This document summarizes key concepts about demand, including:
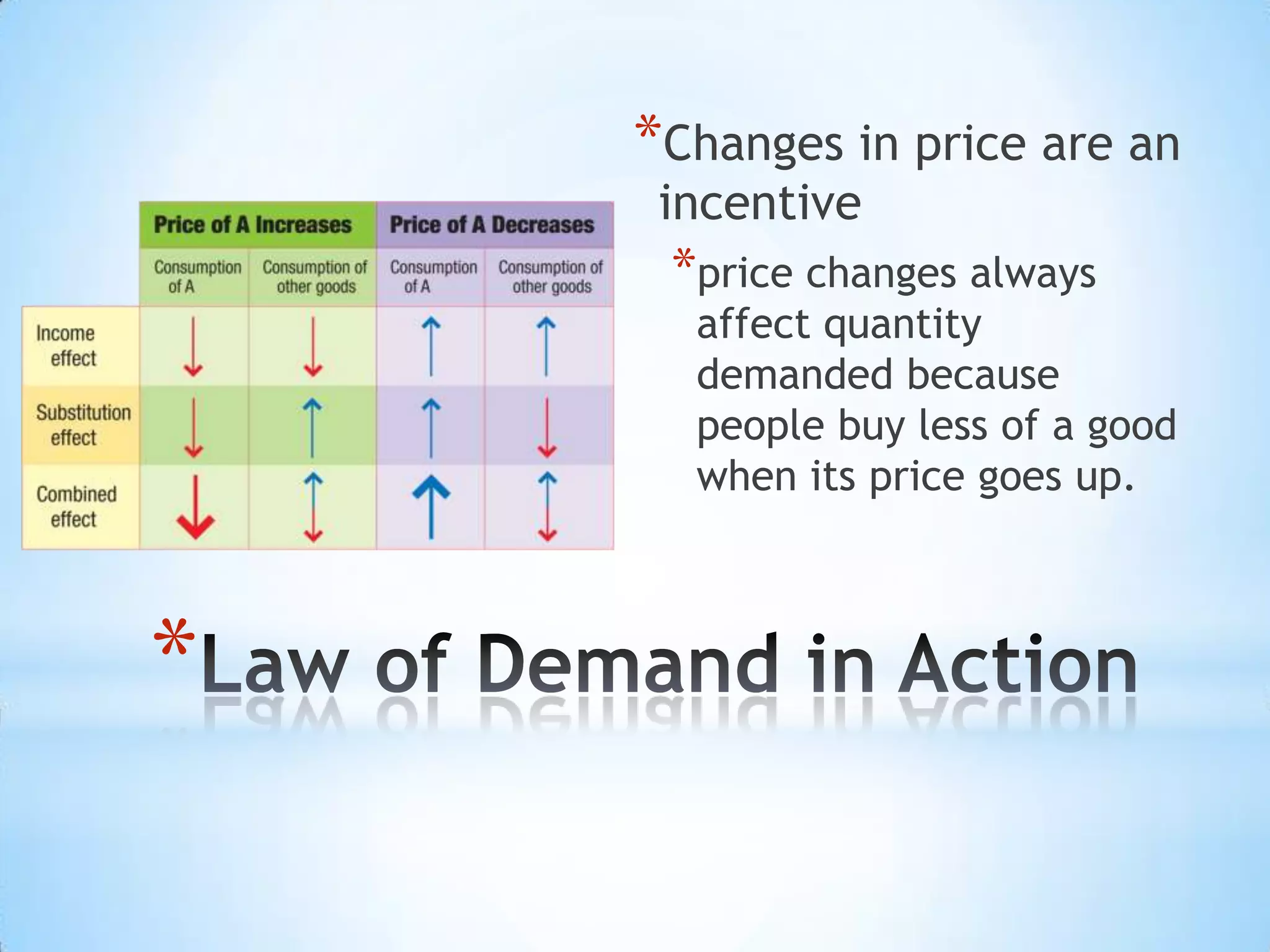
1) The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, due to the substitution and income effects.
