The document discusses various topics related to computer networking including:
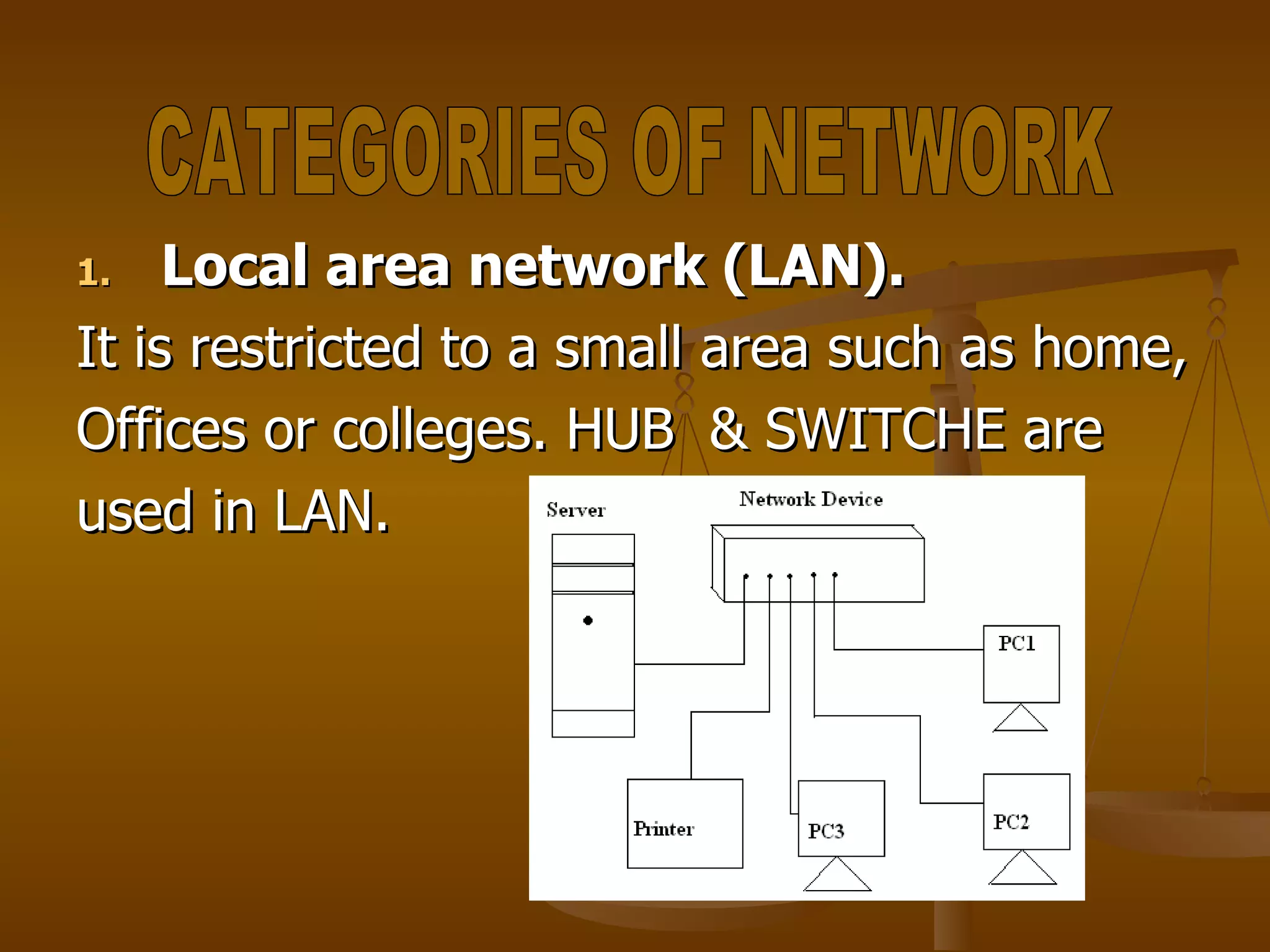
1. Networking involves connecting computing devices like PCs and printers to share information and resources using physical or logical connections.
