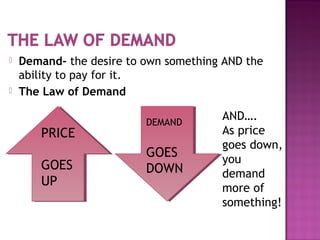
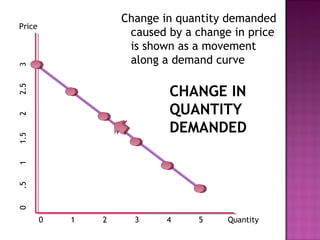
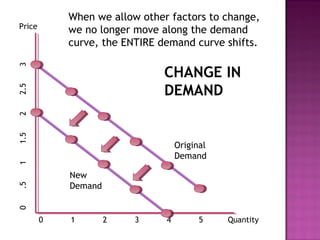
This document discusses the key concepts of demand, including the law of demand, demand curves, and factors that can cause a shift in the demand curve. It explains that the law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. A demand curve illustrates the relationship between price and quantity demanded, and it holds other factors constant. However, when factors like income, population, tastes, or prices of other goods change, it can cause the entire demand curve to shift, not just a movement along the curve. The document provides examples of how changes in these factors would impact demand.