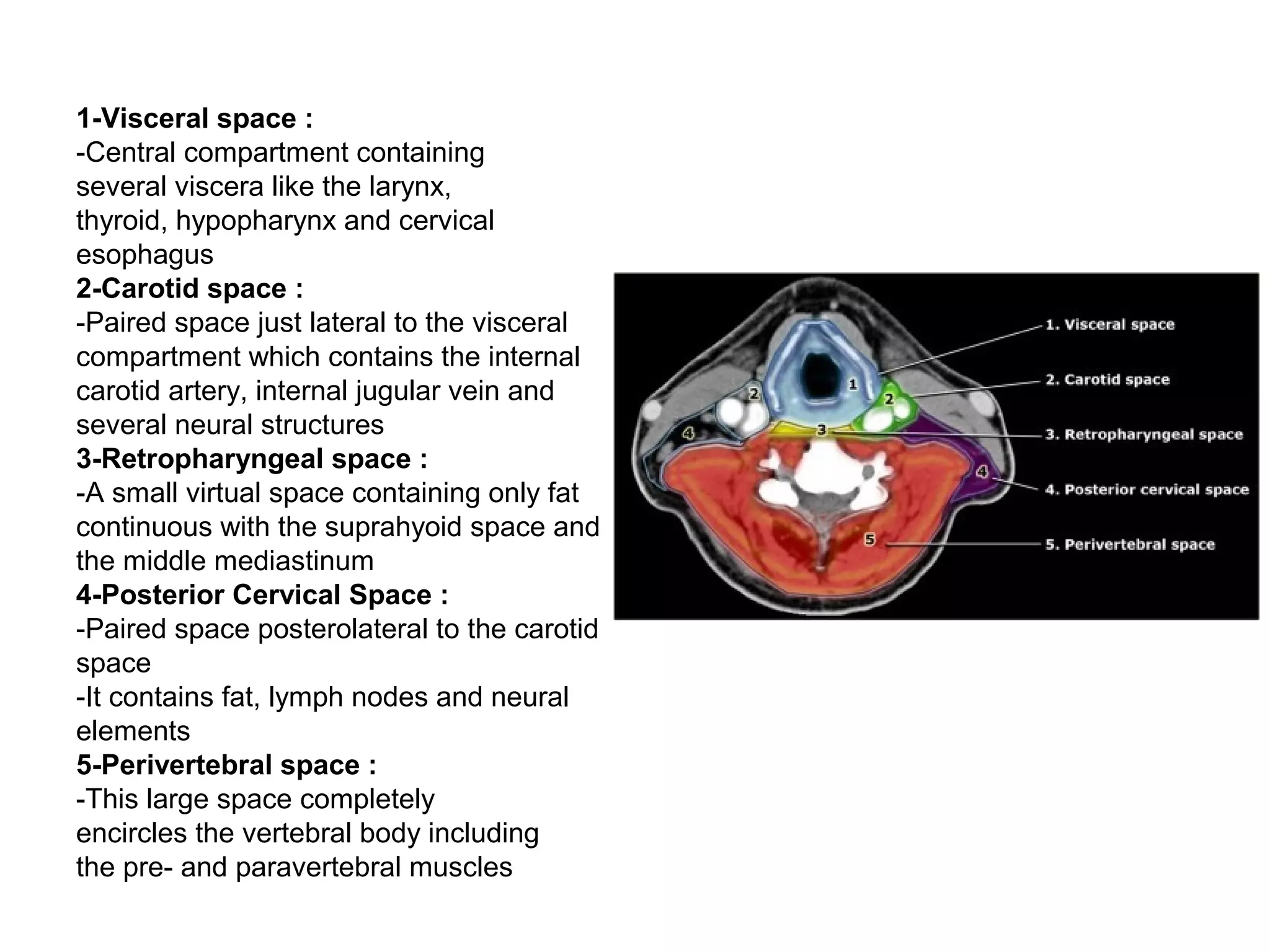
1. The document describes the five deep neck spaces: anterior visceral space, carotid space, retropharyngeal space, posterior cervical space, and perivertebral space.
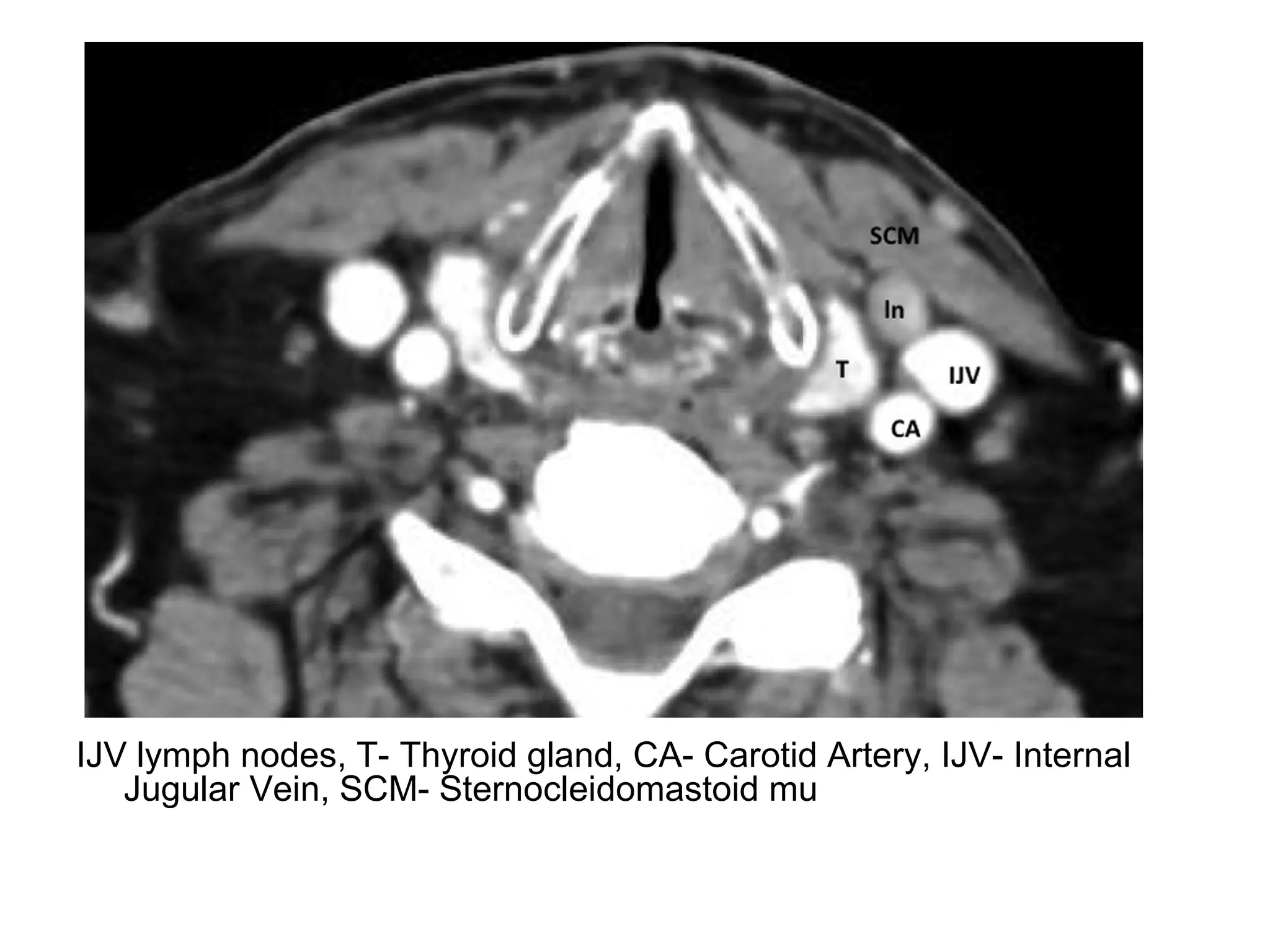
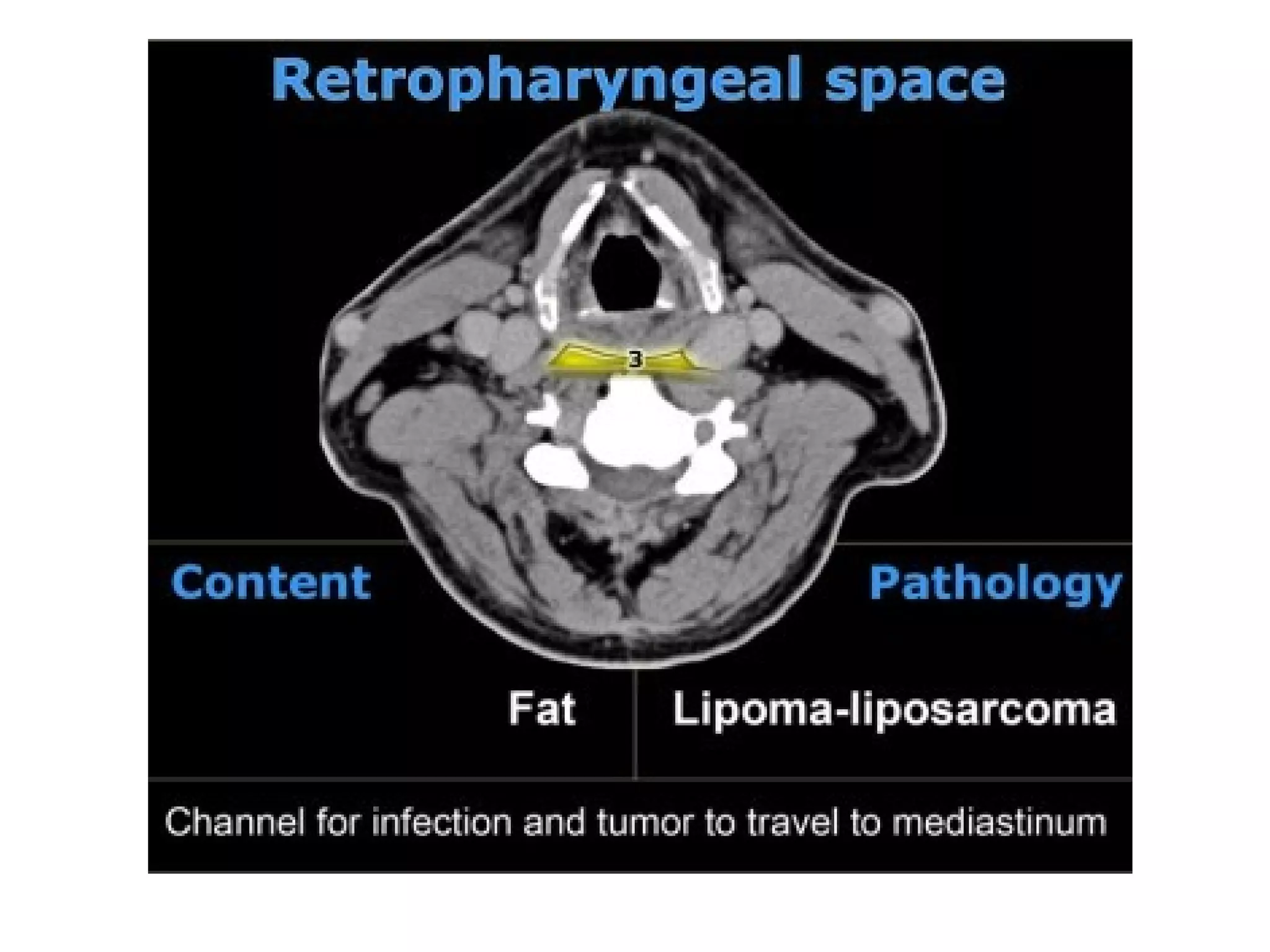