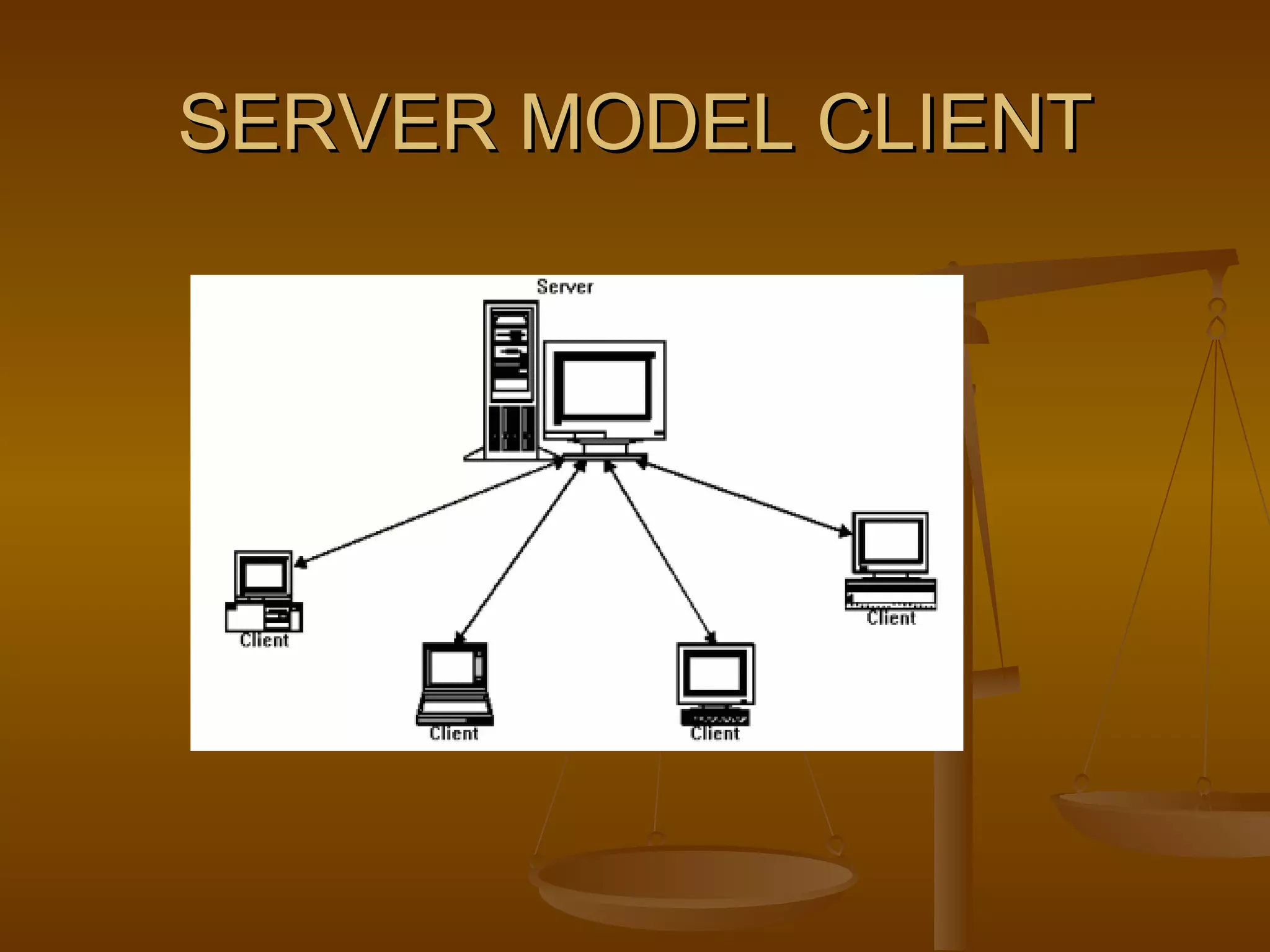
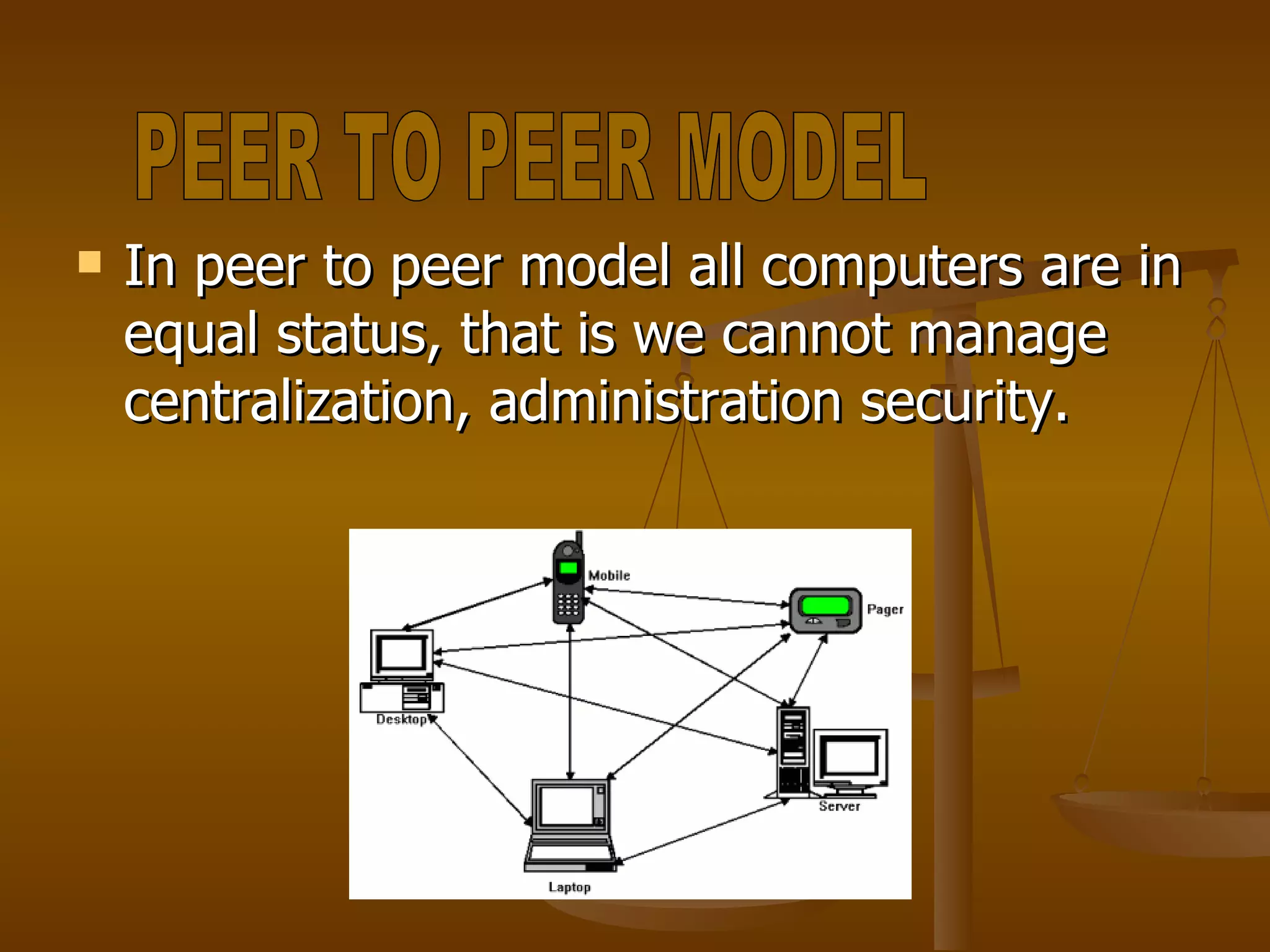
