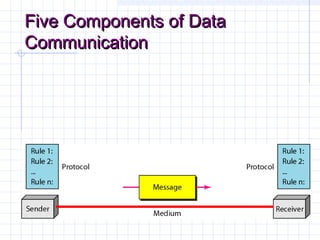
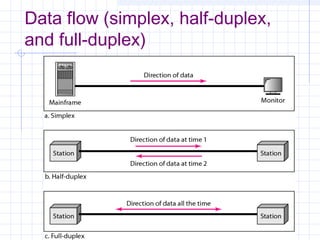
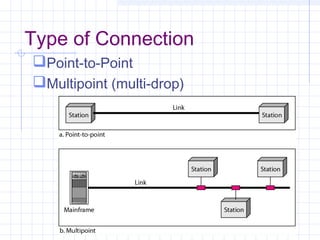
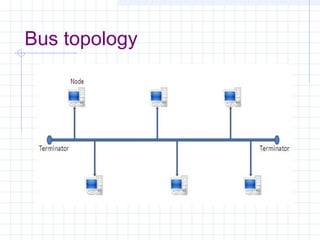
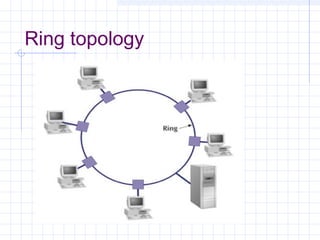
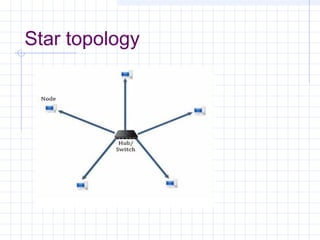
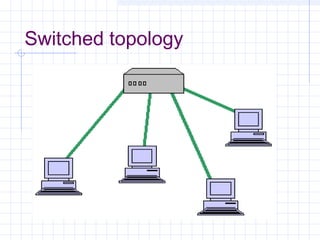
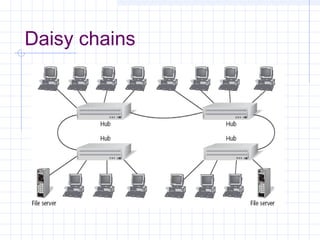
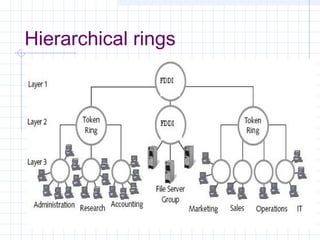
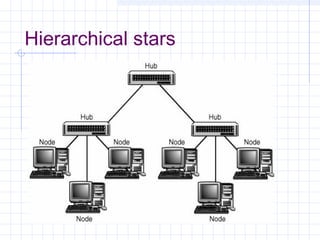
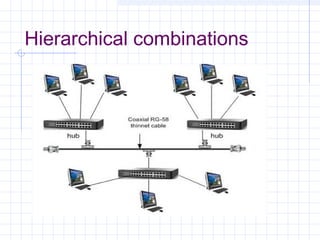
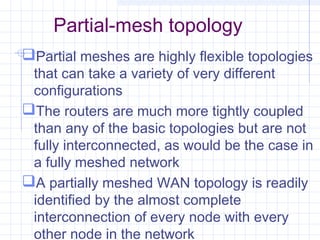
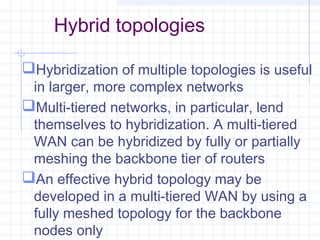
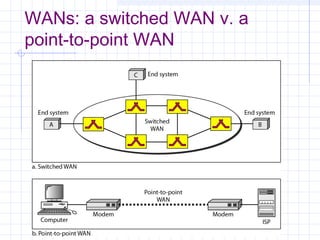
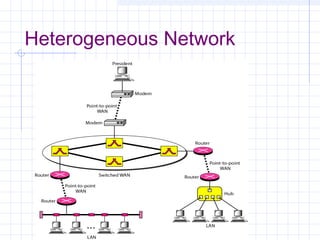
The document provides an overview of data communication and computer networks, detailing key concepts such as telecommunication, data exchange between devices, and the five major components of data communication. It describes various network topologies including bus, ring, star, switched, and hybrid, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers different types of Wide Area Network (WAN) topologies and the role of protocols and standards in ensuring interoperability in data communication technologies.