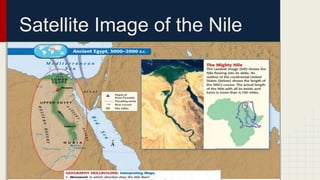
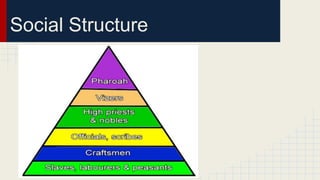
Ancient Egypt and Nubia were connected along the Nile River. Egypt was united into a kingdom around 3000 BC and entered its Old Kingdom period where many pyramids were built. Egyptian culture was centered around the pharaohs and polytheistic religions. Hieroglyphics developed for writing. The New Kingdom expanded Egypt's power and wealth along the Nile and into surrounding regions until invasions caused the empire to decline. Meanwhile, the Kushite kingdom in Nubia grew powerful, conquering Egypt at times and establishing the city of Meroe as a trade center until declining after 350 AD.





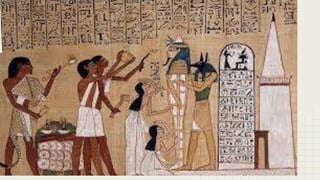


![Mummification
First, they draw out the brains through the
nostrils with an iron hook. . . . Then with a
sharp stone they make an incision in the side,
and take out all the bowels. . . . Then, having
filled the belly with pure myrrh, cassia, and
other perfumes, they sew it up again; and
when they have done this they steep it in
natron [a mineral salt], leaving it under for 70
days. . . . At the end of 70 days, they wash the
corpse, and wrap the whole body in bandages
of waxen cloth.
nHERODOTUS, The History of Herodotus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/egypt-211112135803/85/Egypt-12-320.jpg)