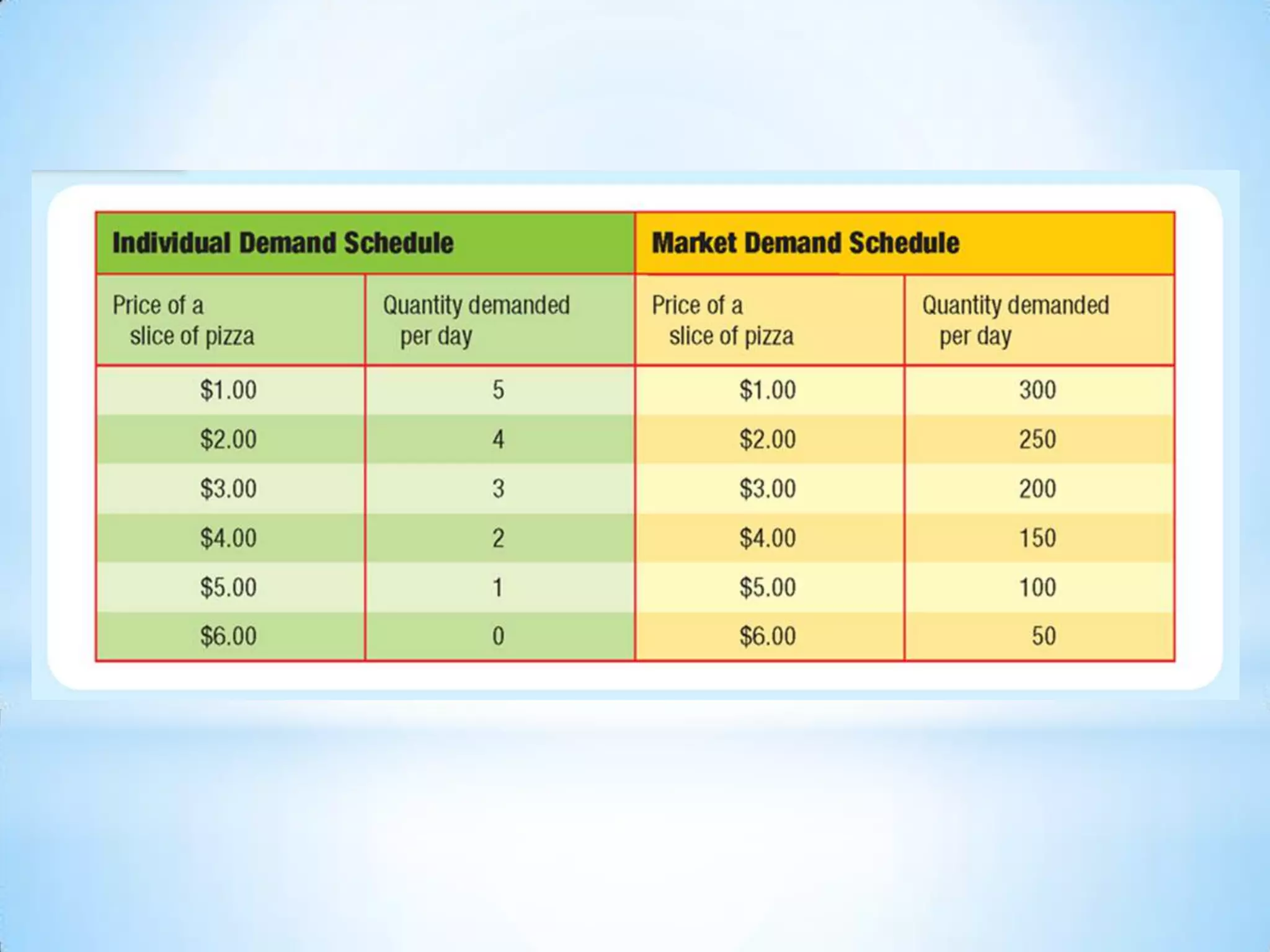
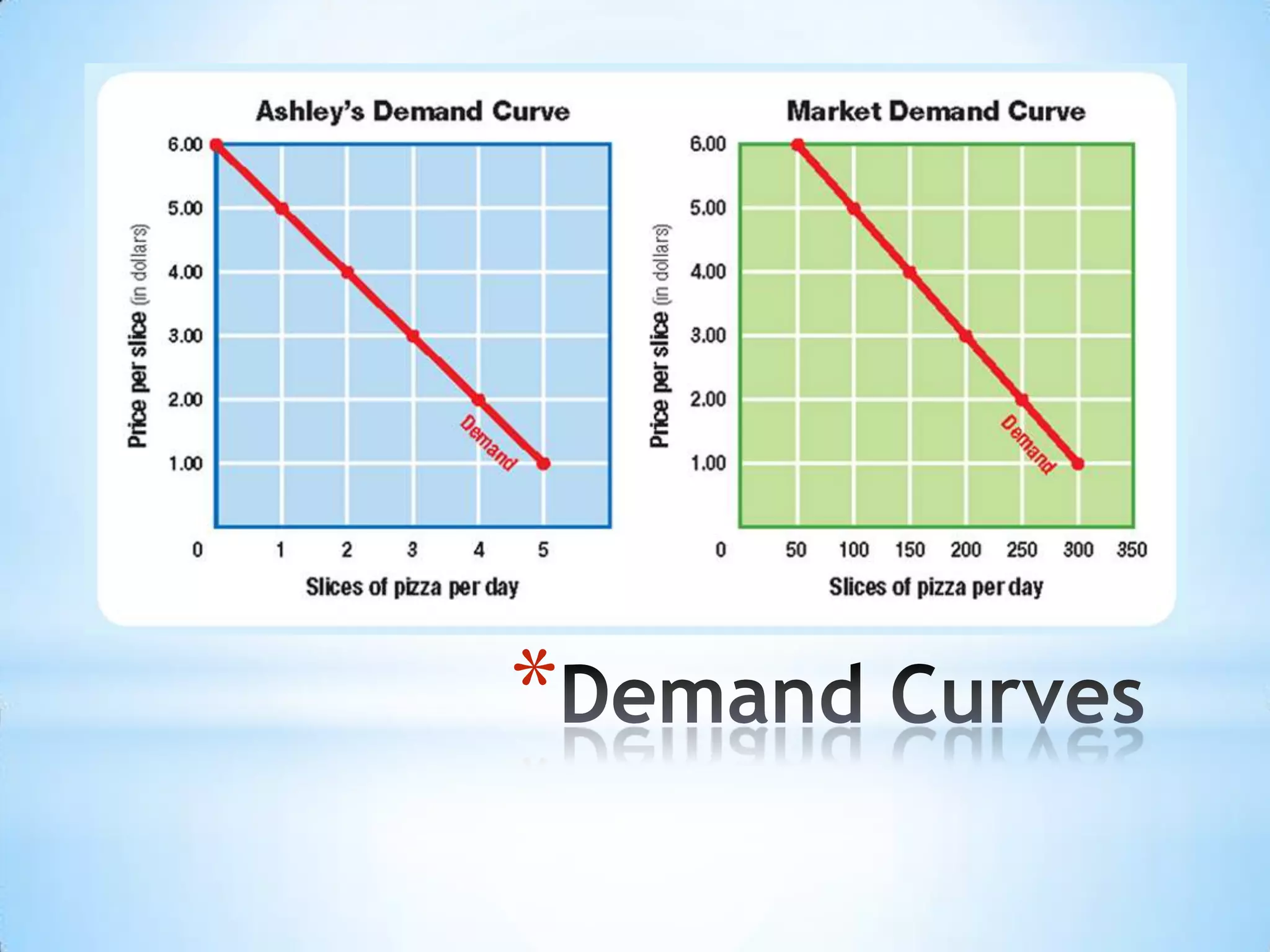
2) A demand schedule shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded, while a demand curve graphs this relationship.
