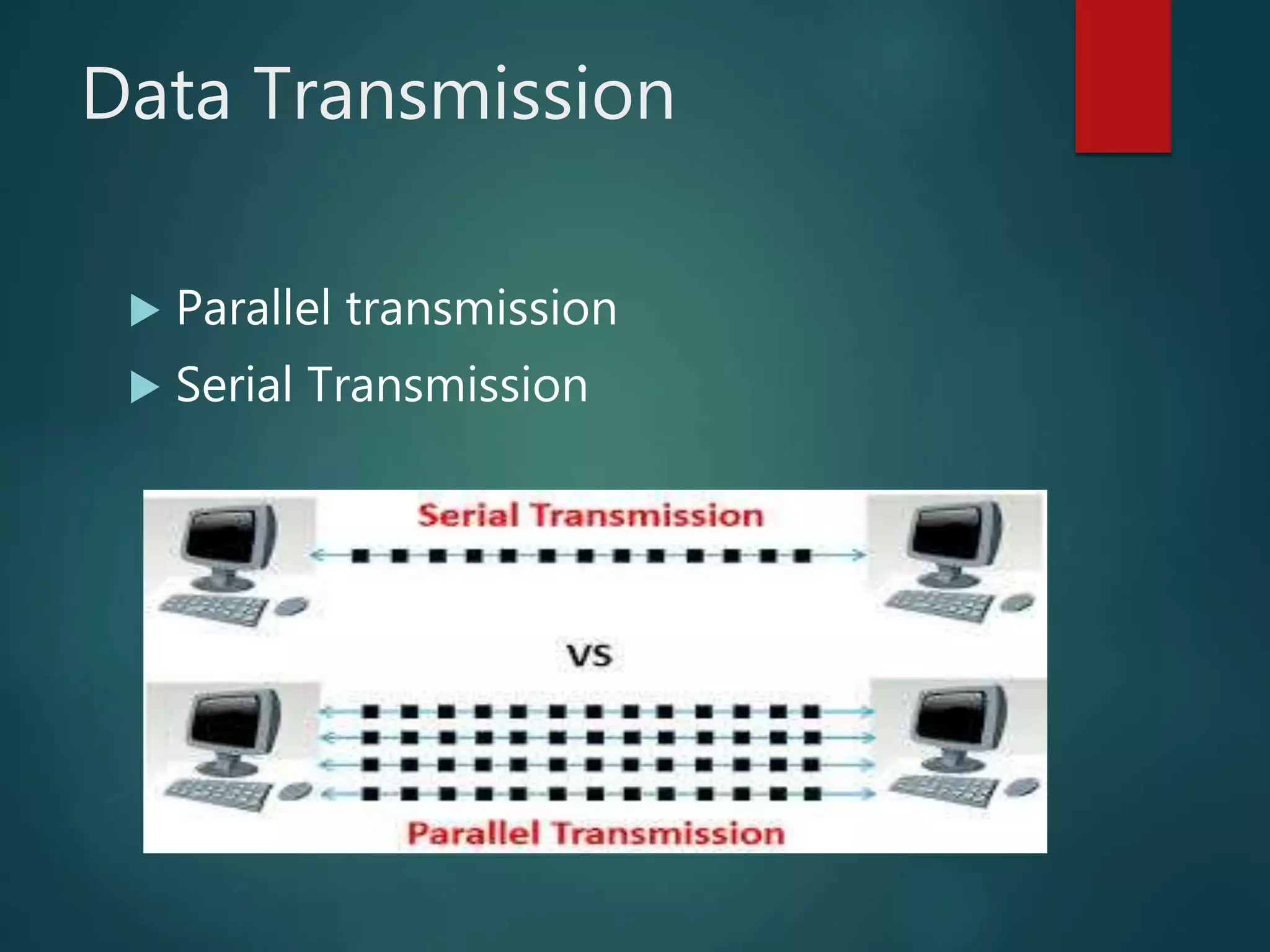
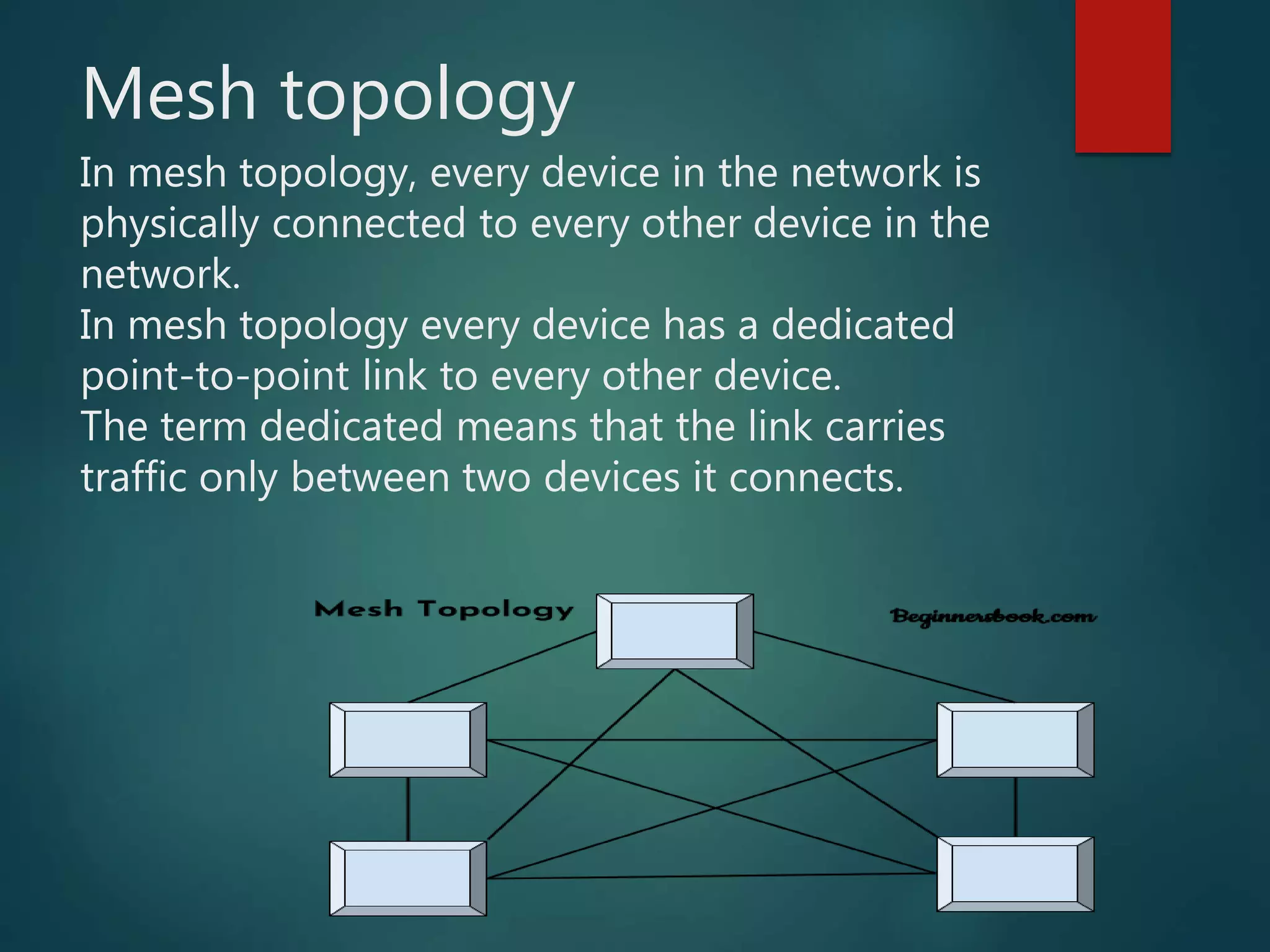
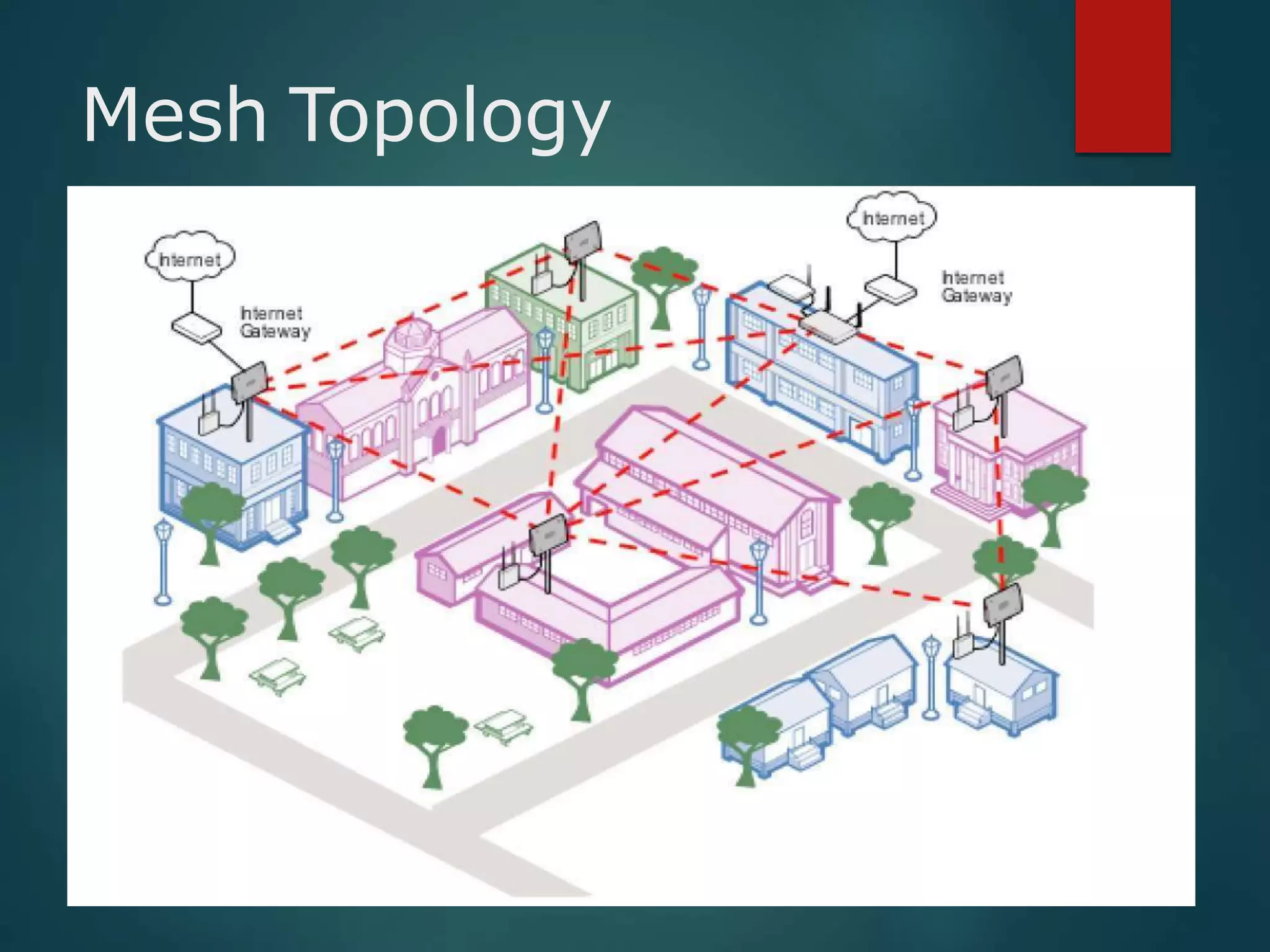