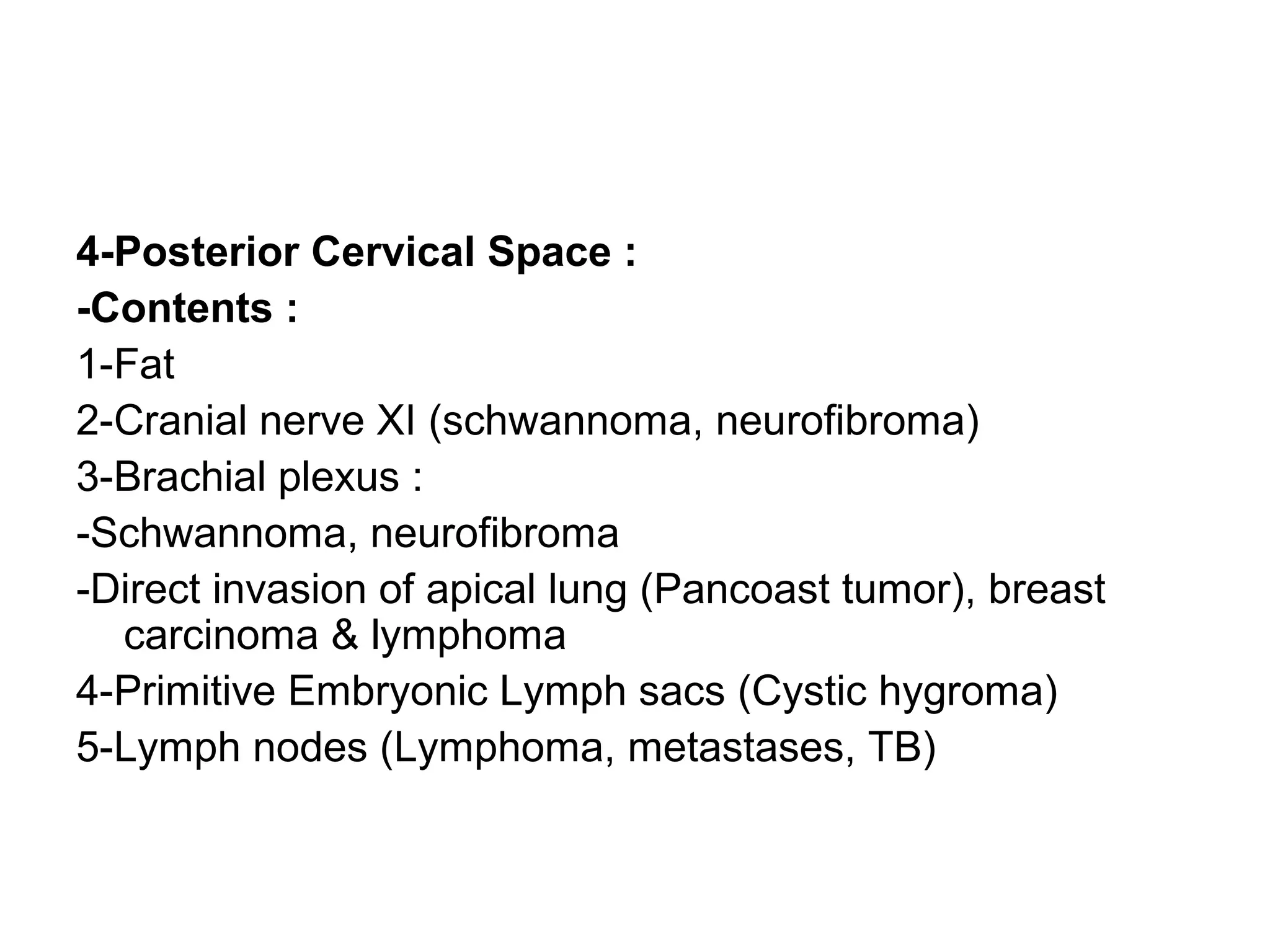
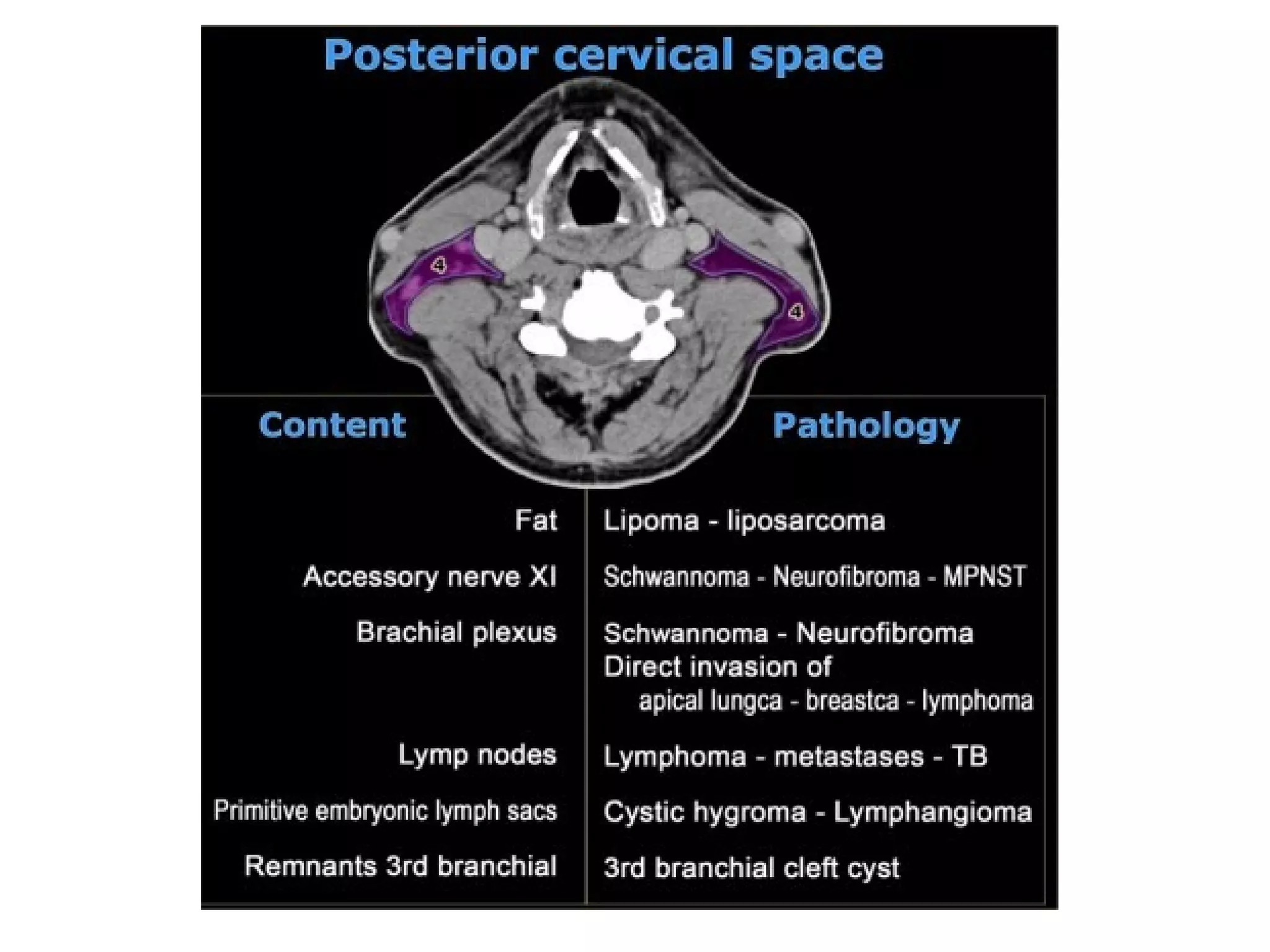
2. Each space is defined by its anatomical boundaries and contents, which can include viscera, blood vessels, nerves, lymph nodes, and pathologies such as tumors, infections, cysts.
