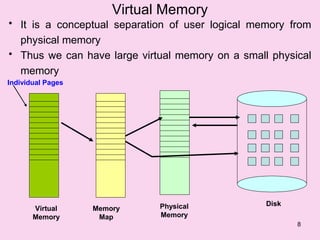
Virtual memory allows treating main memory as a cache for pages on disk. It implements the separation of user logical memory from physical memory, allowing logical address spaces to be much larger than physical memory. Virtual memory can be implemented via demand paging or demand segmentation and gives advantages like higher multiprogramming and allowing very large logical address spaces by paging pages between disk and memory as needed.