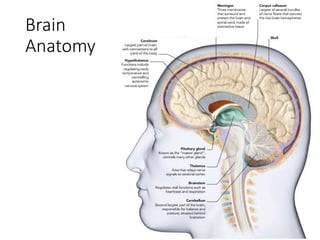
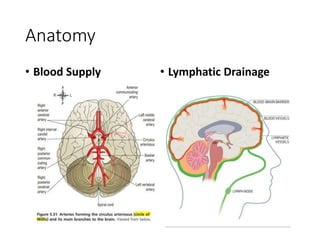
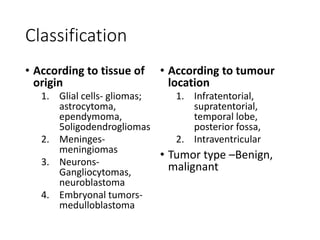
1. Brain tumors can be classified based on their tissue of origin, location in the brain, and tumor grade according to the WHO system. Common types include gliomas, meningiomas, and pituitary adenomas.
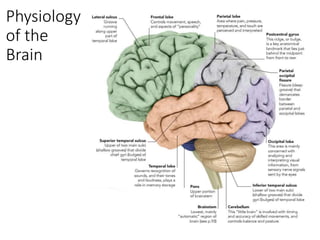
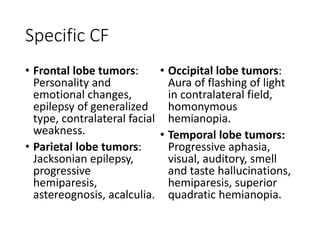
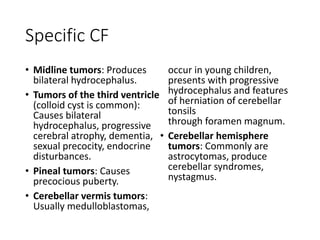
2. Symptoms of brain tumors are often non-specific but can include headaches, nausea, seizures, and changes in mental status. Specific symptoms depend on the location of the tumor in the brain.
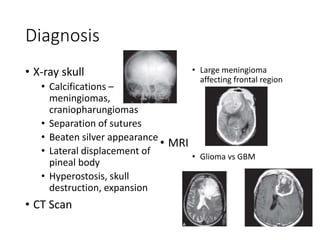
3. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT and MRI scans and may include biopsy for pathological examination. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and corticosteroids depending on the tumor type and grade. Prognosis varies based on these factors.