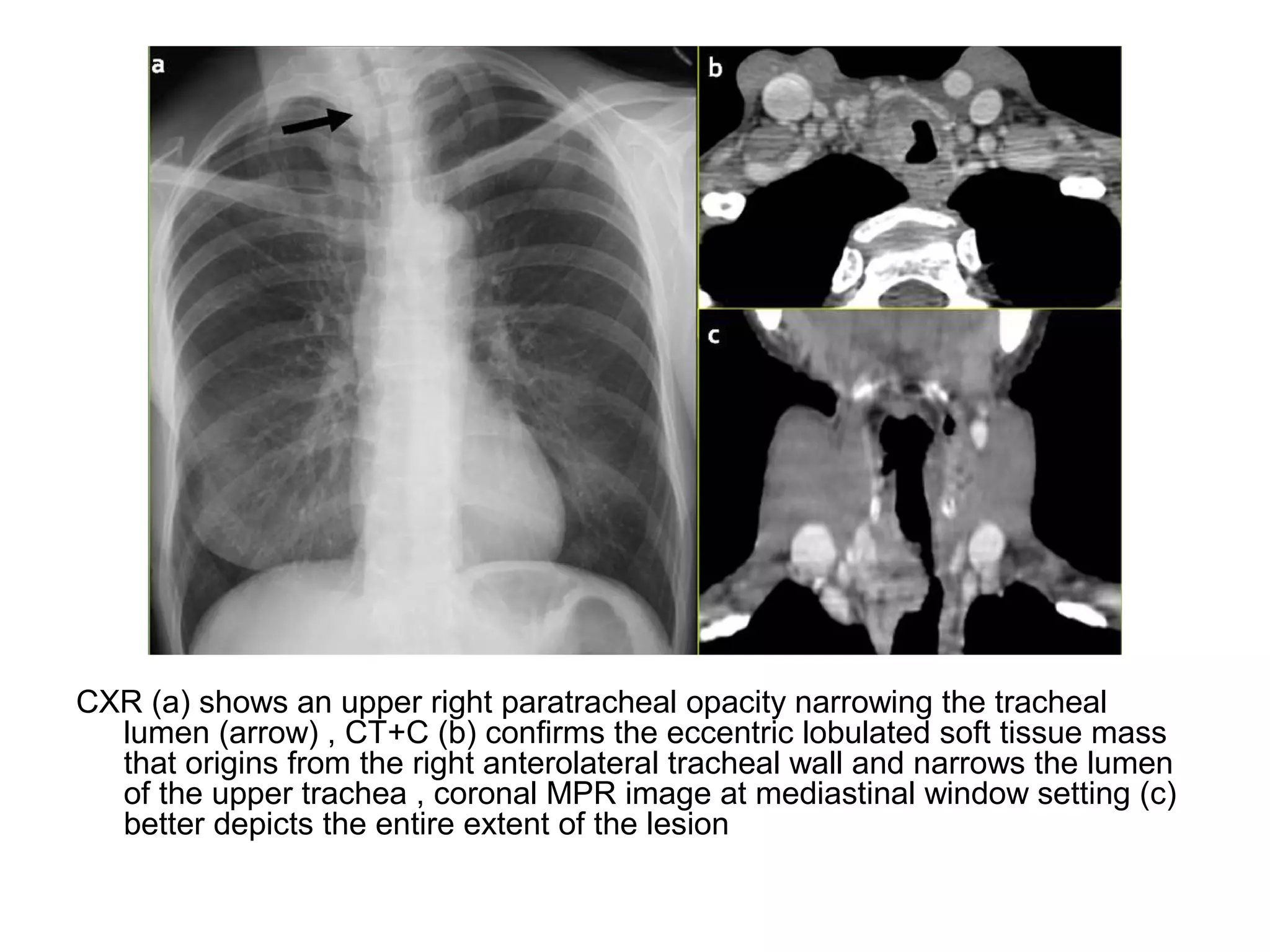
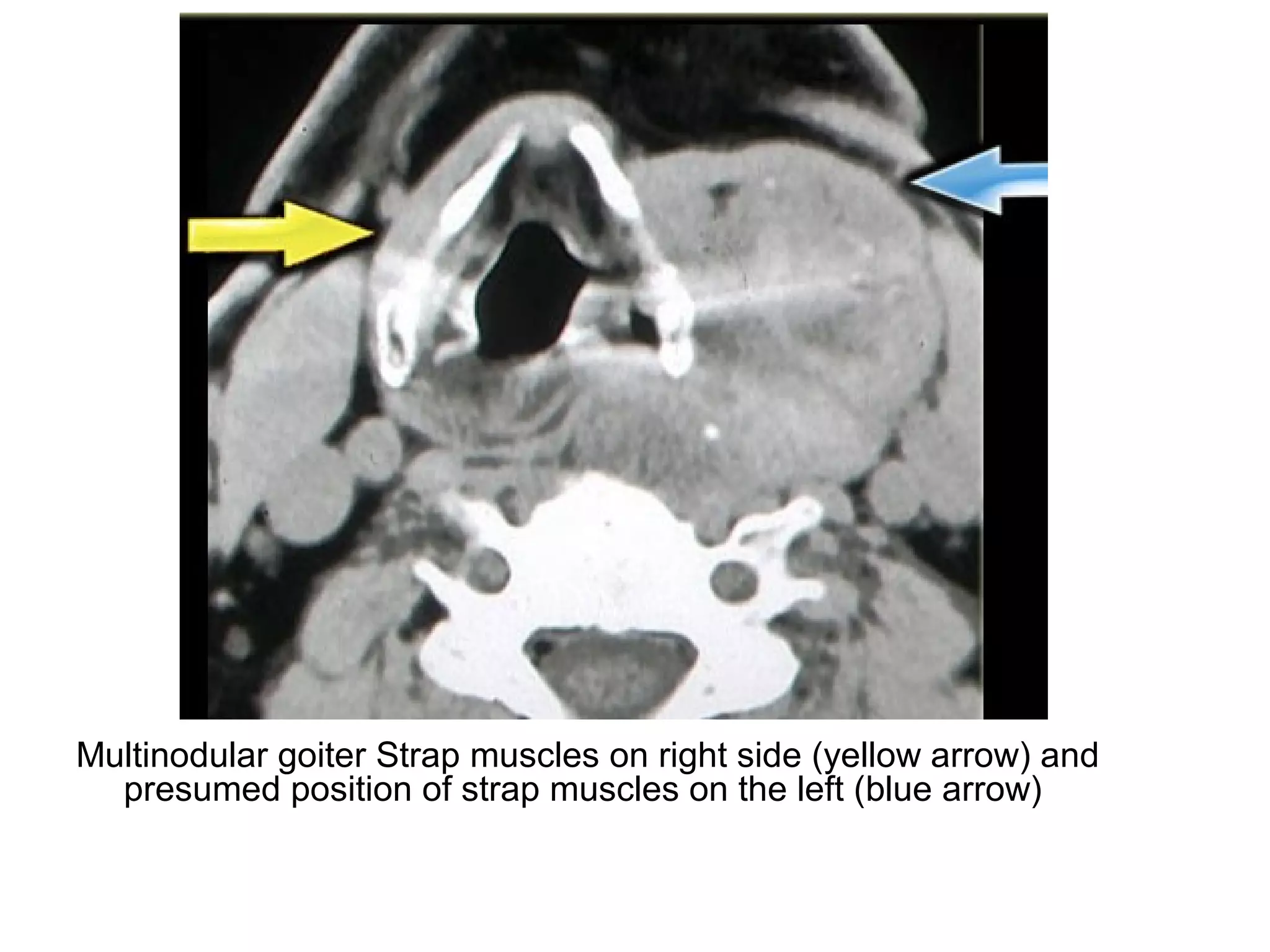
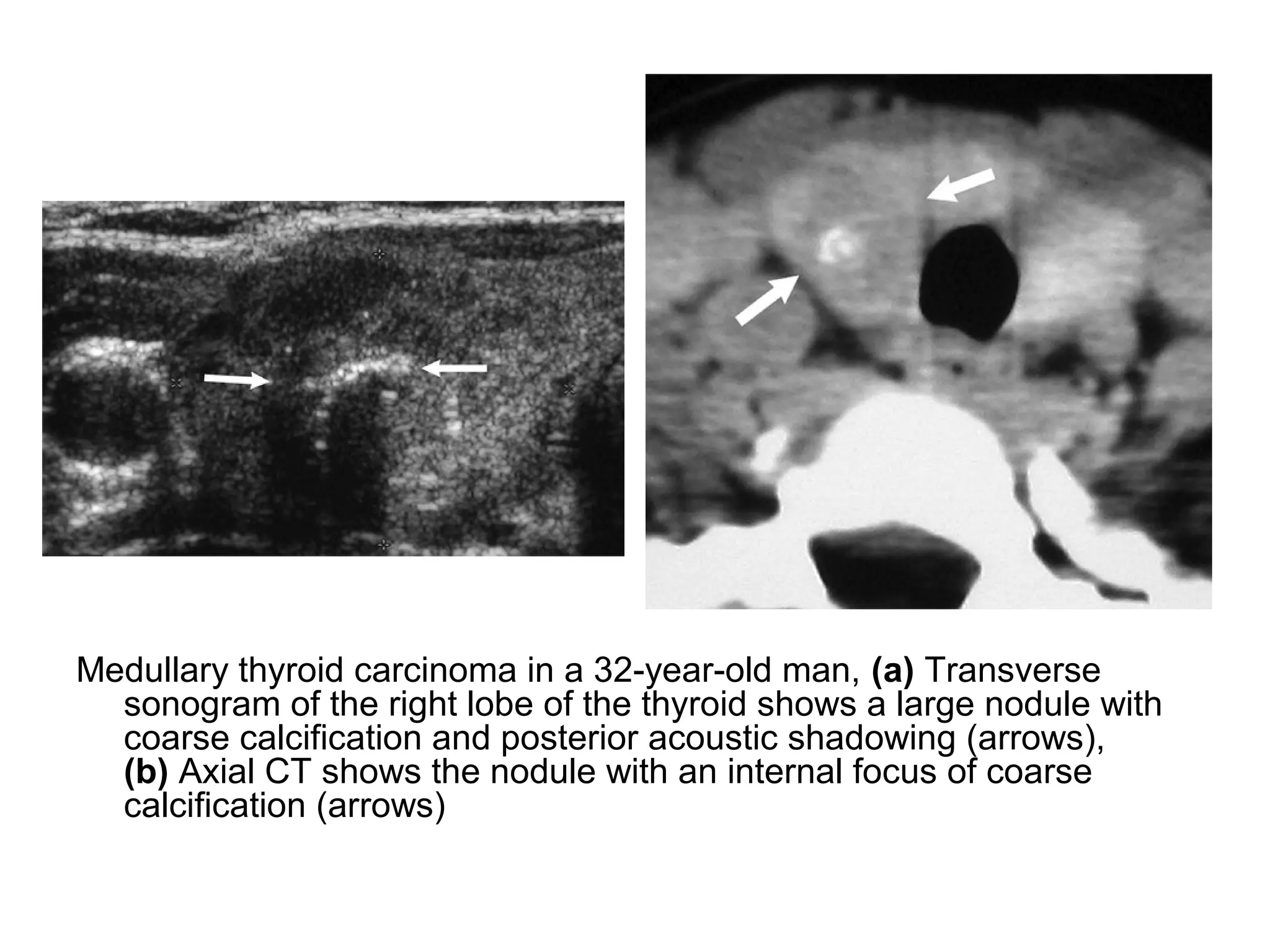
