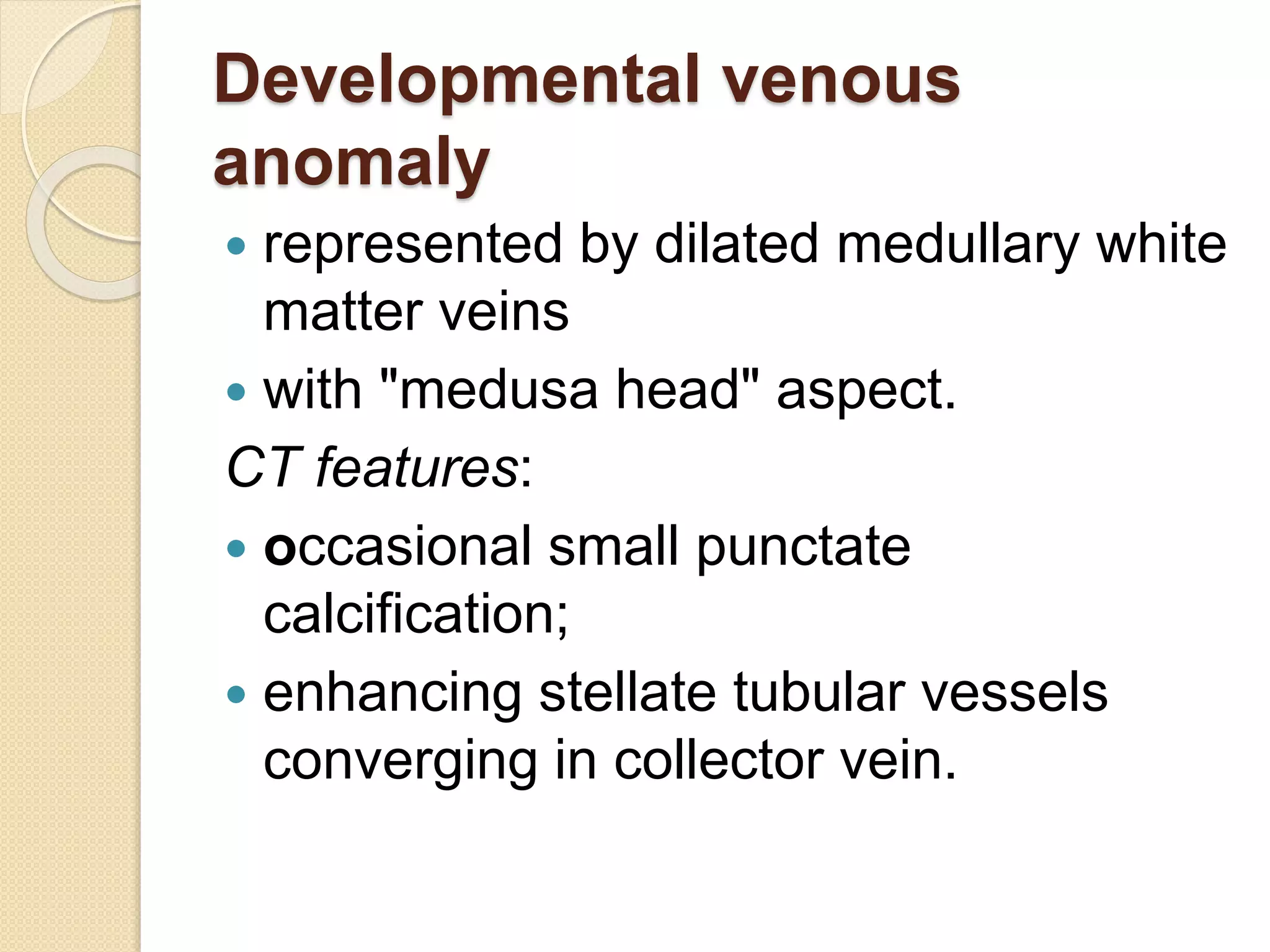
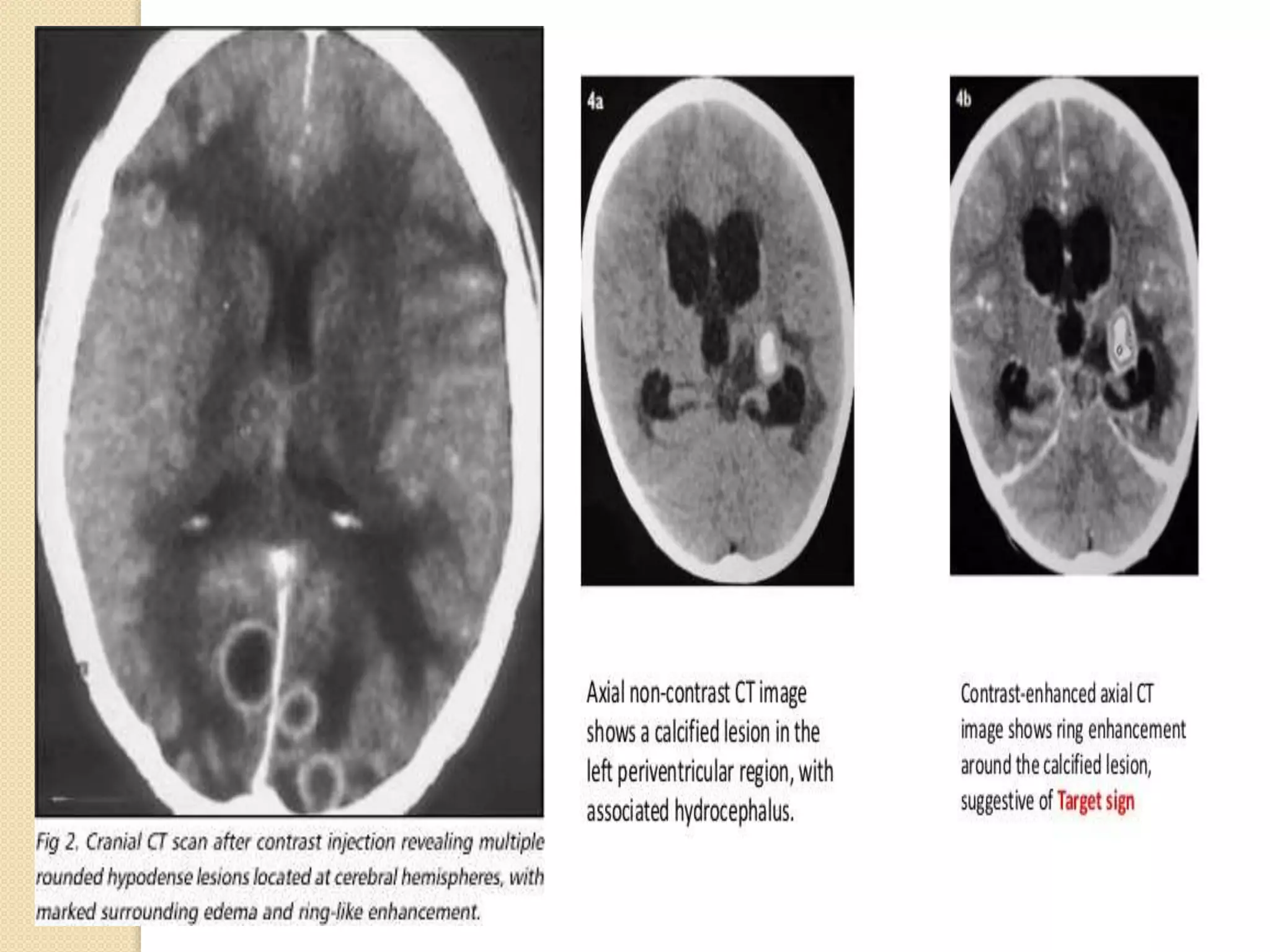
The document discusses the classification, etiology, and clinical significance of intracranial calcifications as observed in CT imaging. It outlines six primary categories of calcifications, including physiological, congenital, infectious, endocrine, vascular, and neoplastic causes, with detailed descriptions of each type and their implications for diagnosis. The importance of recognizing the specific patterns and locations of these calcifications is emphasized for accurate clinical interpretation and differentiation from pathological conditions.































































![references
Mathias Prokop - Computed Tomography of the
Body [1]. Greenberg H, Chandler WF, Sandler
HM. Brain tumors. Oxford University Press, USA.
(1999) ISBN:019512958X.
K#ro#lu Y, Call# C, Karabulut N et-al.Bennett
Greenspan, MD Instructor of Radiology,
Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
University School of Medicine , Tuberous
Sclerosis Imaging - Intracranial calcifications on
CT. DiagnIntervRadiol.2010.
EriniMakariou, MD, and Athos D. Patsalides, MD-
Intracranial calcifications.
Neuroradiology Unit, S P Institute of
Neurosciences,Solapur,Maharashtra, INDIA
MarkS. Greenberg Handbook of Neurosurgery
Seventh edition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/braincalcification-160913215613/75/intracerebral-calcification-70-2048.jpg)