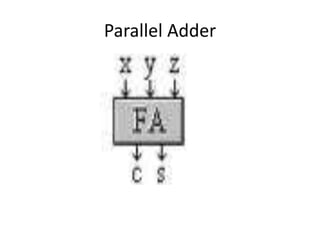
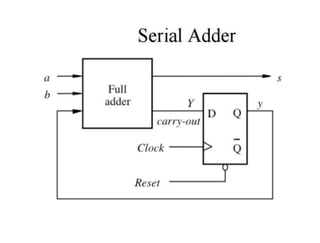
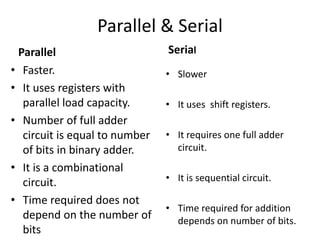
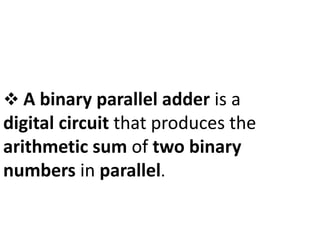
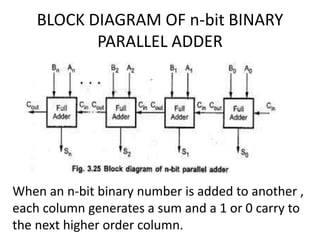
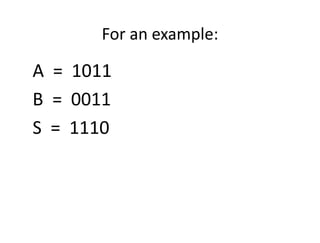A binary parallel adder is a digital circuit that produces the sum of two binary numbers in parallel using a cascade of full adders. It is faster than a serial adder since all bits are added simultaneously. The number of full adders used equals the number of bits. Each full adder generates a sum and carry output, with the carry output connected to the next stage as input carry. This structure is known as a ripple carry adder and has a worst case delay equal to the time for a carry to propagate through all stages. Parallel adders can be constructed using IC chips and cascaded to handle more bits.