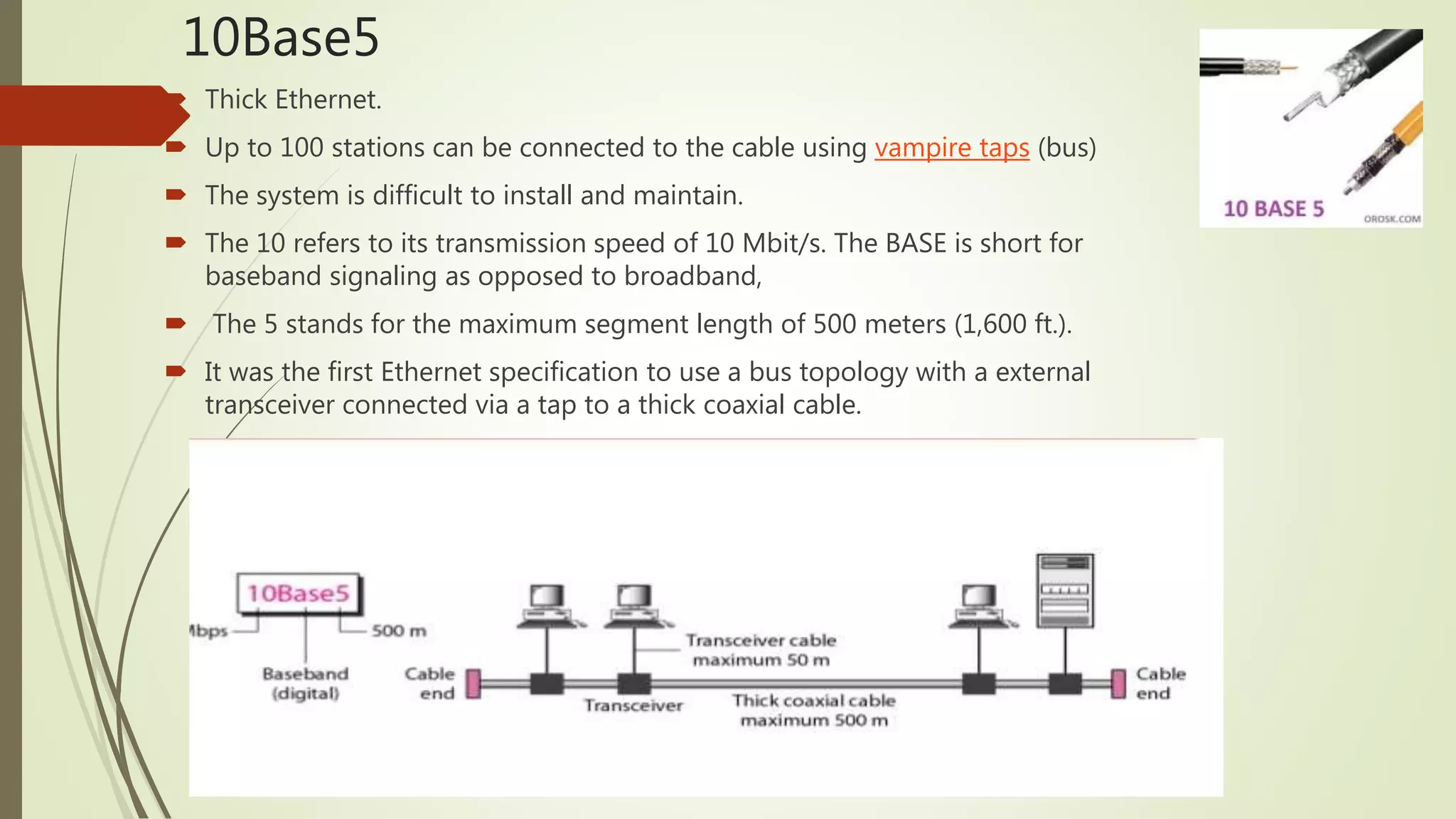
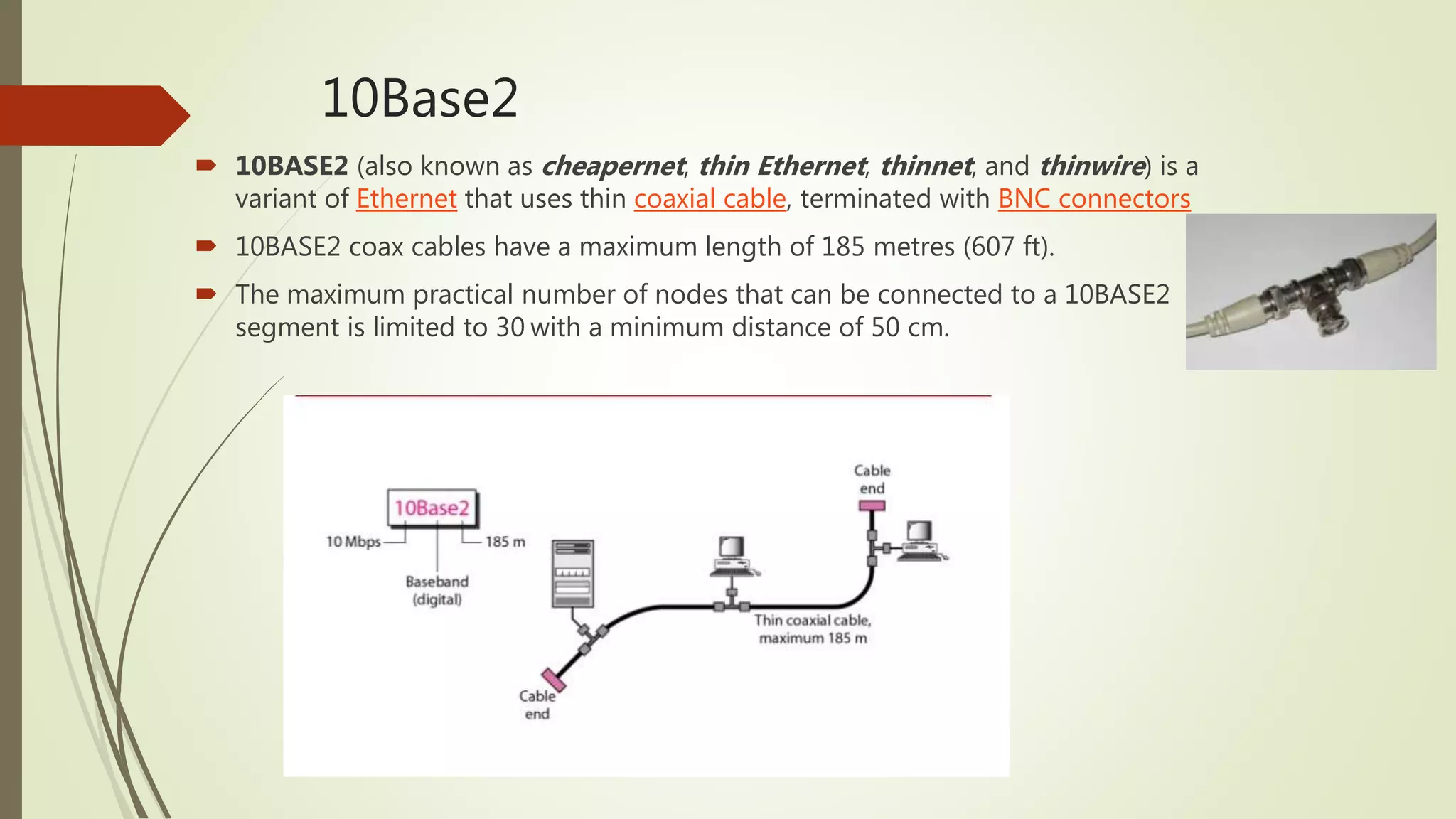
Ethernet is a widely used networking protocol for local area networks (LANs). It uses cables to connect multiple computers together to allow them to send data to each other. Common cable types are thick coaxial cable, thin coaxial cable, and twisted pair cables. Ethernet uses encoding schemes like Manchester encoding and differential Manchester encoding to transmit data over the cables. Ethernet has evolved over time to support higher speeds through standards like Fast Ethernet that supports 100 Mbps and Gigabit Ethernet that supports 1 Gbps, while maintaining compatibility with previous versions.