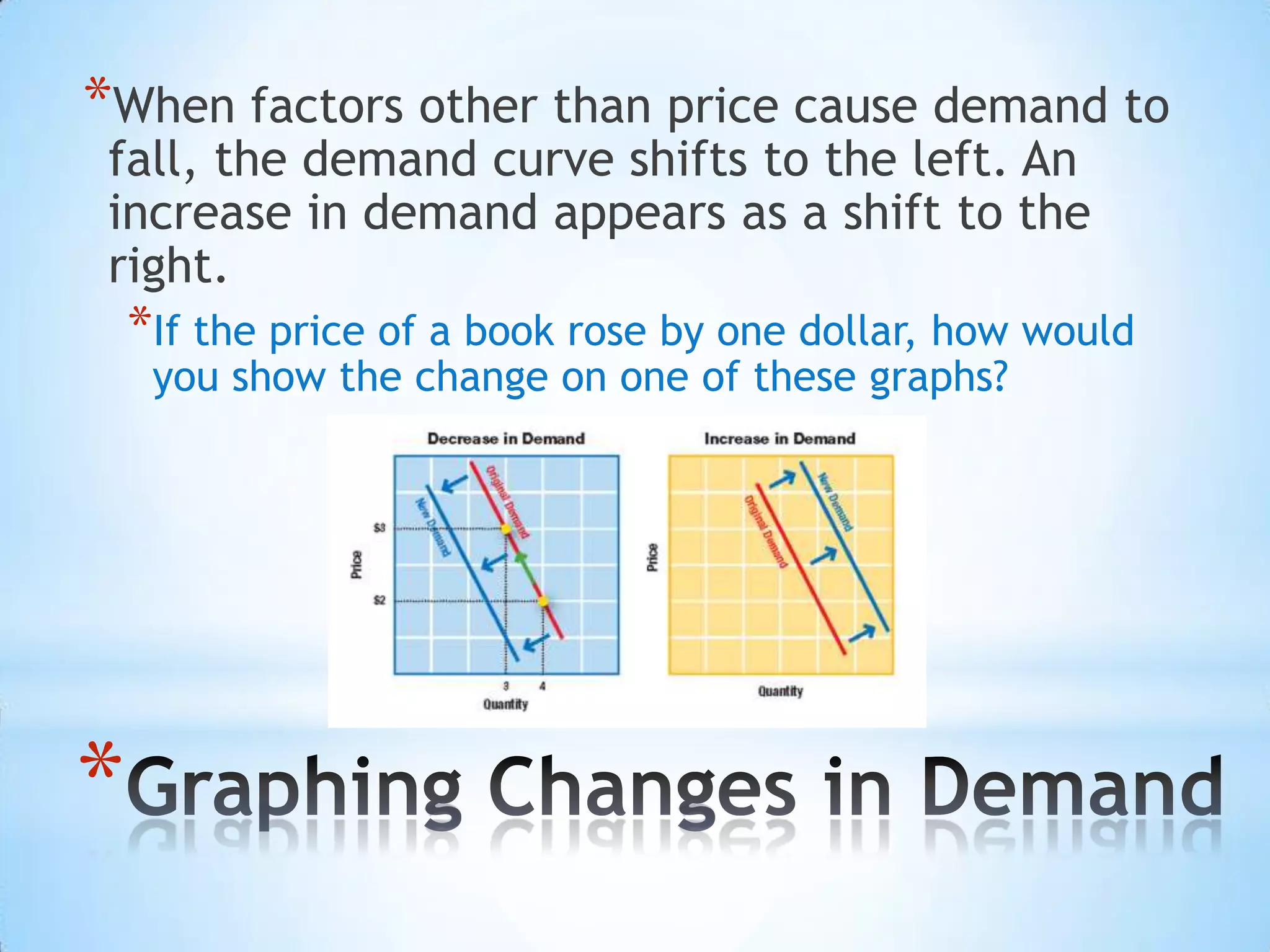
3) A shift in the demand curve occurs when non-price factors, like income, tastes, or expectations change, affecting the entire curve.
