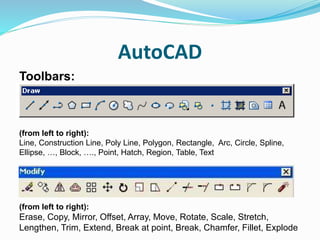
This document discusses data collection methods for spatial and non-spatial data. It describes different types of data like raster, vector, and attribute data. Methods of data collection include land surveying techniques like chain surveying and using total stations, as well as remote sensing using aerial photography and satellite imagery. Common data sources are provided by organizations like the Survey of India and ISRO. The document also covers topics like digitization in GIS and using software like AutoCAD.