2. Common network models include client-server, peer-to-peer, and domain models.
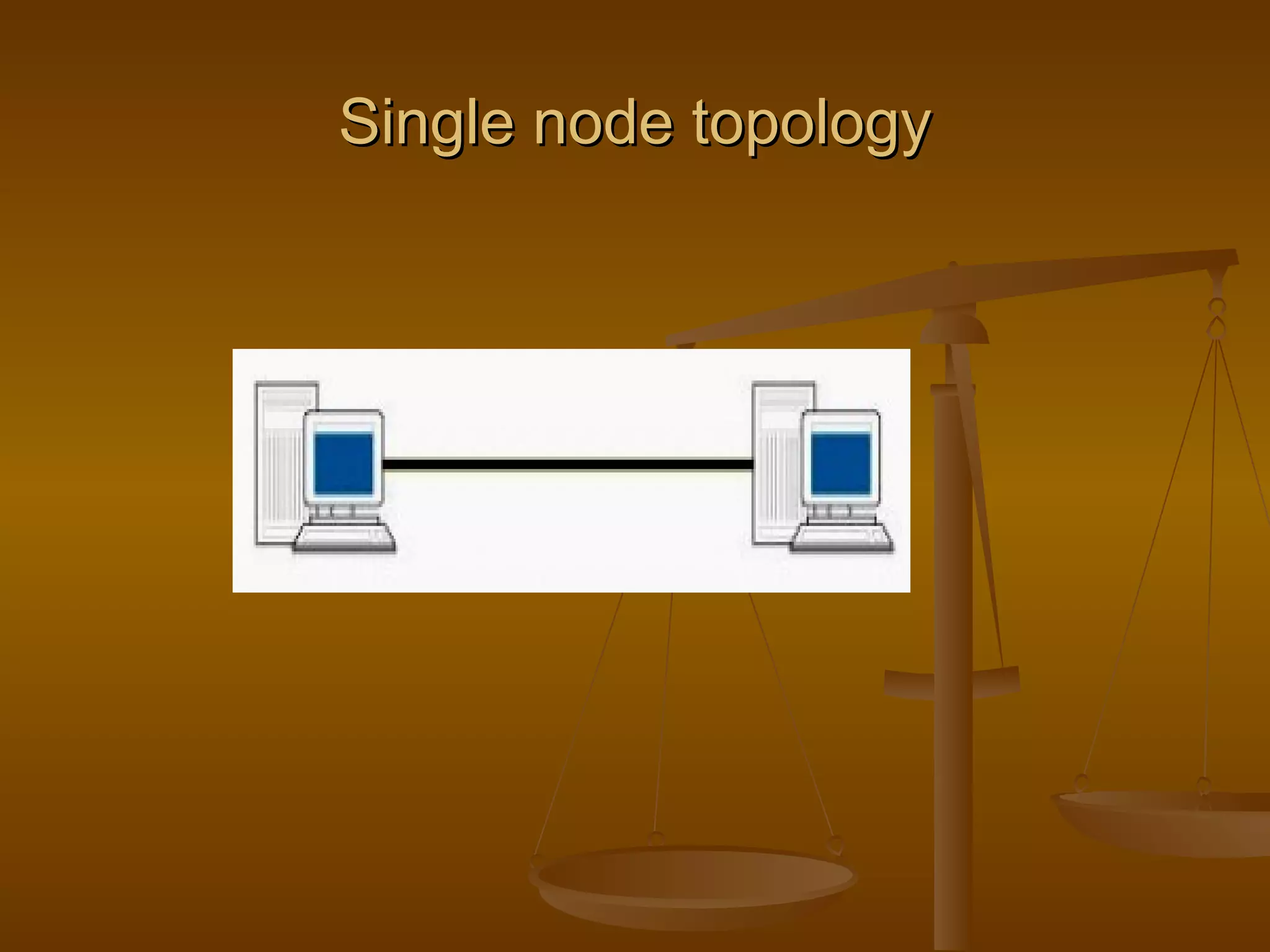
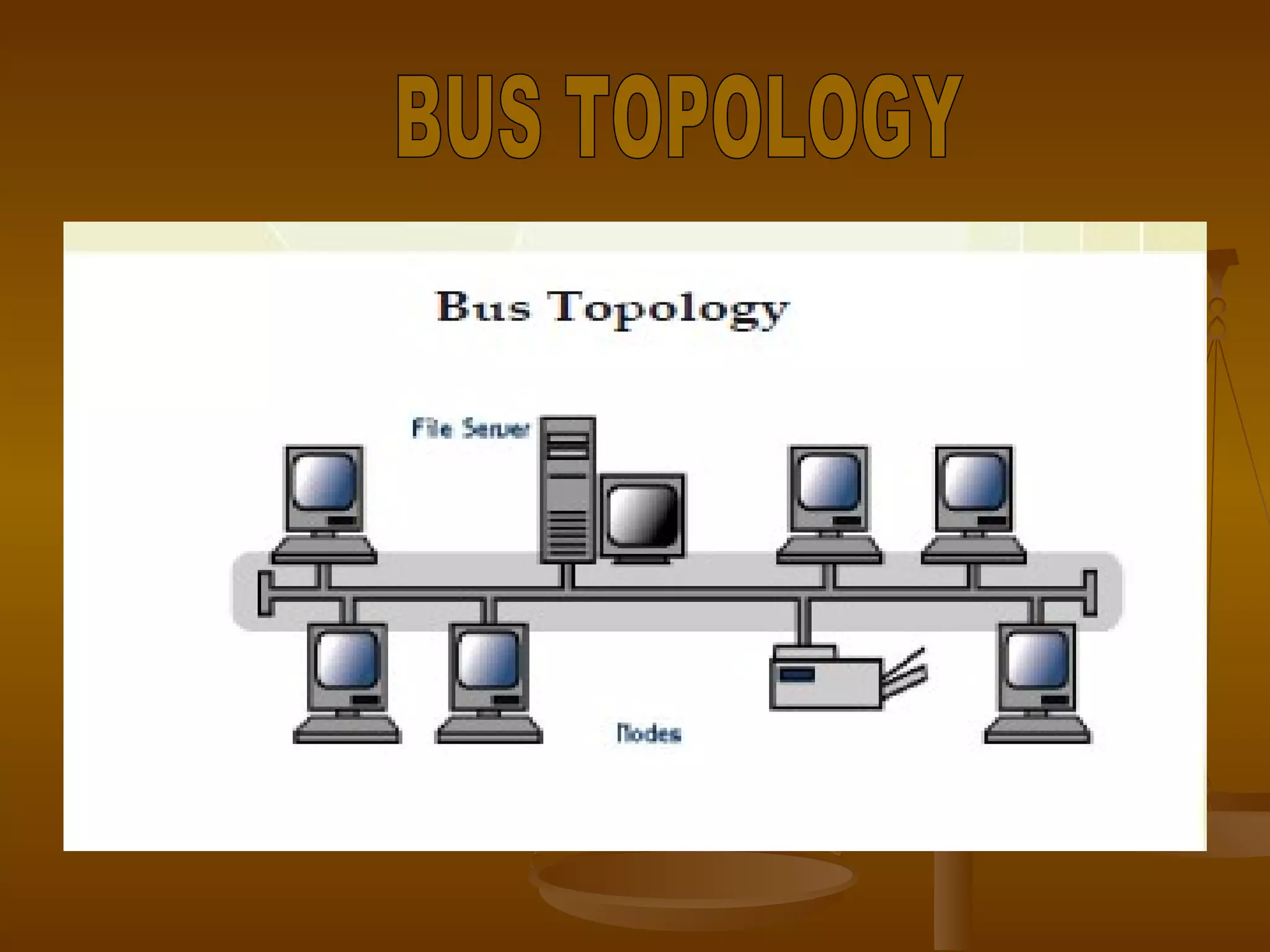
