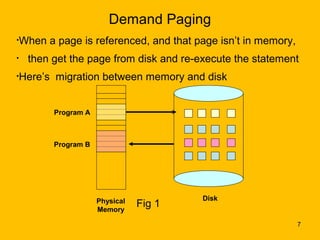
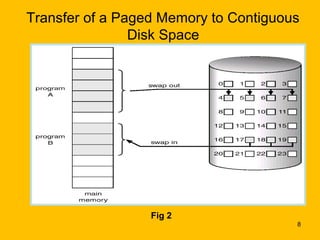
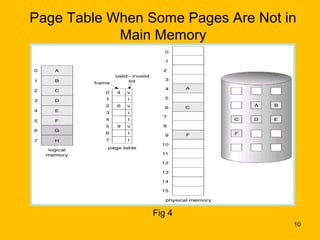
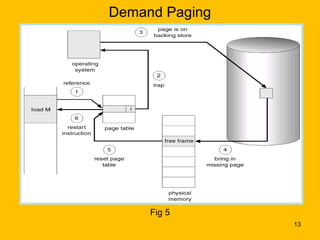
Demand paging is a virtual memory technique where pages are brought into memory only when needed, reducing I/O and memory usage compared to swapping. When a process references a page not currently in memory, the system checks permissions and retrieves the page from disk if valid. It finds a free frame, loads the page, updates the page table, and restarts the faulting instruction. This lazy loading approach brings pages in only as needed rather than pre-loading the entire process address space.