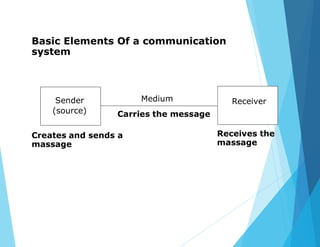
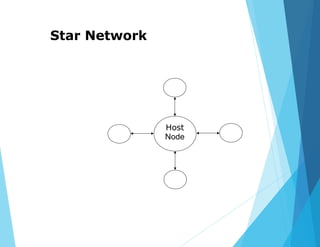
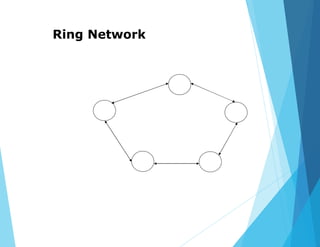
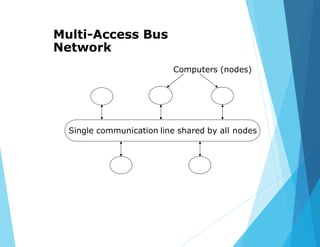
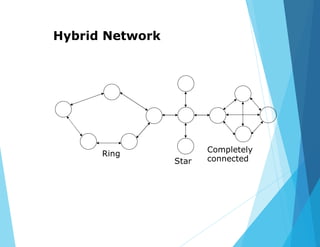
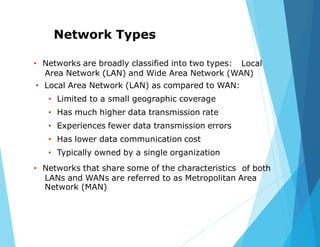
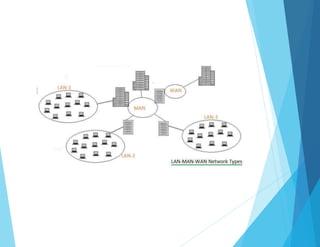
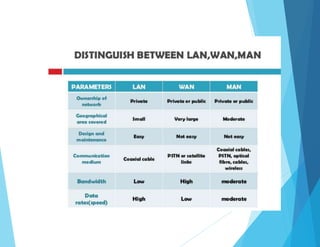
This document provides an overview of data communications and computer networks. It discusses the basic elements of a communication system including senders, receivers, and transmission media. It then describes different types of transmission media such as twisted pair wire, coaxial cable, microwave systems, and optical fibers. The document also covers digital and analog data transmission, network topologies including star, ring, bus and hybrid networks. It defines local and wide area networks and describes some common networking devices like network interface cards.