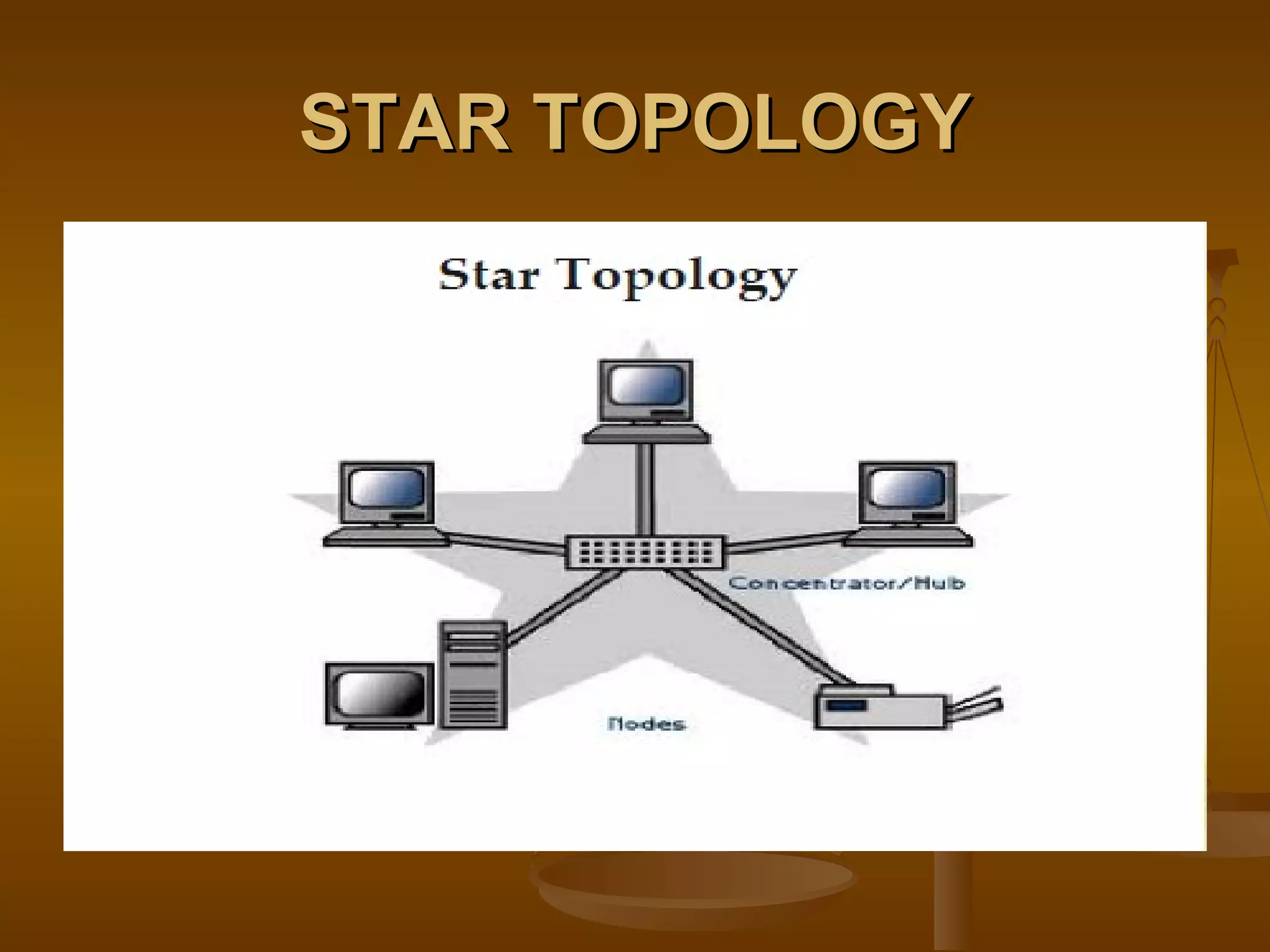
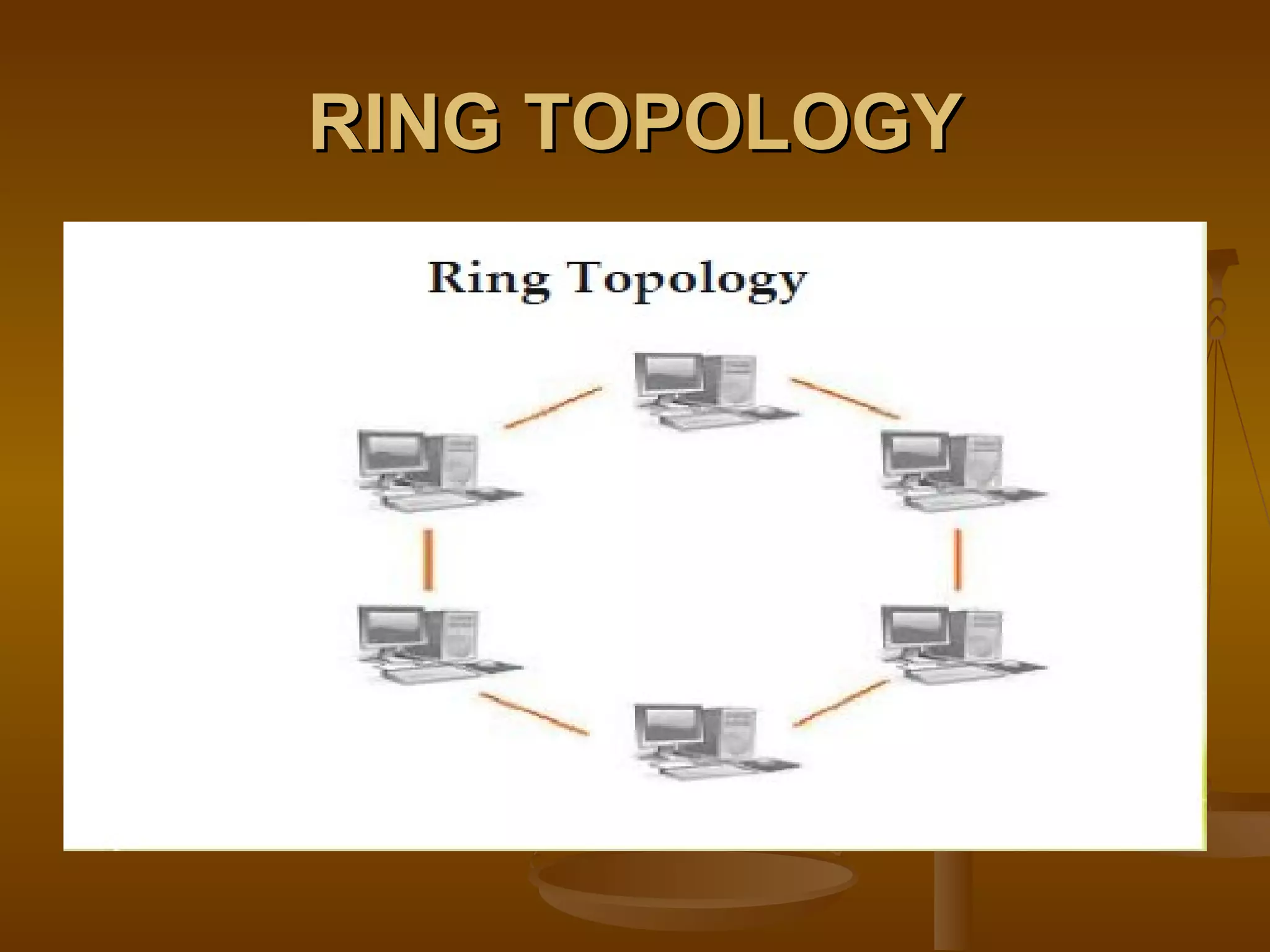
