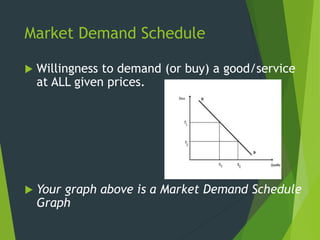
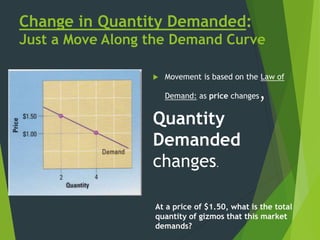
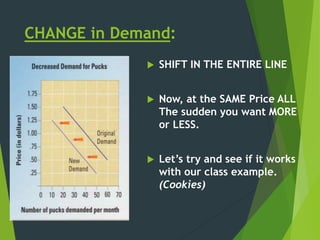
The document discusses the law of demand and factors that can cause a shift in demand. It explains that according to the law of demand, as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and as price decreases, quantity demanded increases. It then lists several factors that can cause the entire demand curve to shift, representing a change in demand: consumer income, substitutes, expectations about the future, consumer tastes, complements to the product, and changes in the number of consumers or market size.