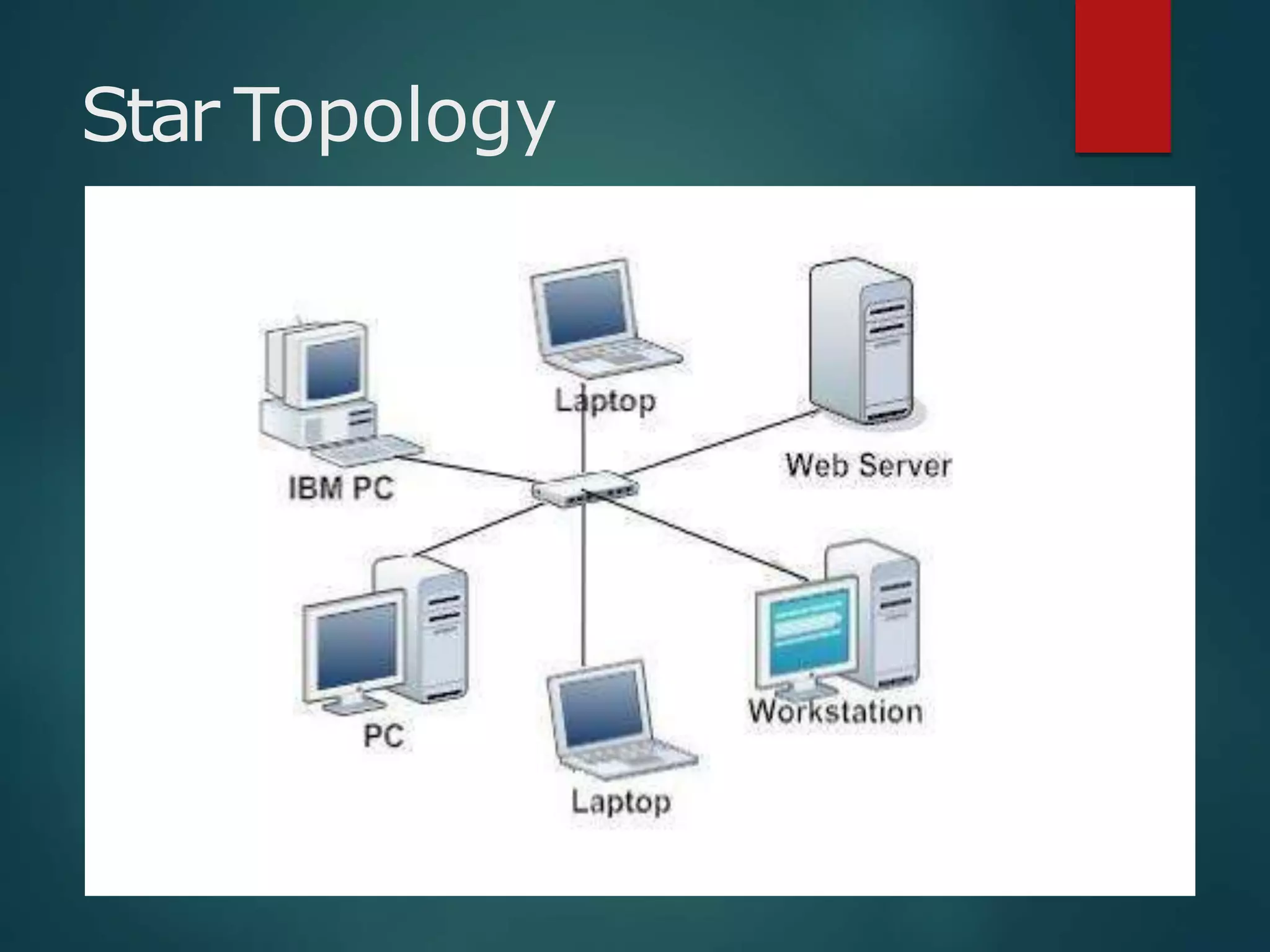
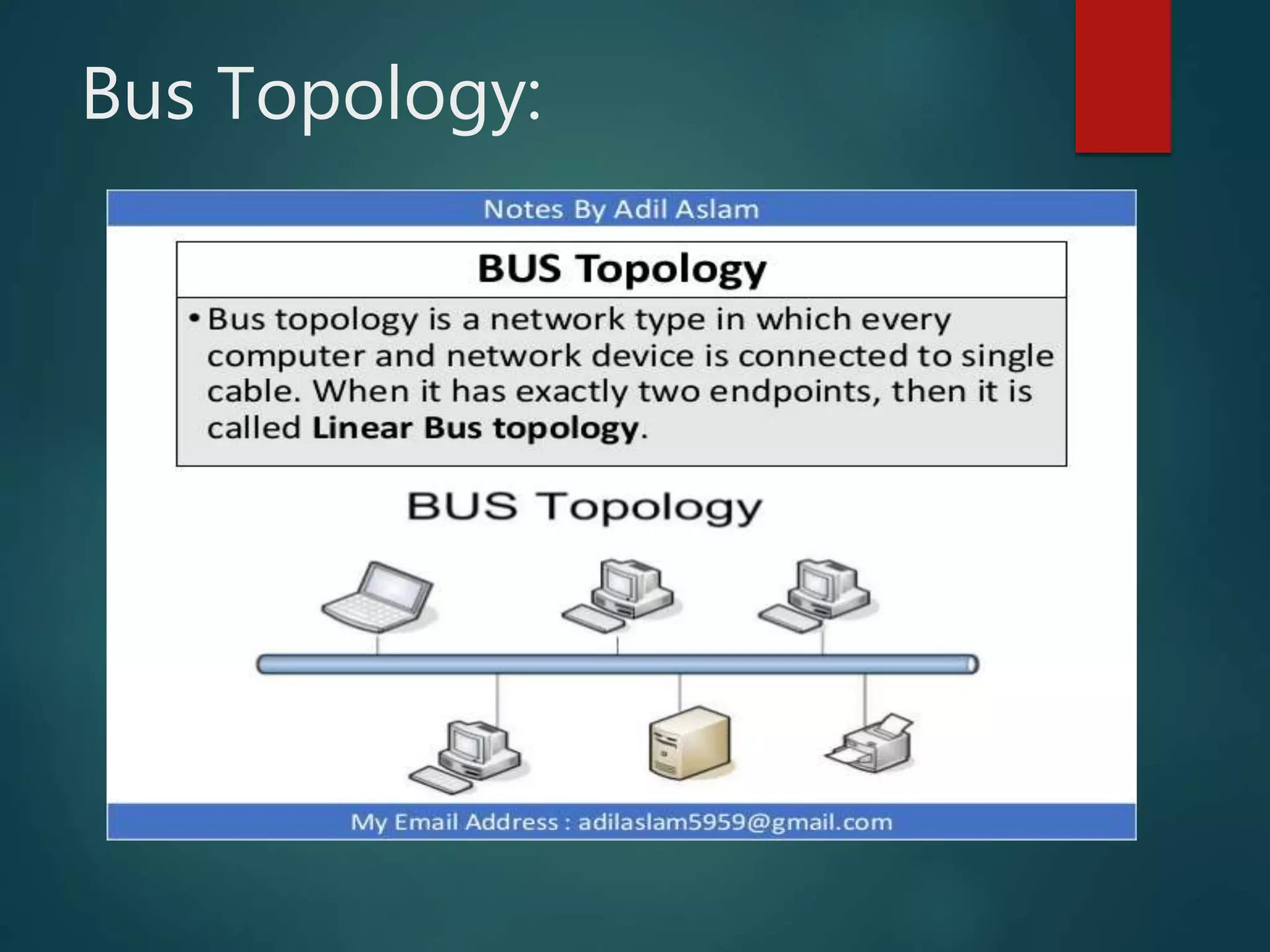
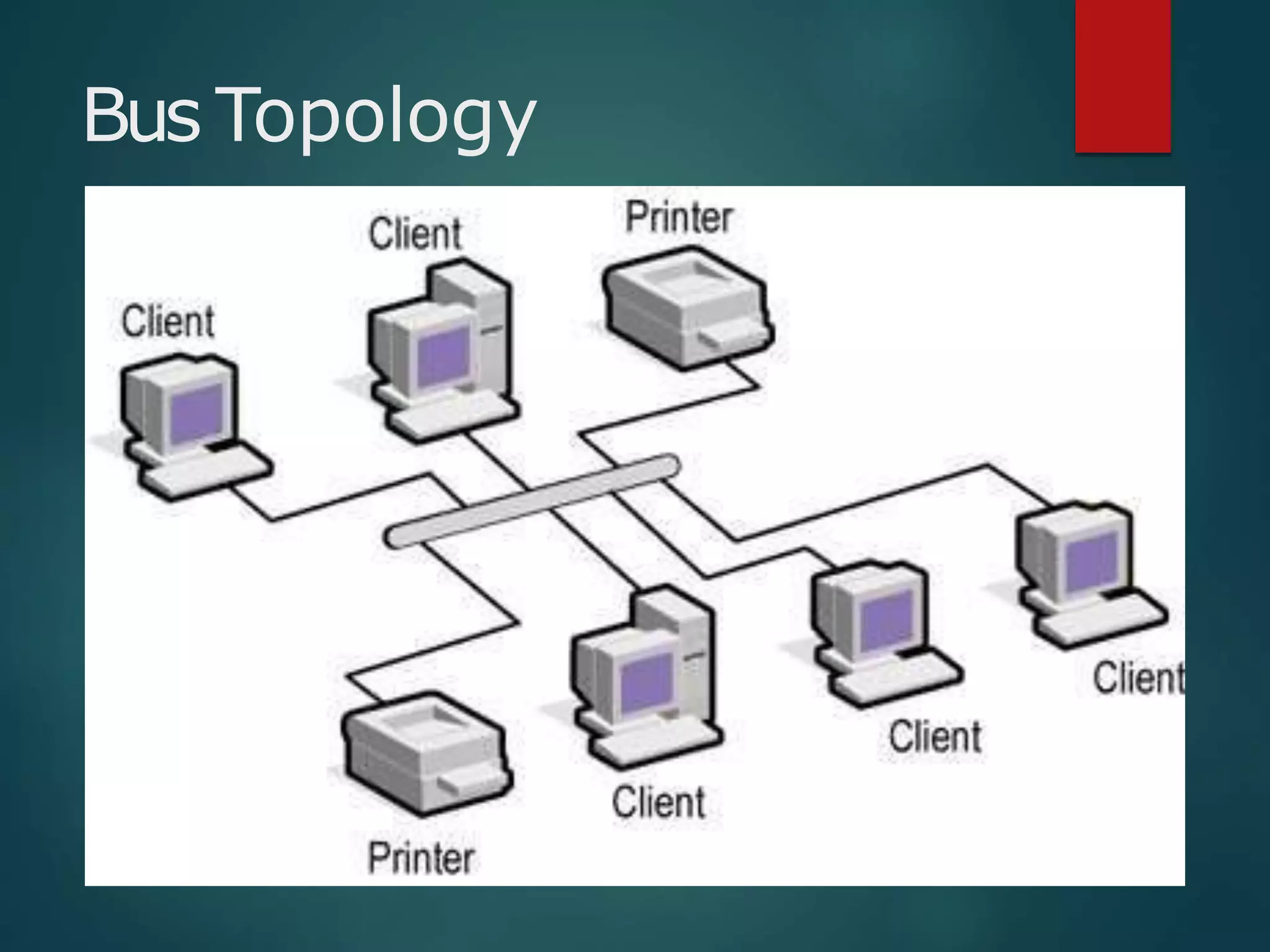
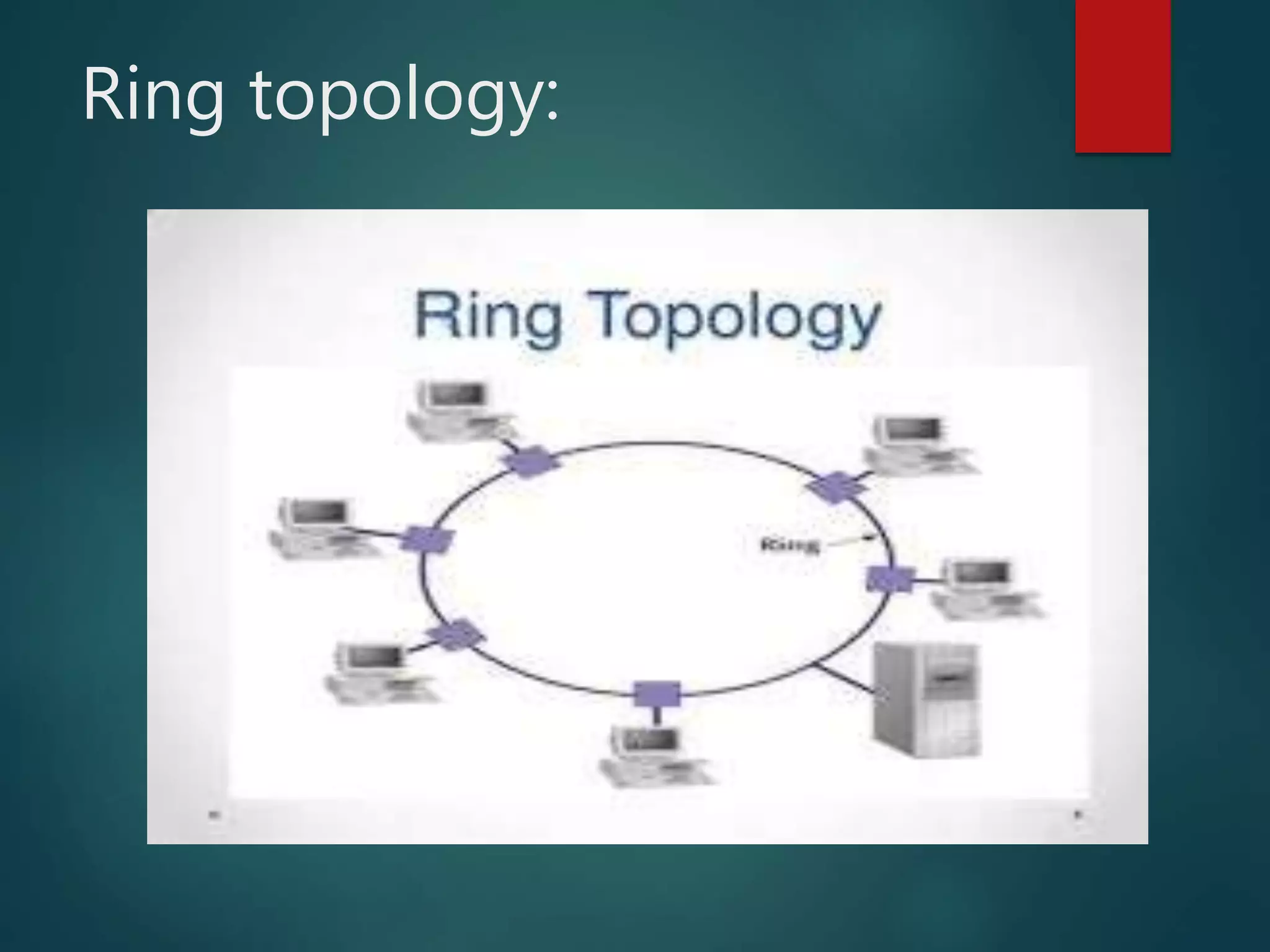