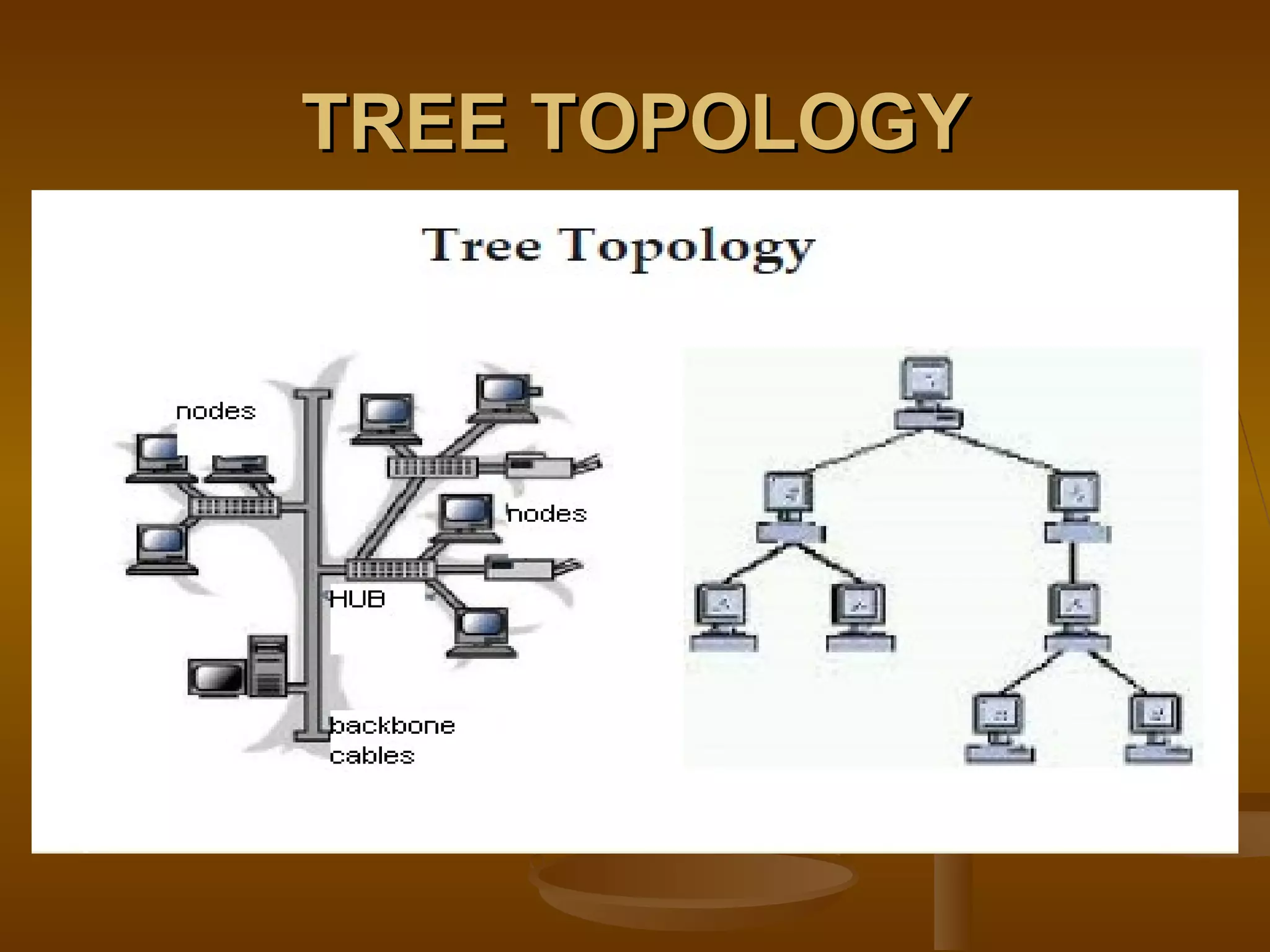
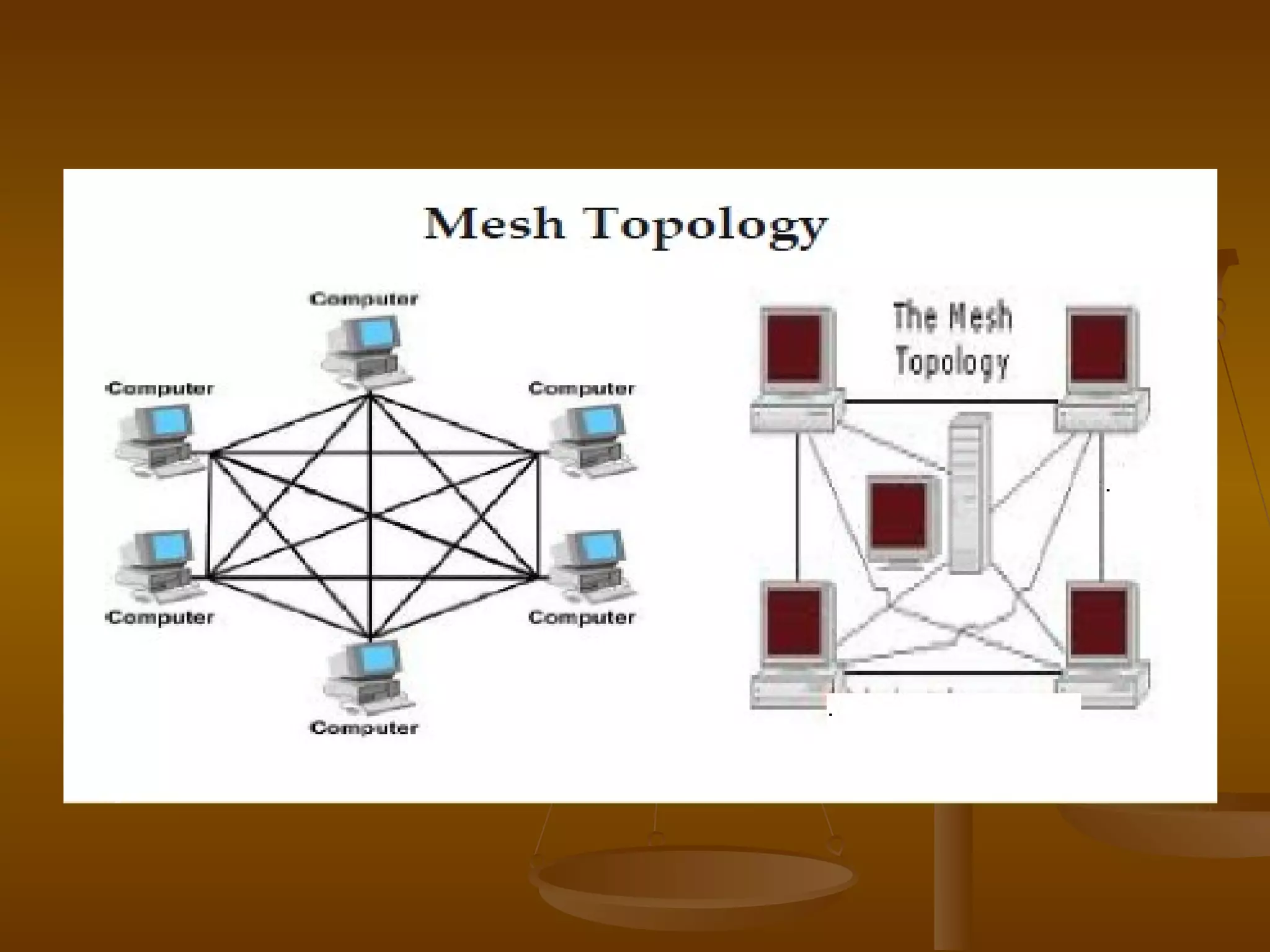