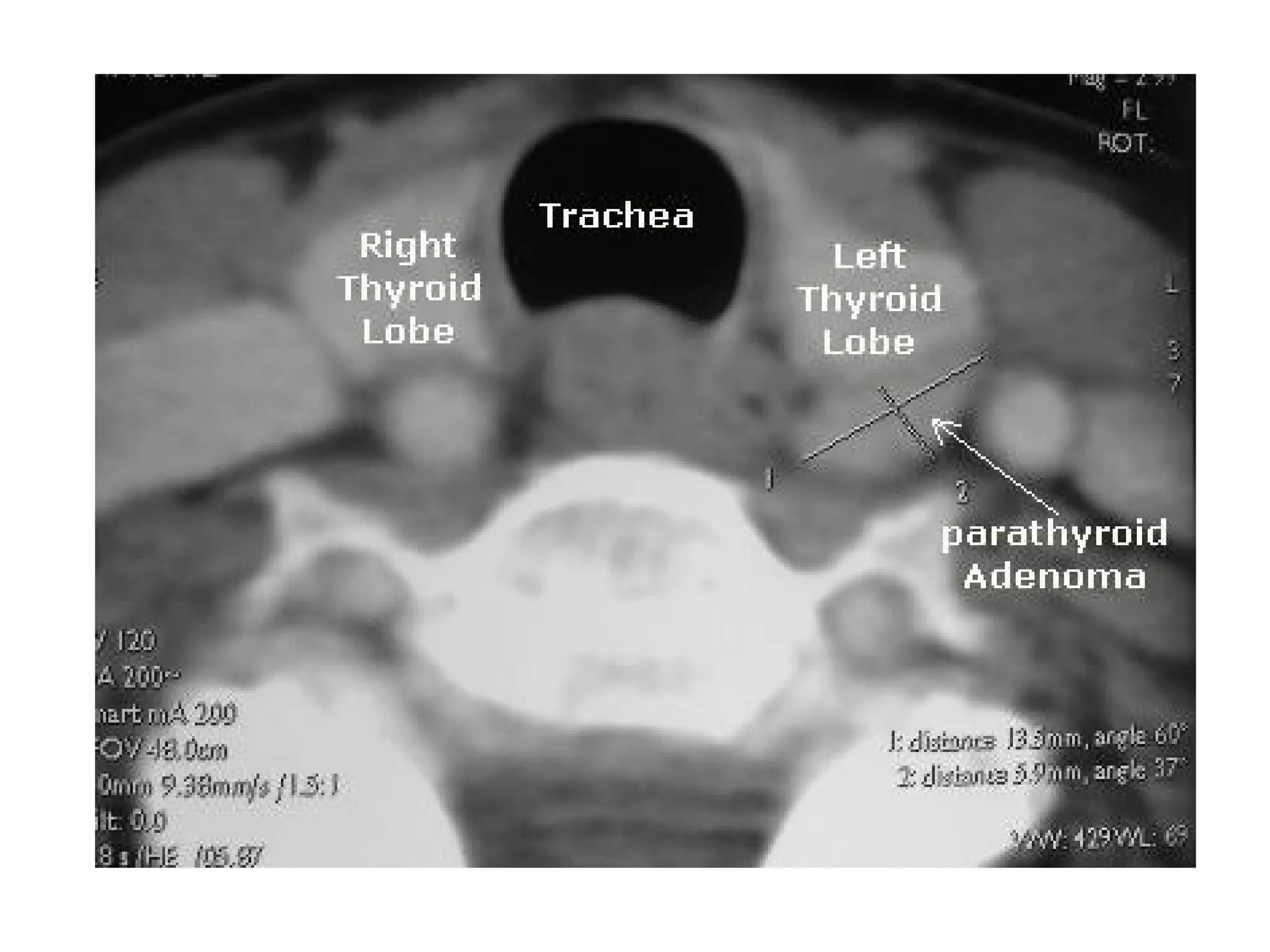
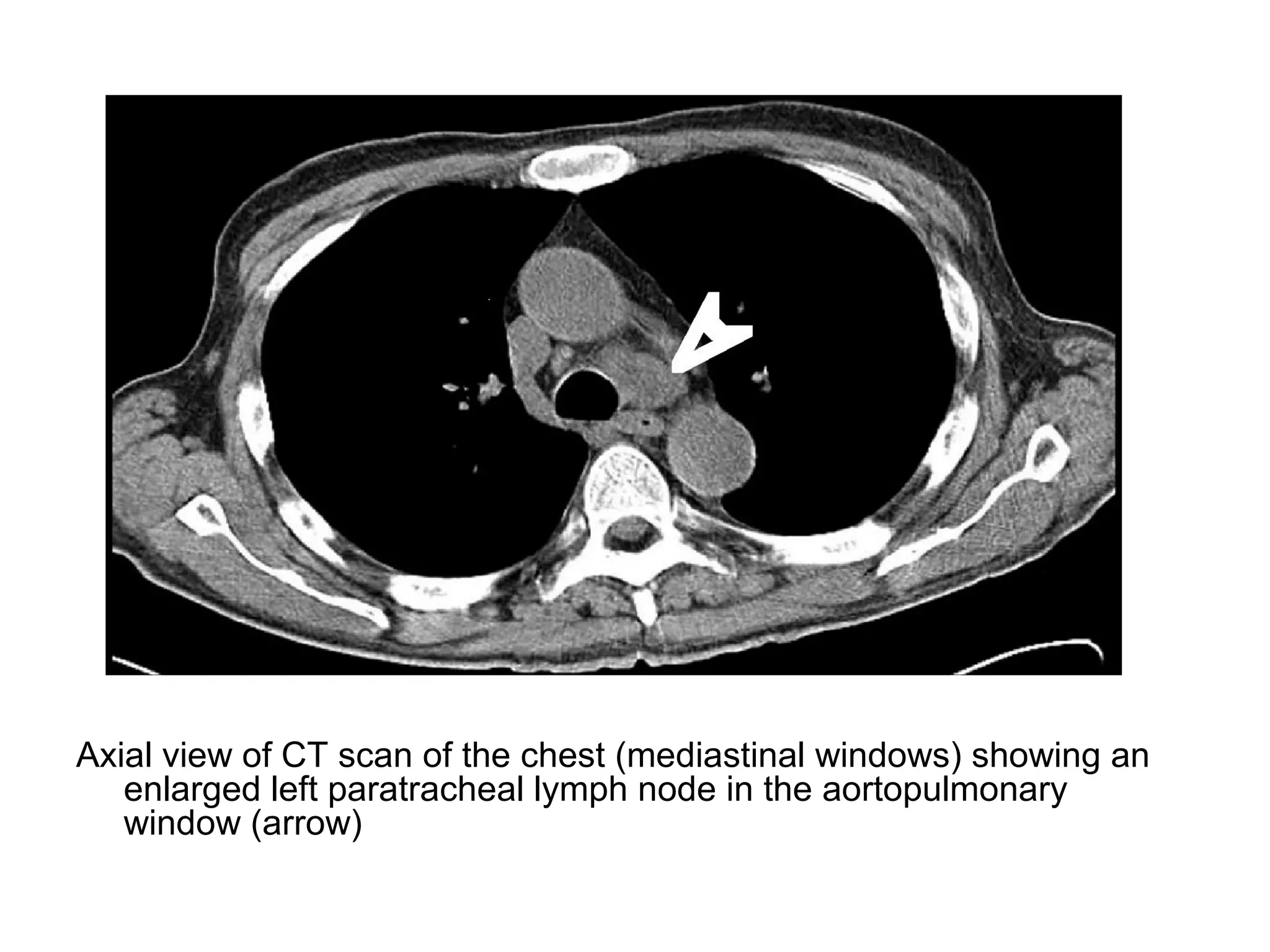
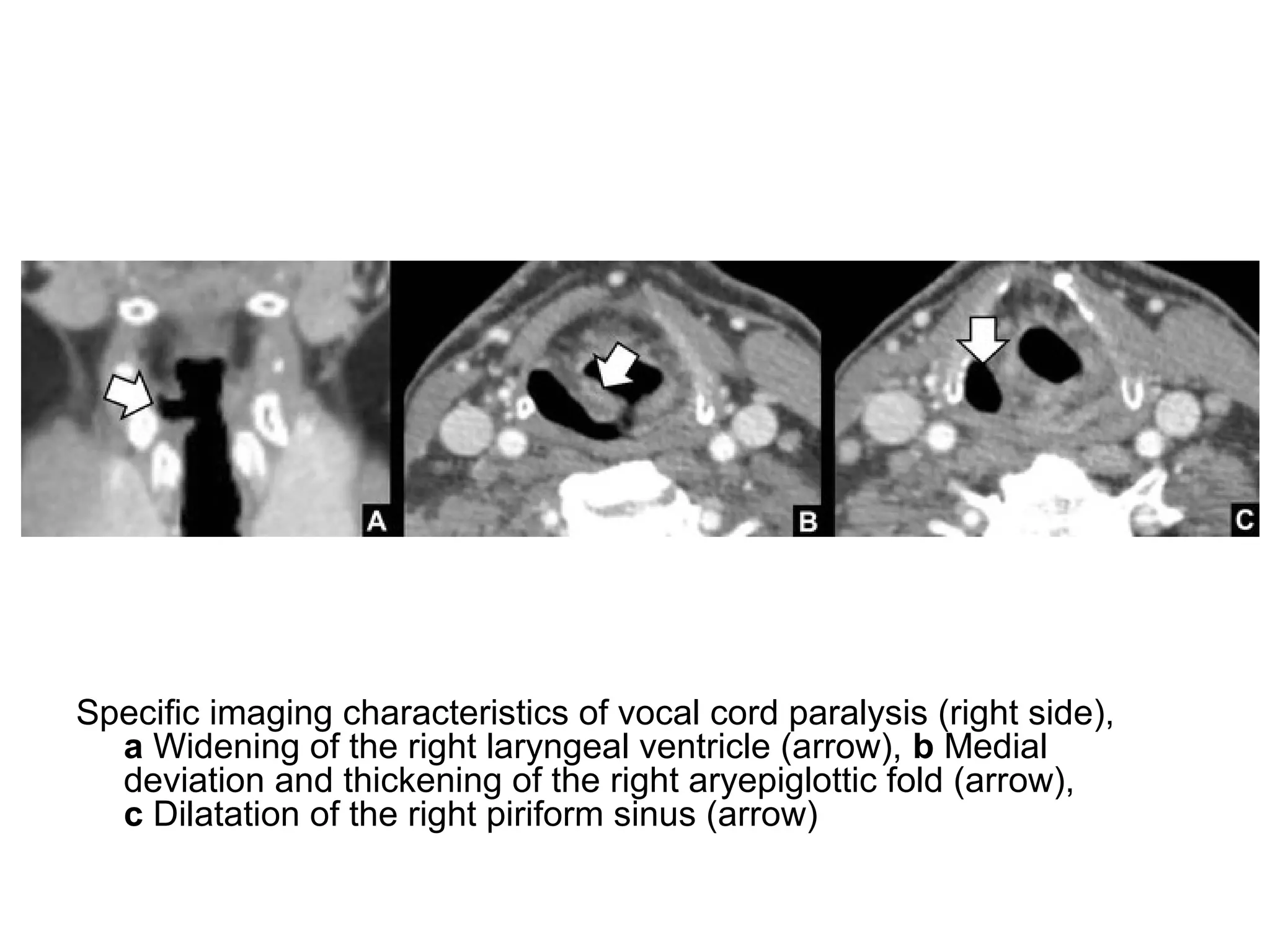
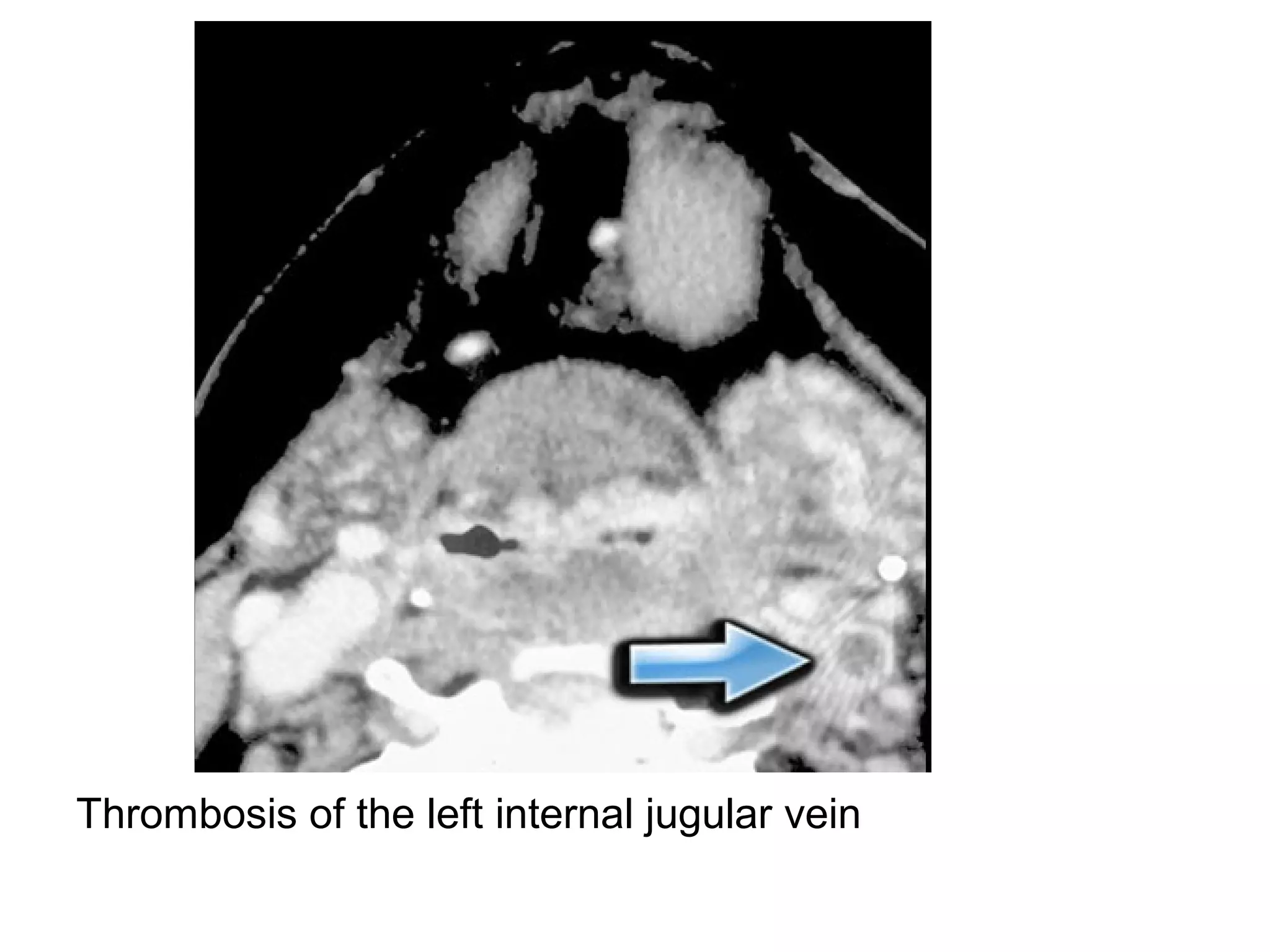
