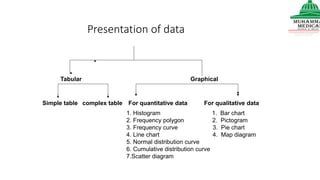
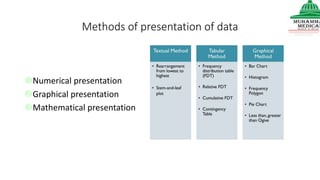
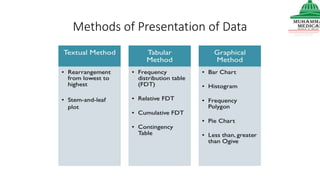
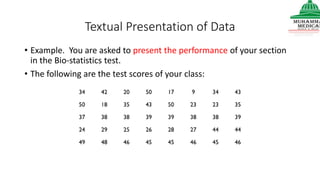
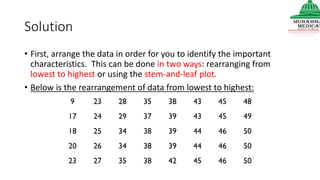
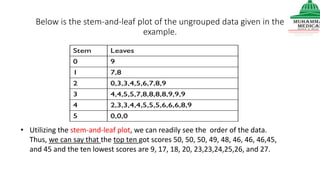
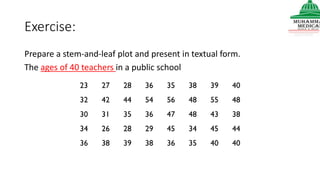
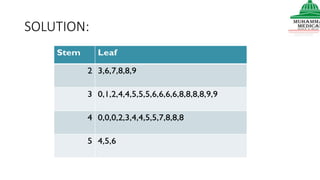
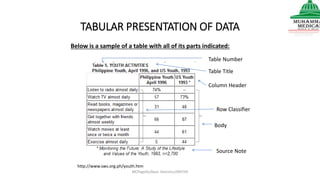
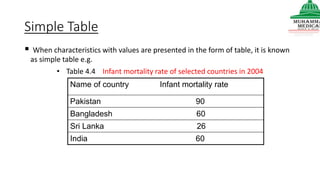
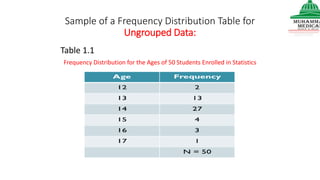
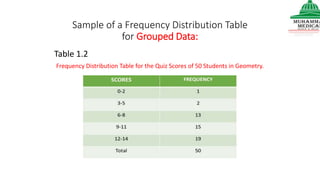
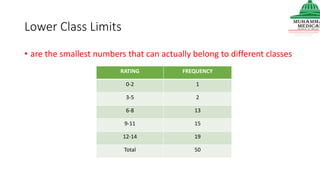
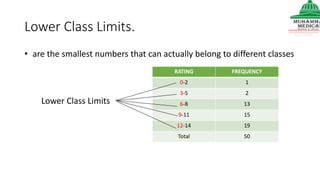
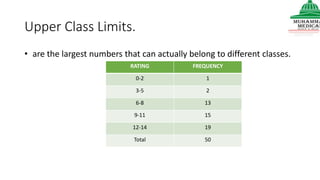
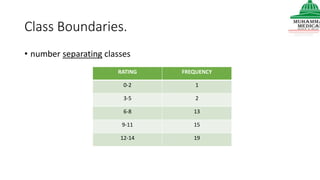
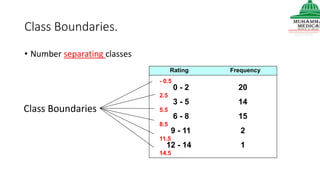
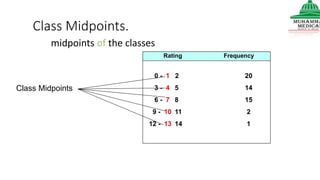
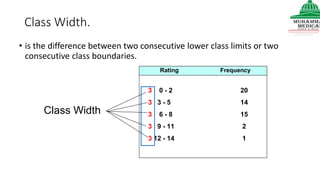
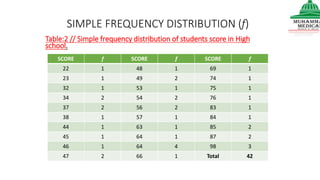
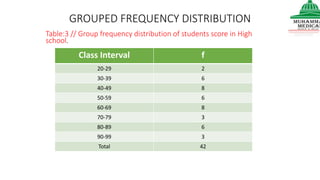
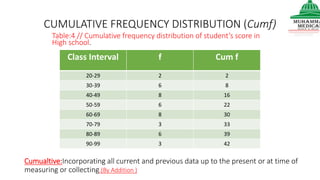
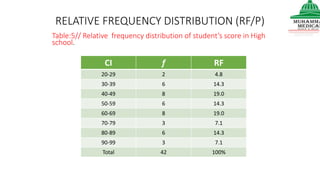
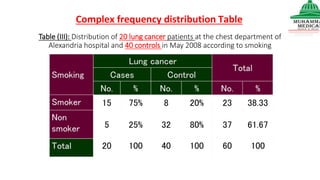
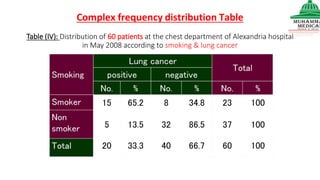
