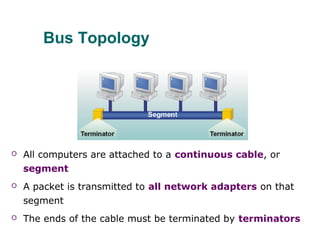
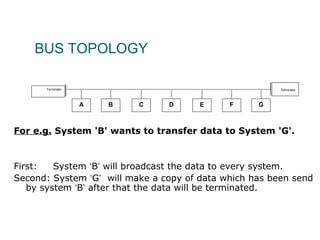
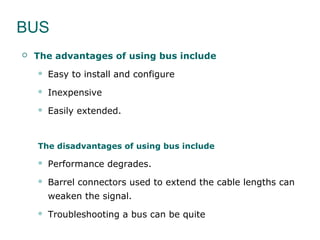
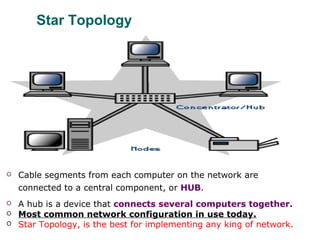
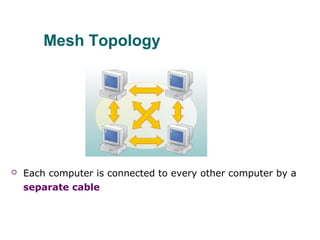
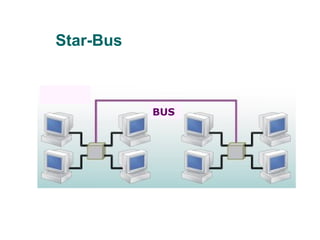
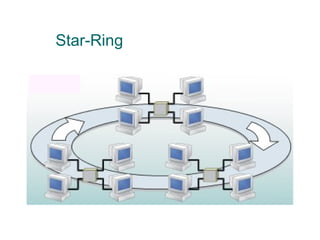
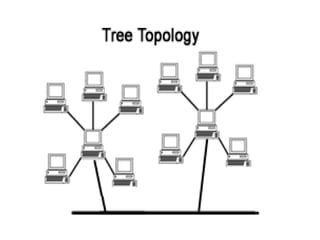
The document discusses various network topologies, including physical and logical arrangements of devices within a Local Area Network (LAN). It details six basic physical topologies: bus, star, ring, tree, mesh, and hybrid, along with their advantages and disadvantages, such as ease of installation versus performance issues. Additionally, it highlights Dr. Kamal Gulati's qualifications and contributions to the field of computer science and networking.
















![Dr. Kamal Gulati
Associate Professor |
University Quality Support Head |
Mentoring Programme Coordinator
]Ph. D., M.Sc. (Computer Science), M.C.A., M.B.A[
Professional Certifications:
Certified Microsoft Innovative Educator
Data Science 101 Certification from Big Data University
R Language 101 Certification from Big Data University
SQL Certification from SOLOLEARN.com
Certified IBM Big Data 101 from Big Data University
R Program & Python Certified from DataCamp
Wiley Certified Big Data Analyst [WCBDA[
Certification on DBMS from IIT Mumbai
Certified Cisco Certified Network Associate [CCNA[
Certified Microsoft Certified Professional [MCP[
Certified Brainbench in Computer Fundamentals, Microsoft Access, MySQL
5.7 Administration & Microsoft Project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networktopologies-171208050453/85/Network-Topologies-in-Simple-Logical-Physical-and-Types-30-320.jpg)