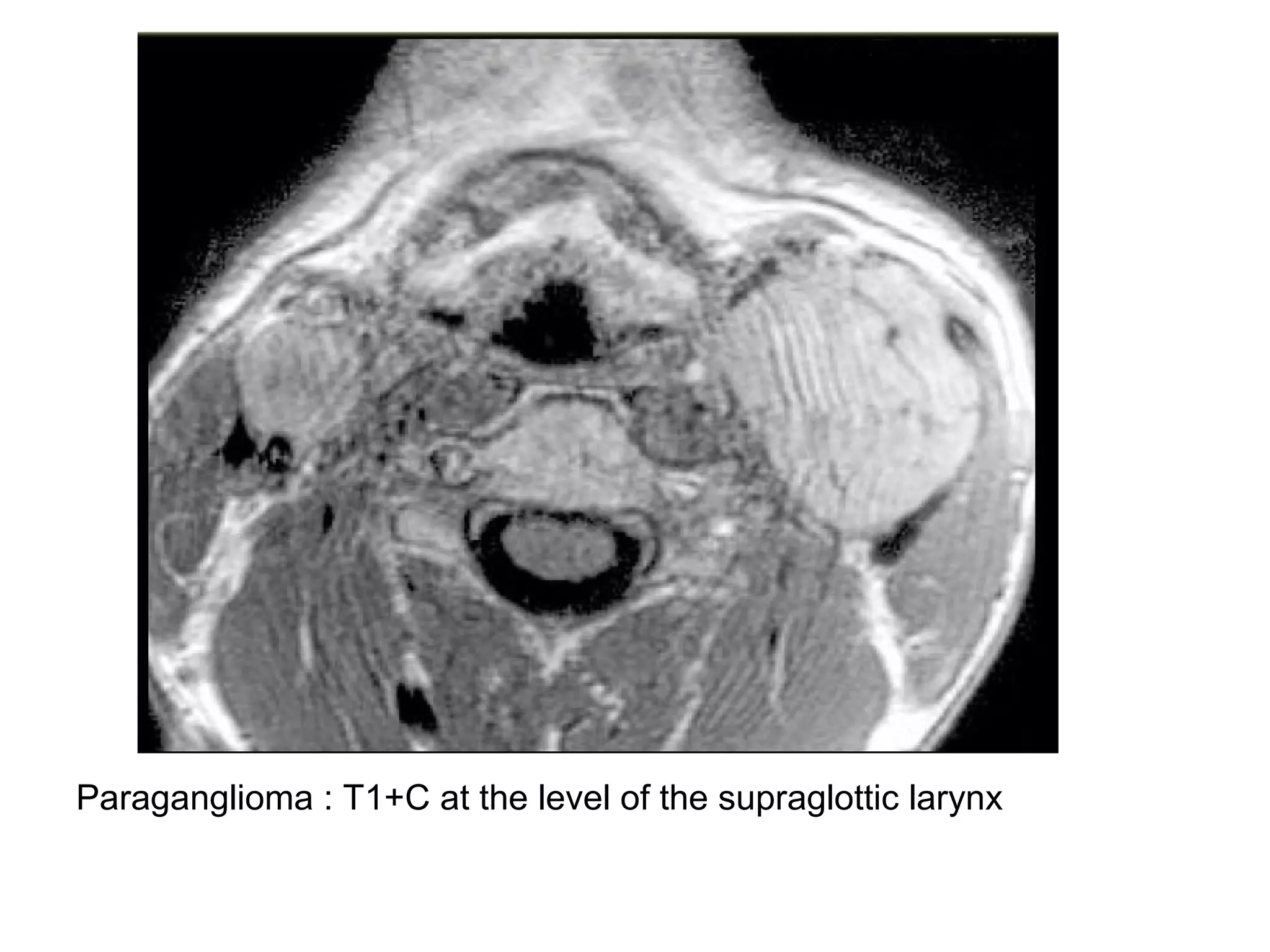
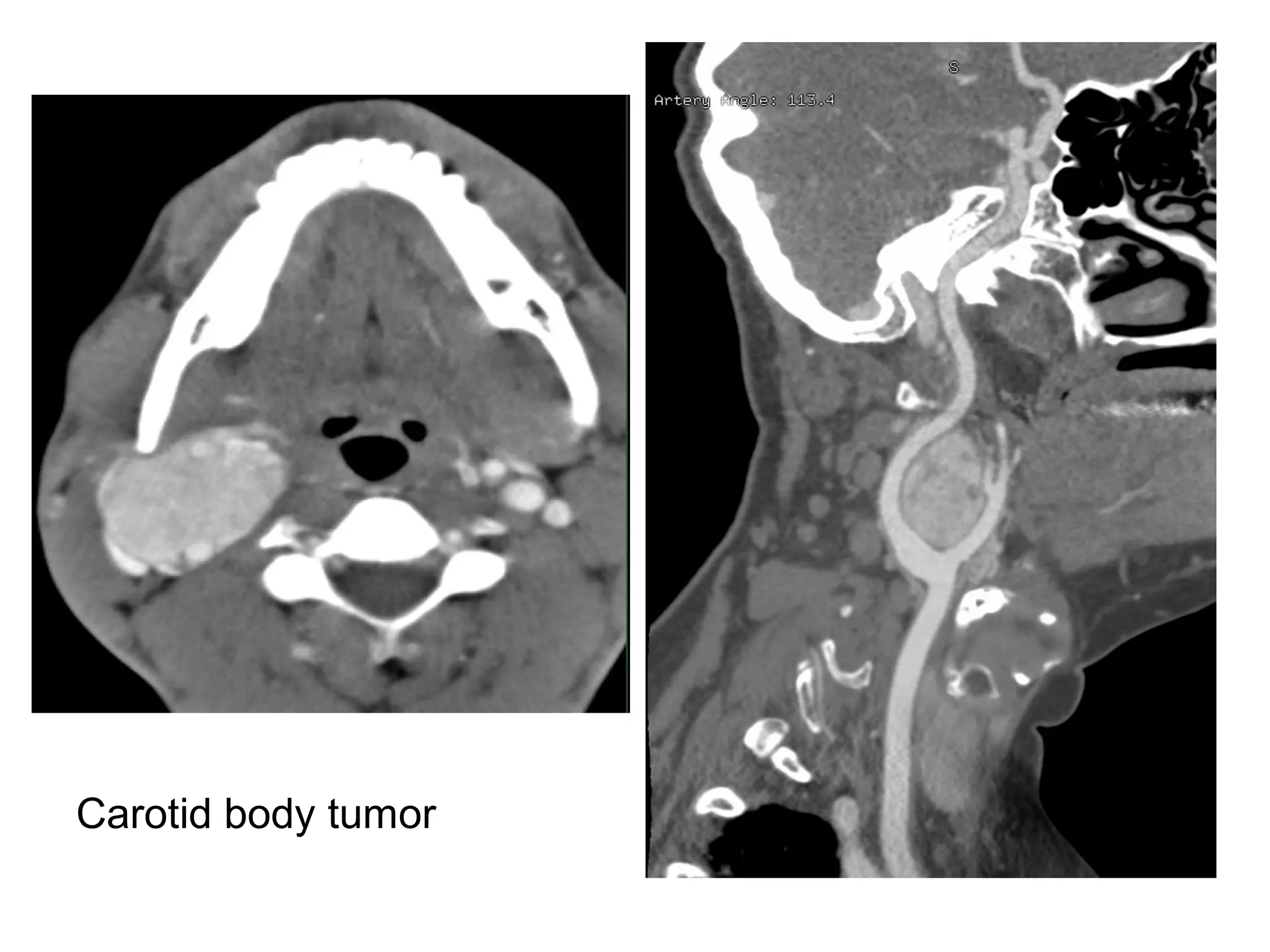
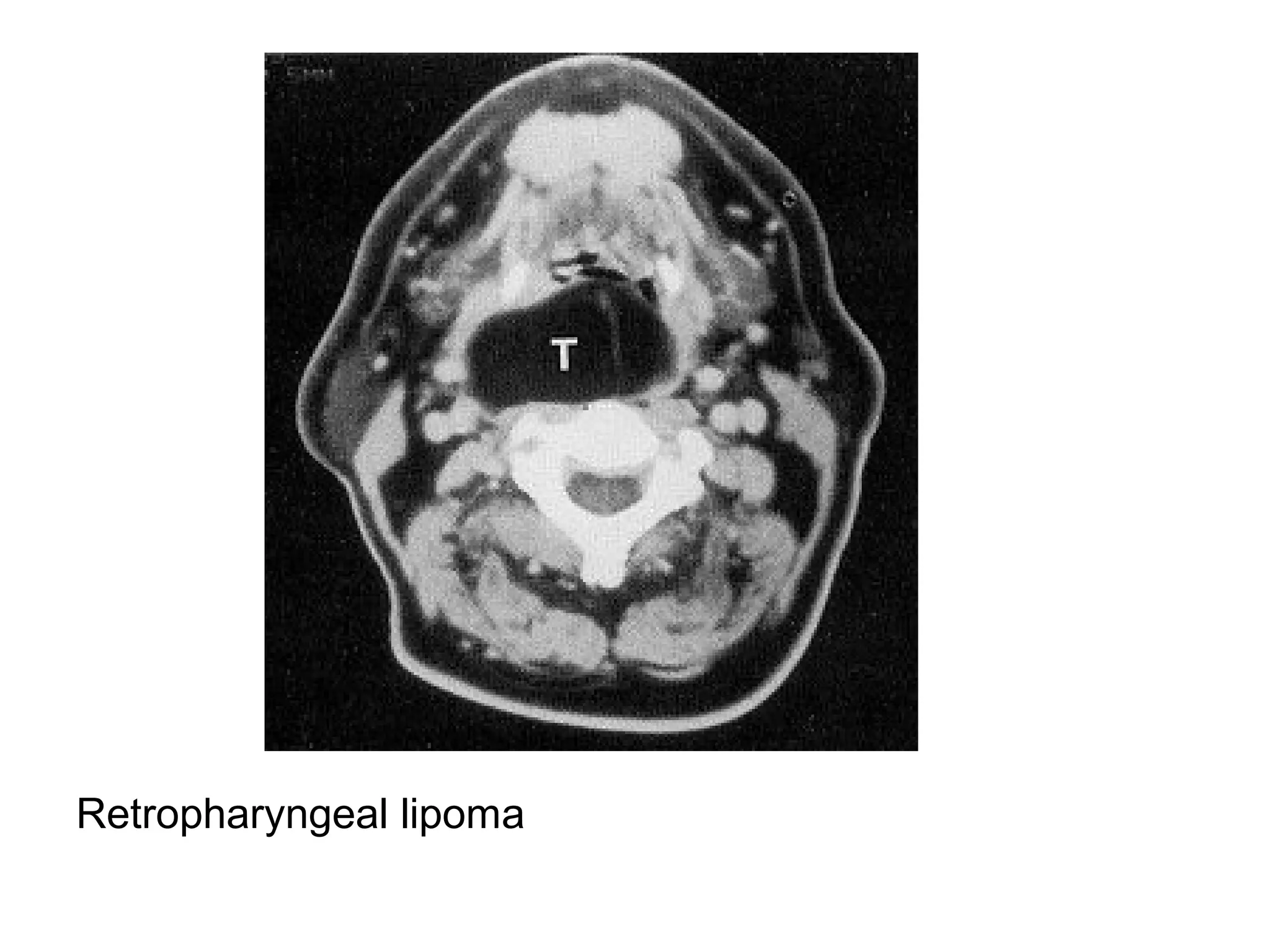