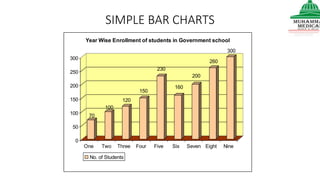
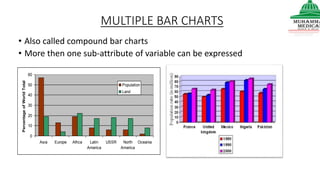
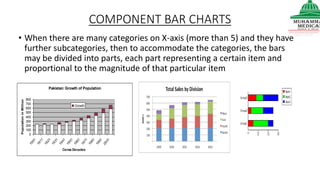
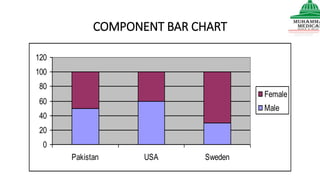
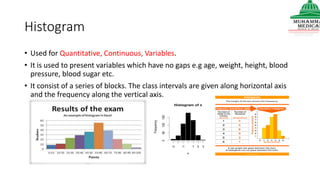
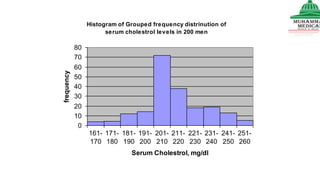
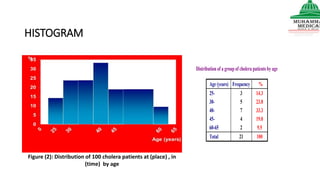
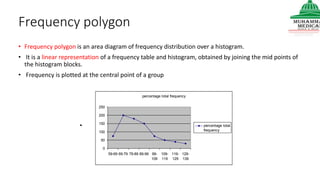
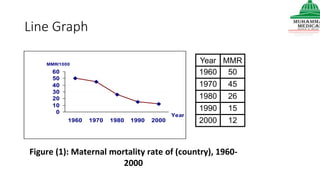
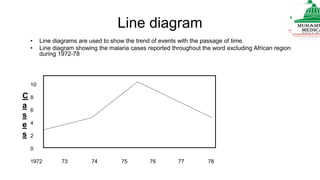
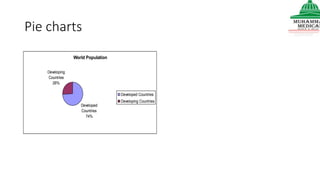
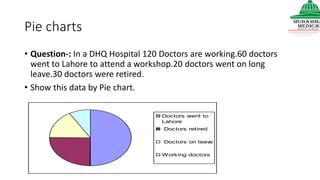
This document provides information on various methods of presenting data, including tabular, graphical, and textual presentation. It discusses principles of data presentation and different types of tables, charts, and diagrams that can be used including simple tables, frequency distribution tables, bar charts, histograms, line graphs and pie charts. It also covers concepts like class intervals, frequency, relative frequency and discusses worked examples of various methods of data presentation.