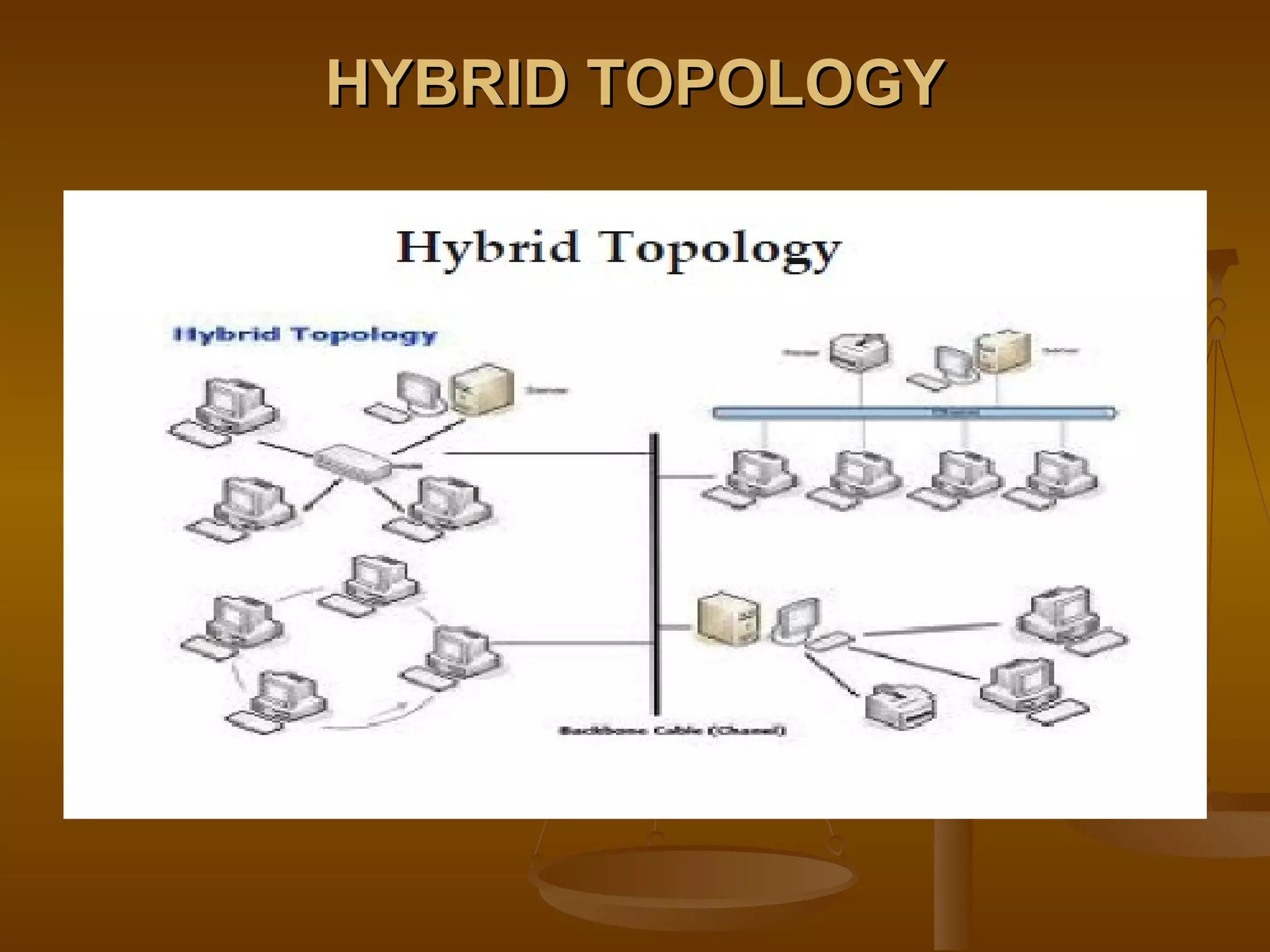
3. Network topologies describe how network elements are physically connected and include bus, star, ring, tree, mesh, and hybrid topologies.