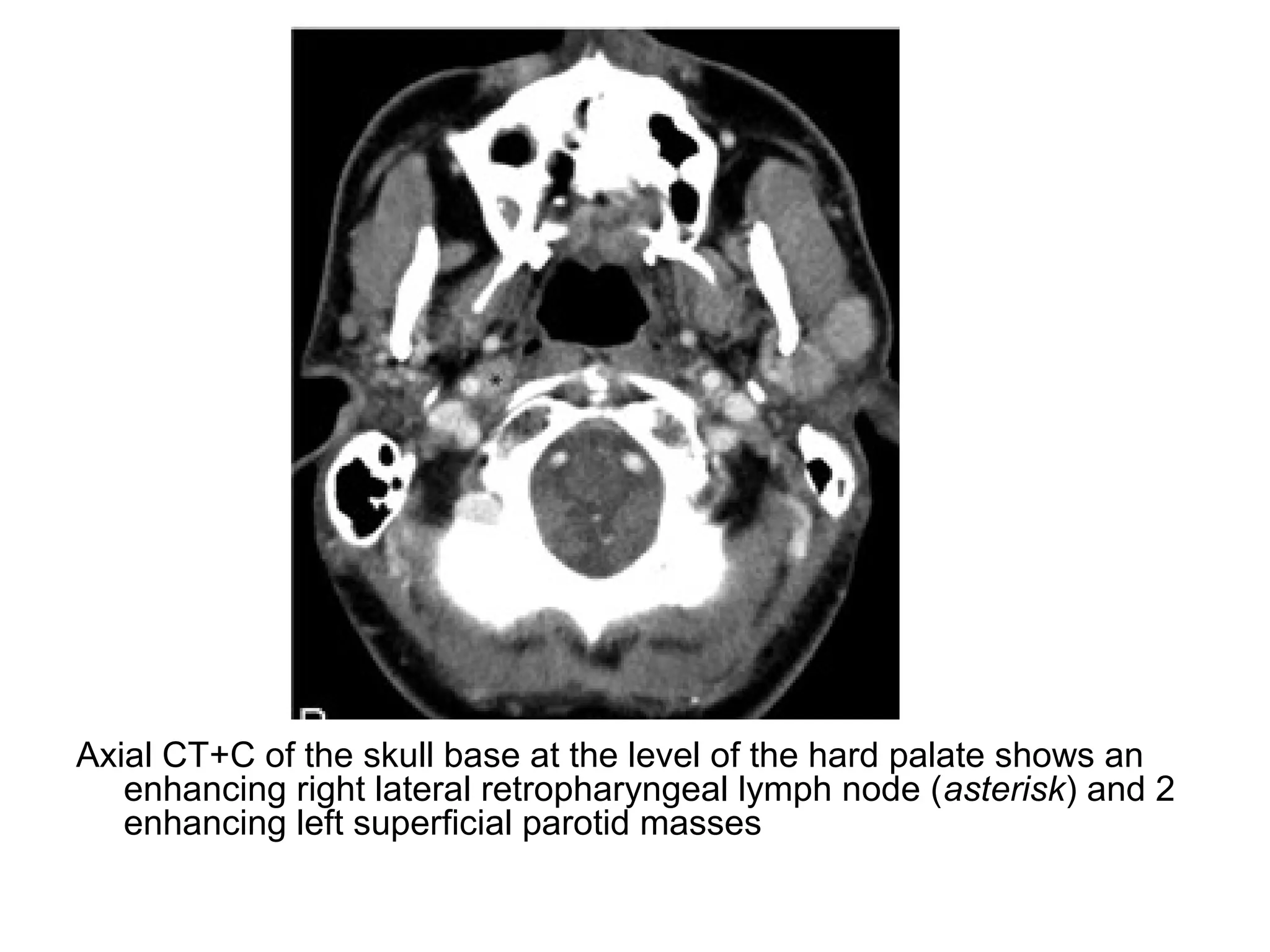
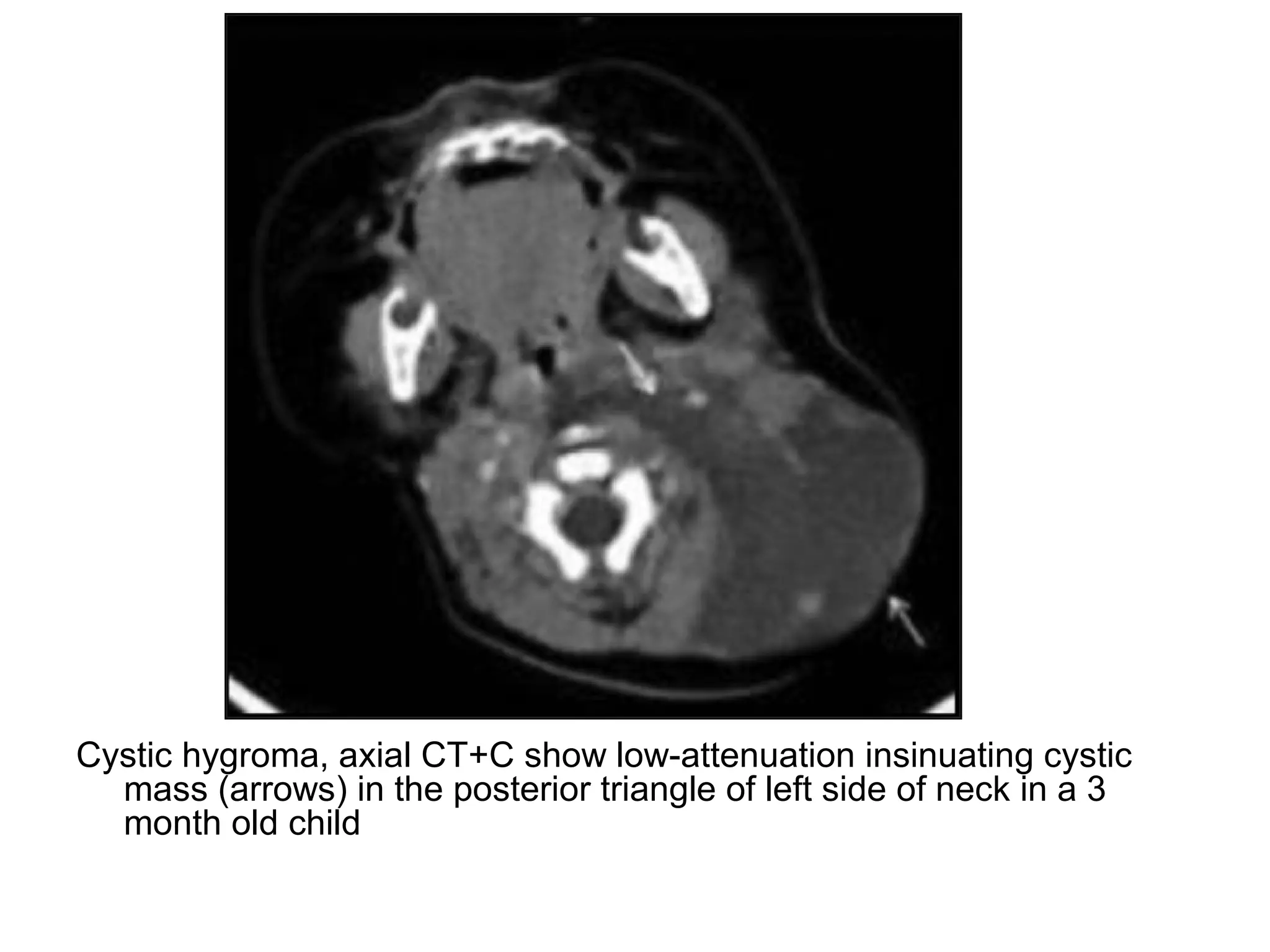
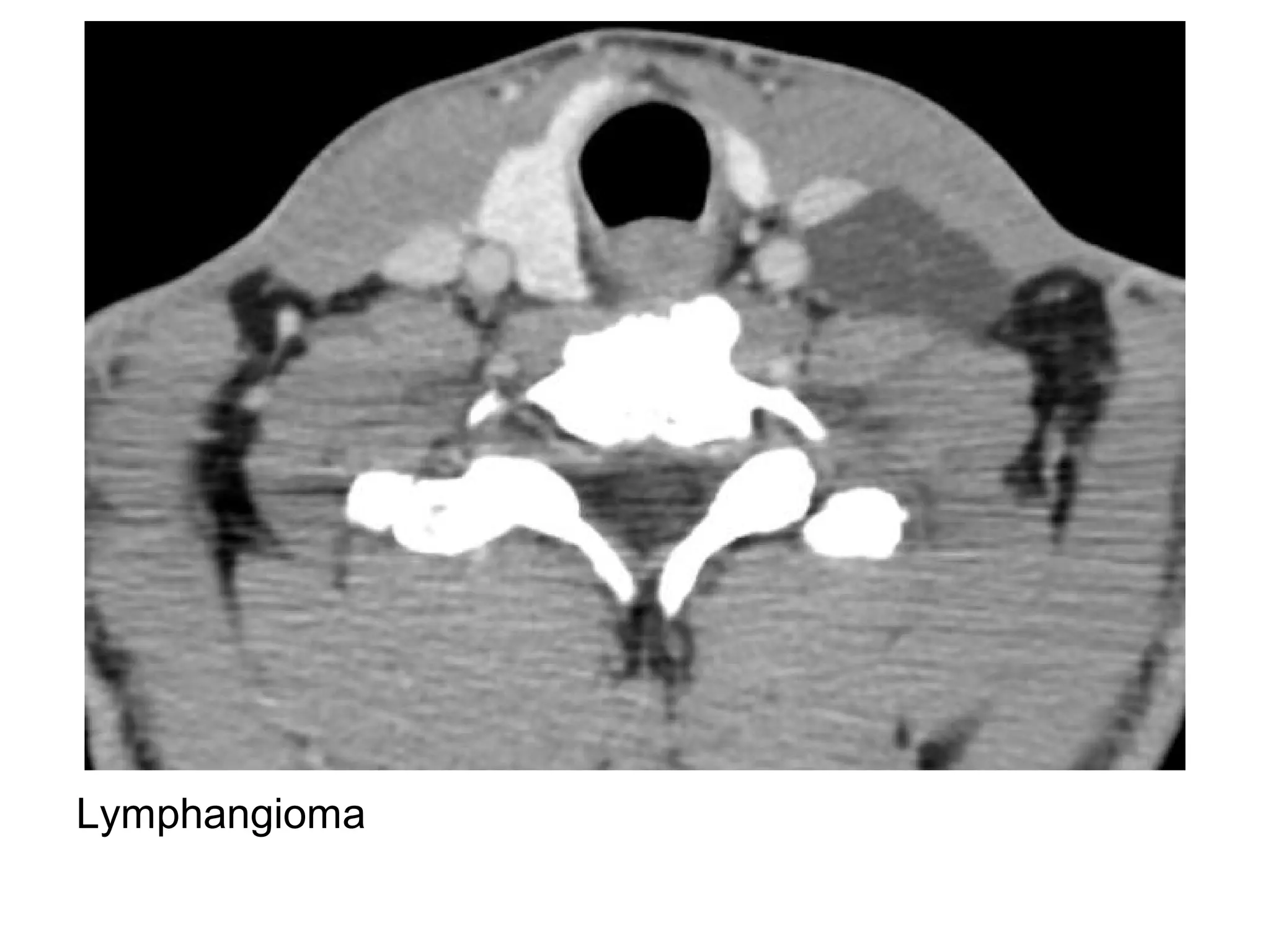
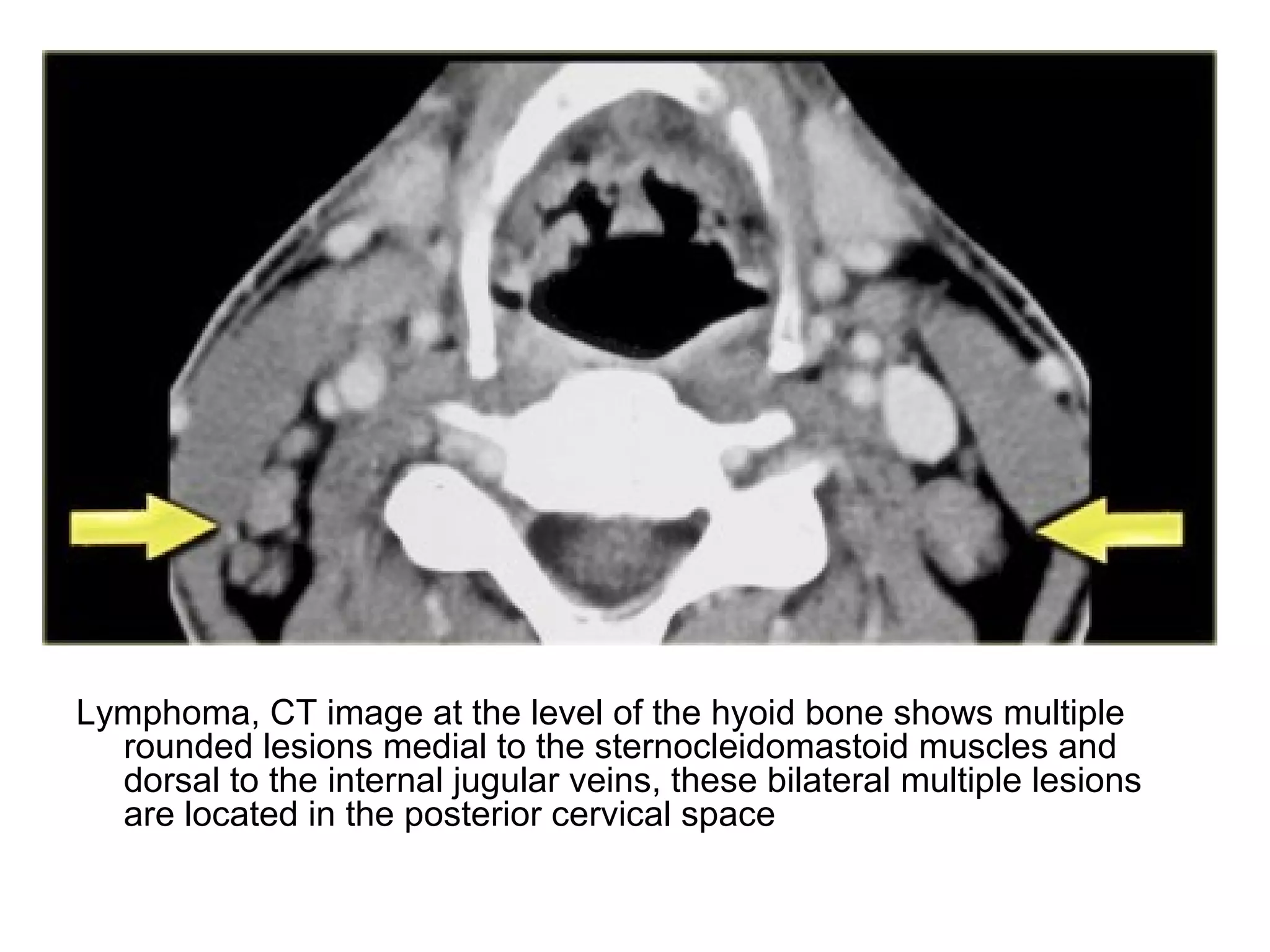