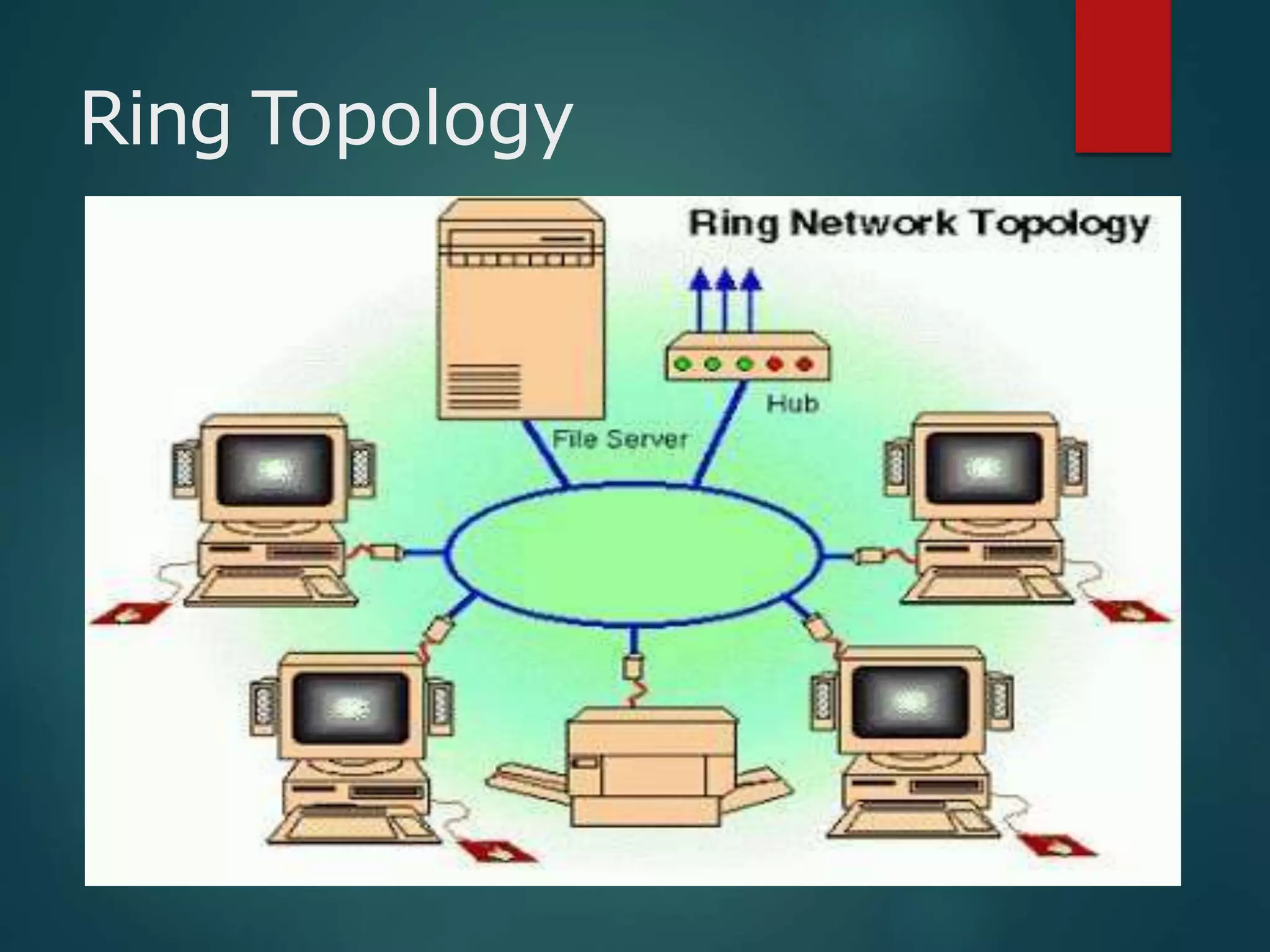
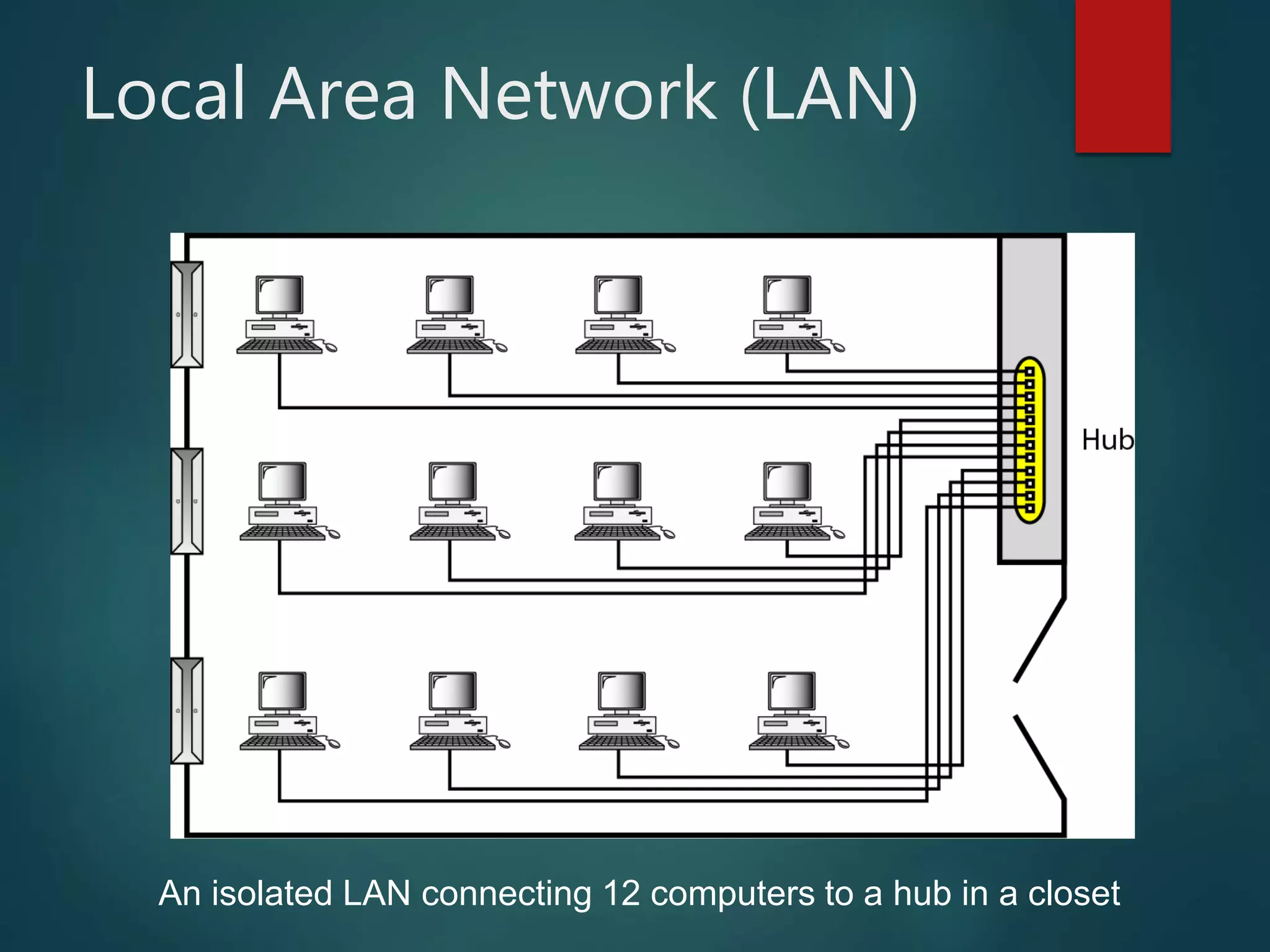
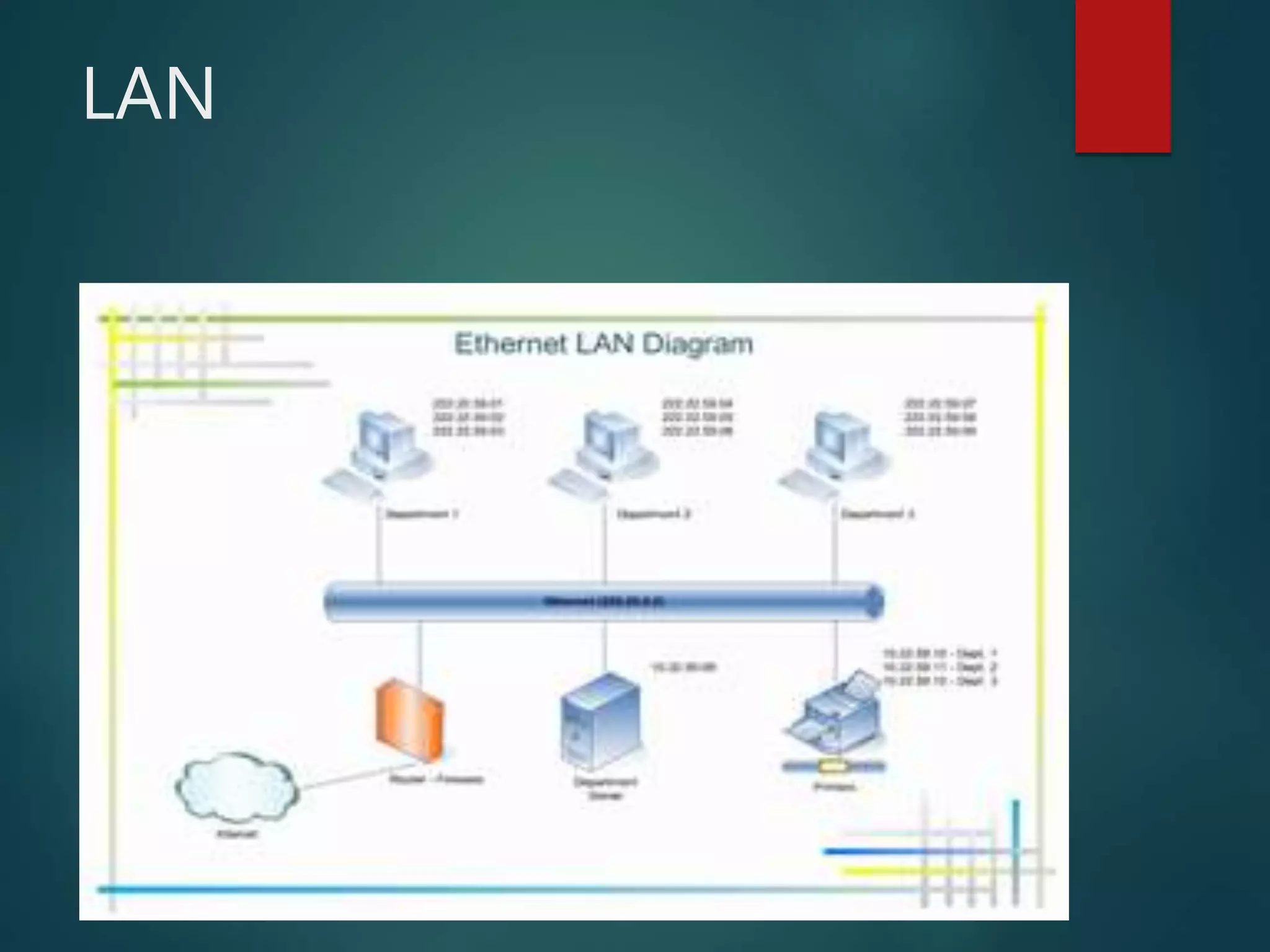
