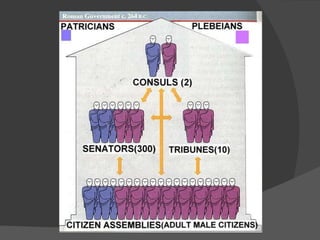
1. The document provides an overview of the origins and early history of Rome, including its transition from kingdom to republic. It discusses the influence of the Latins, Greeks, and Etruscans on early Roman culture.
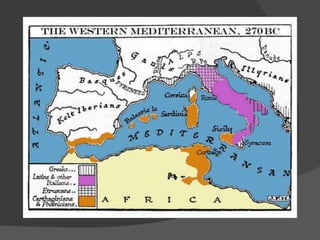
2. It then focuses on the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage, in which the brilliant Carthaginian general Hannibal crossed the Alps into Italy but was ultimately defeated by Rome.
3. Rome went on to defeat Carthage in the Third Punic War, extending its power and territory across the Mediterranean and marking its emergence as an early empire that made significant contributions to architecture, democracy, philosophy, and other areas of culture around the world.