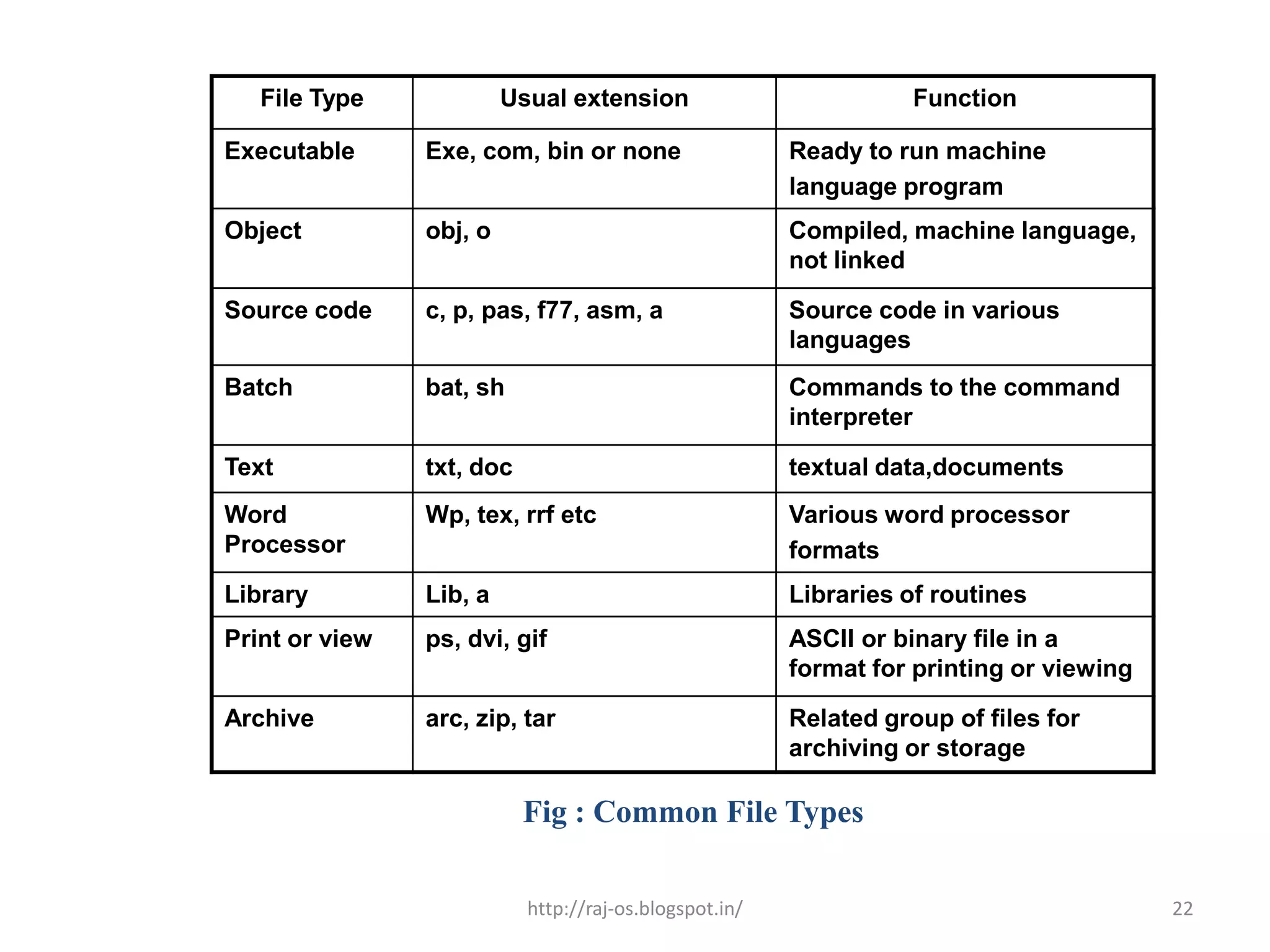
The document discusses file management and operations. It describes how files are organized through creating, storing, removing, opening, and closing files. It also covers file attributes like name, type, location, size, date/time of creation and modification, and protection. Common file operations are also summarized such as creating, writing, reading, repositioning, deleting, truncating, and appending files. The document also discusses file types and how operating systems can recognize and support different file extensions.