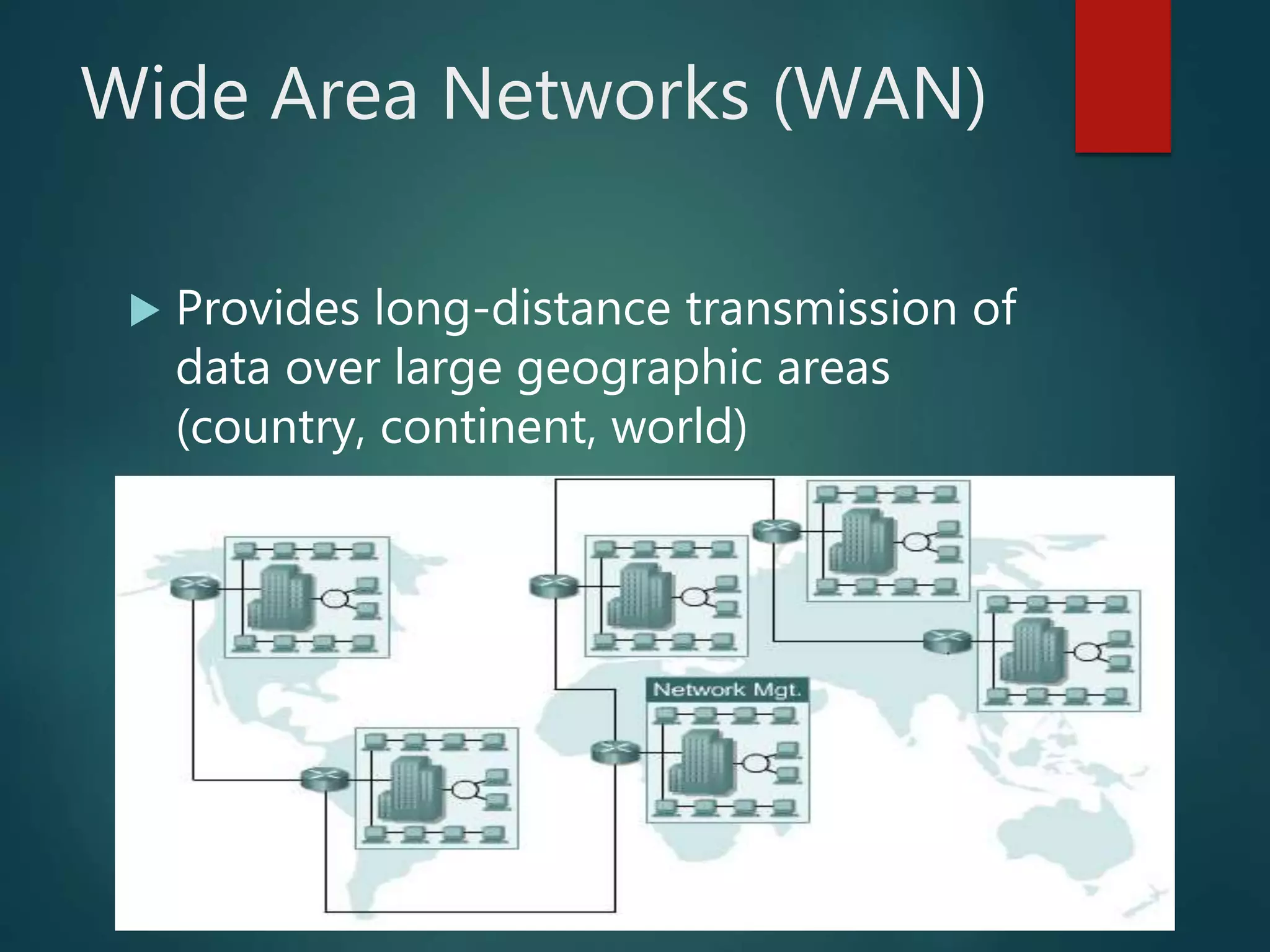
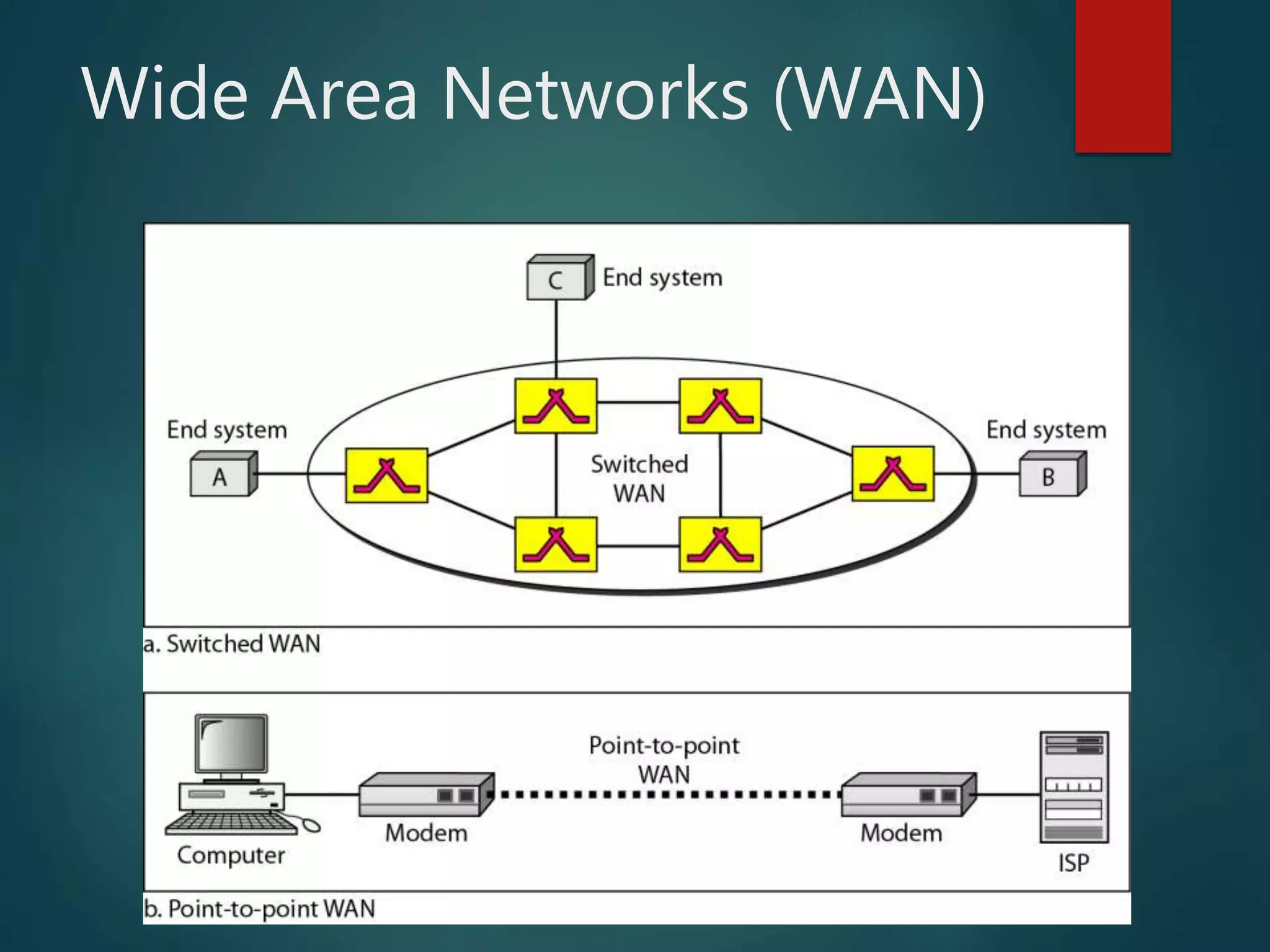
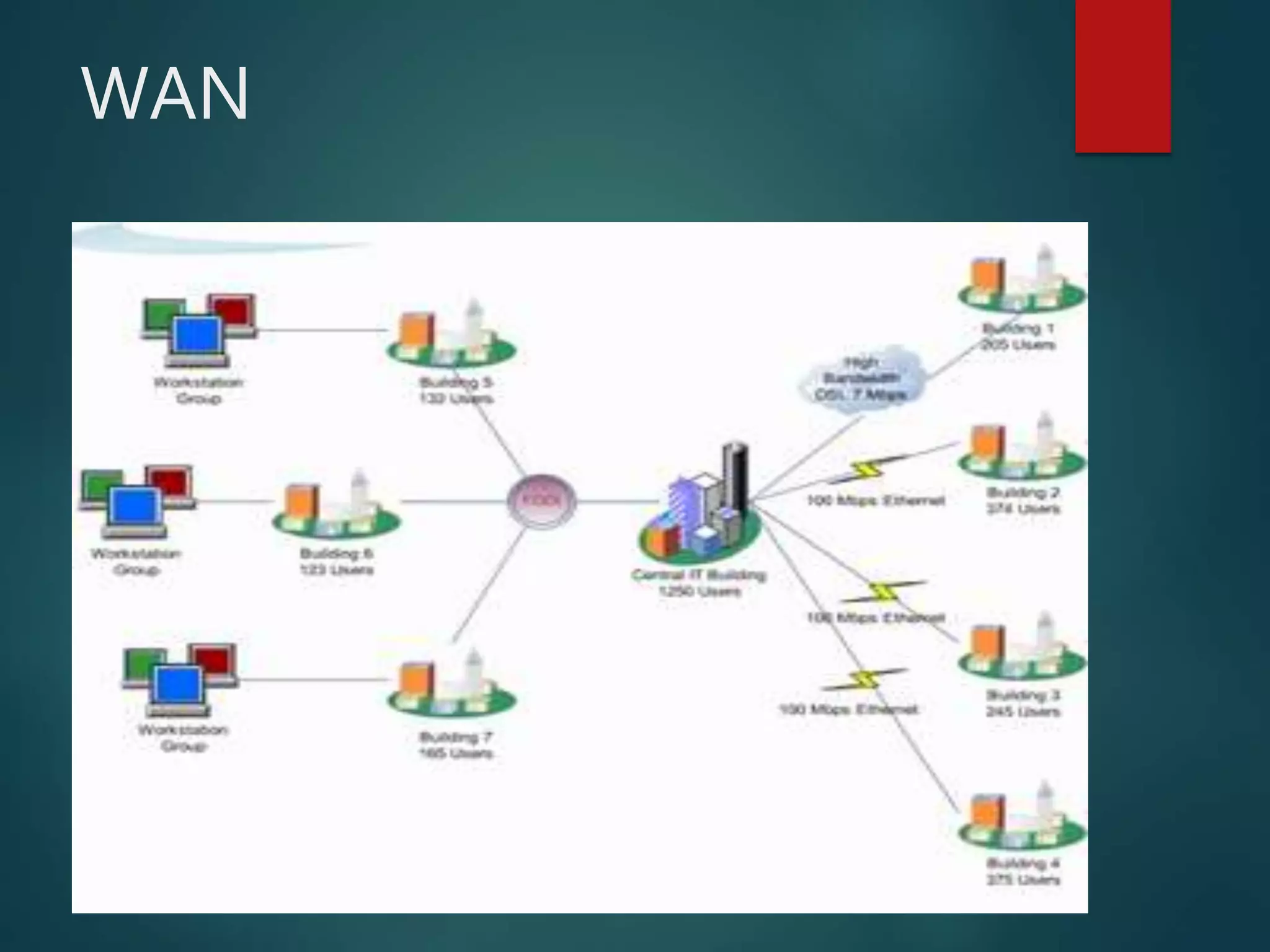
The document discusses data communication and networks, detailing how data is exchanged between devices and the various components of communication systems, including messages, senders, receivers, transmission mediums, and protocols. It explores different network topologies such as mesh, star, bus, and ring, along with their advantages and disadvantages, as well as the categories of networks including LAN, WAN, and MAN. Key characteristics of data communication, including performance and reliability criteria, are also addressed.