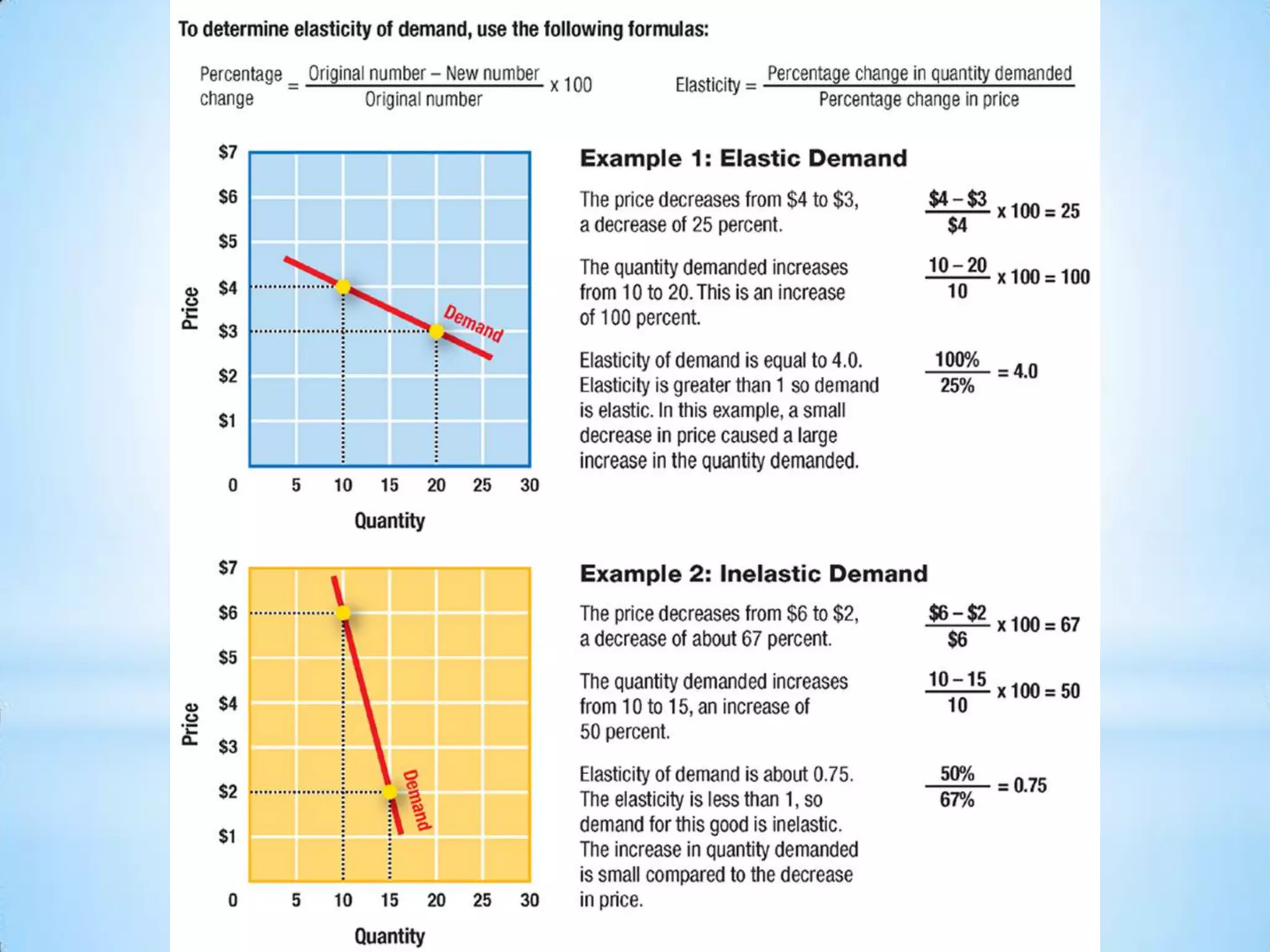
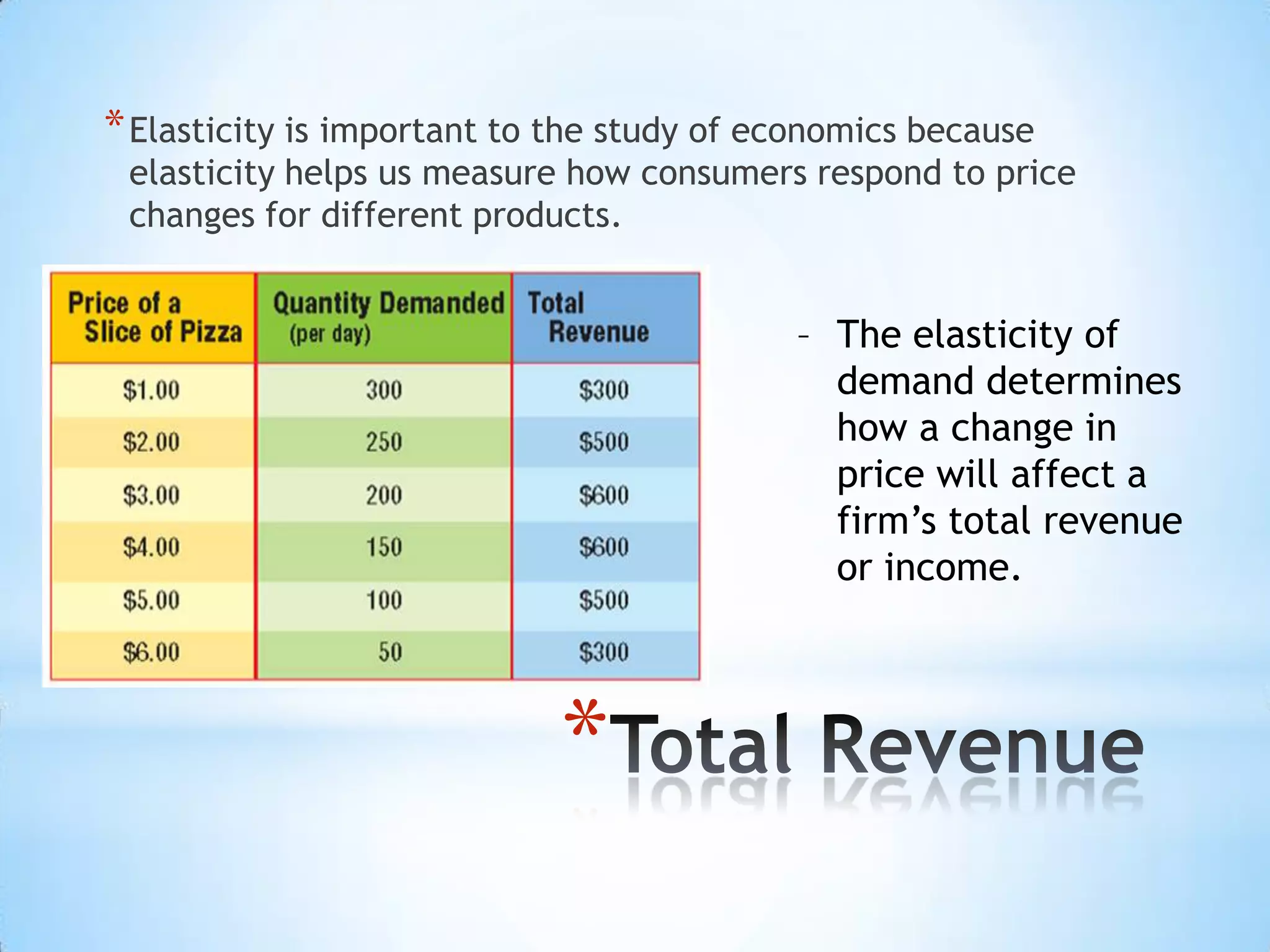
4) Elasticity measures how responsive quantity demanded is to price changes, and depends on availability of substitutes, importance of the good, and time. It helps firms set prices to maximize total revenue.