1. The document discusses various ways that computers represent integers and floating point numbers for processing, including unsigned, sign magnitude, one's complement, two's complement, and biased representations for integers. It also discusses the typical components of the floating point format including the sign, exponent, and significand.
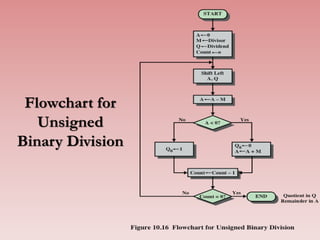
2. Key aspects of arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are described for different number representations. The two's complement system is highlighted as the most common approach used in computers due to its simplicity.
3. Standards like IEEE 754 are covered which define floating point standards to help ensure portability of numeric programs across systems.