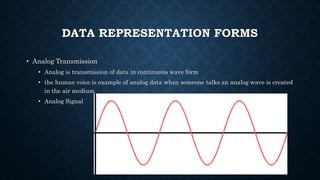
Data communication involves the transmission of electronic data between nodes through a communication medium. There are several fundamental principles and basic elements of a communication system. The principles include delivery of data to the correct destination, accuracy of the data, and timely delivery. The basic elements are the message, sender, medium, receiver, and protocols. Common wired media include twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable. Wireless media include Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks. Protocols like TCP/IP govern how devices communicate by handling delivery and addressing. Data can be transmitted in analog or digital form.