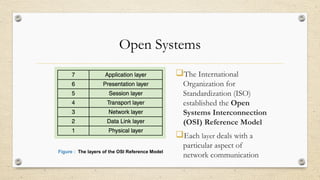
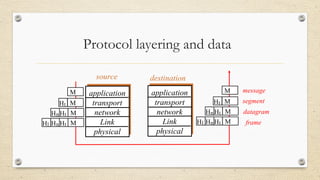
The document discusses the concepts of protocol layers, the advantages of layering in network systems, and the role of protocols in communication between peers. It highlights the distinction between proprietary and open systems, emphasizing the importance of interoperability and the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model in facilitating communication. Additionally, it outlines the Internet protocol stack and the relationship between various network protocols in supporting communication processes.