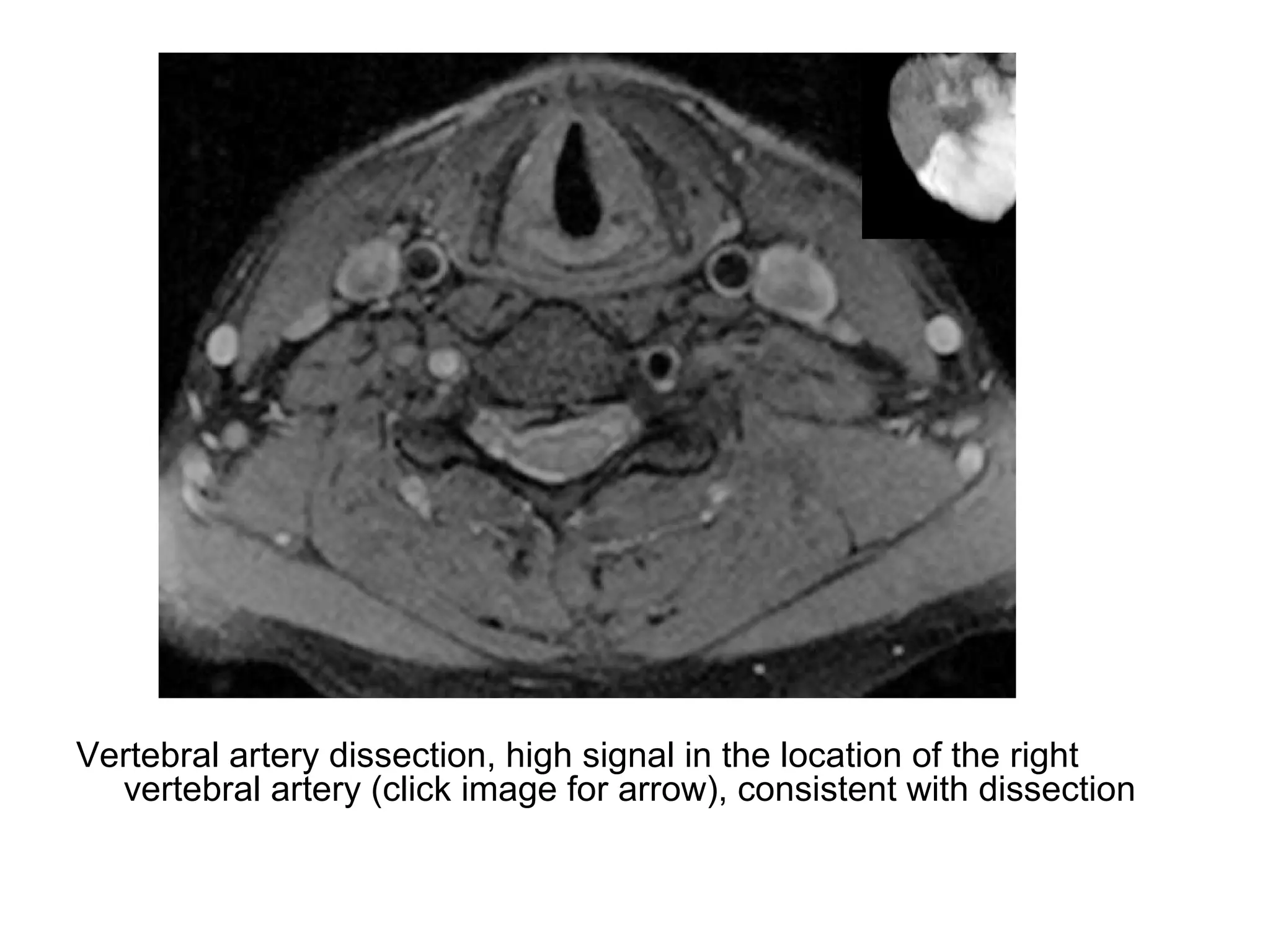
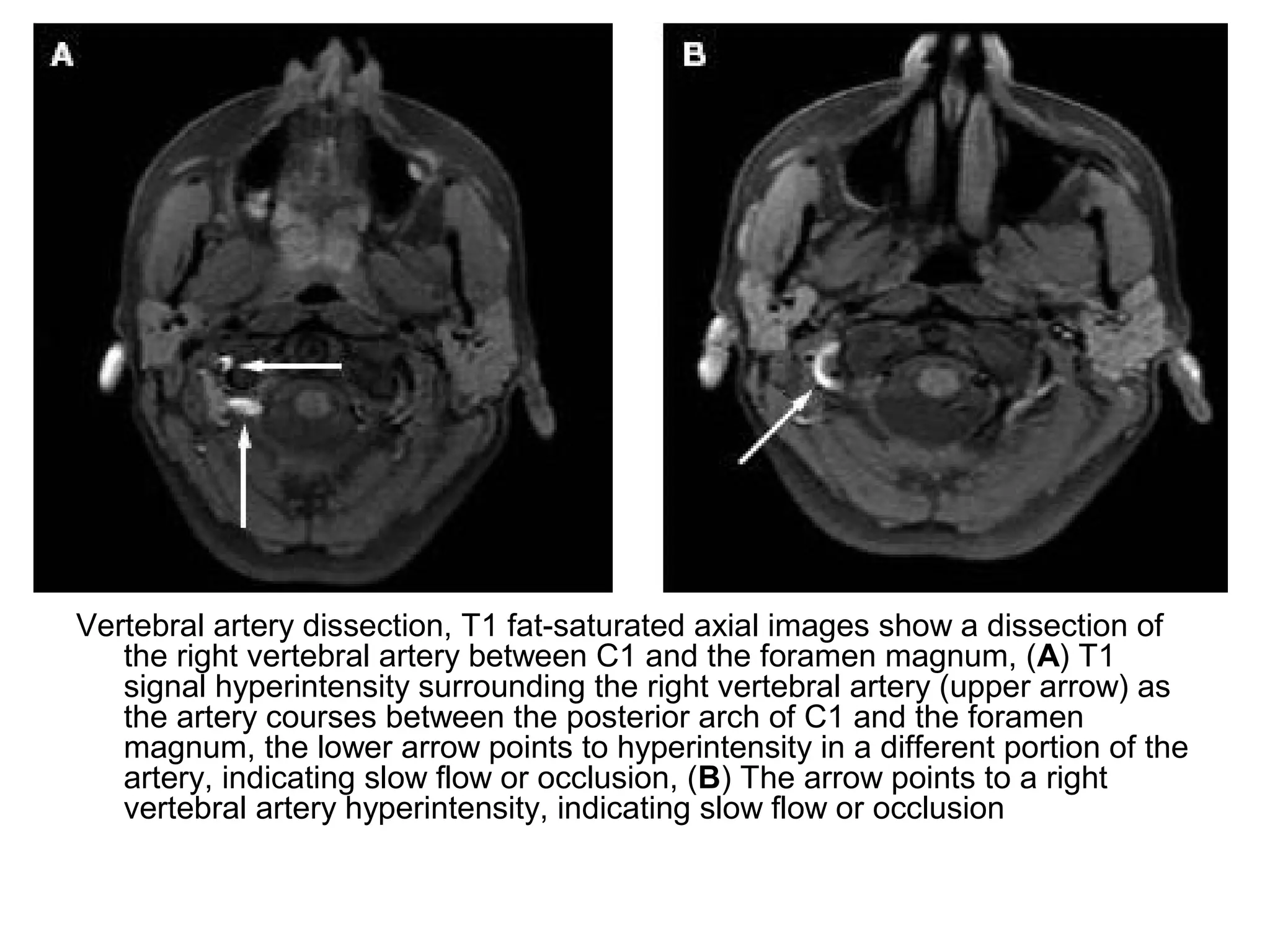
3. CT and MRI images are presented to illustrate normal anatomy as well as various diseases found within the deep neck spaces, such as abscesses, aneurysms, lymphadenopathy, tumors.