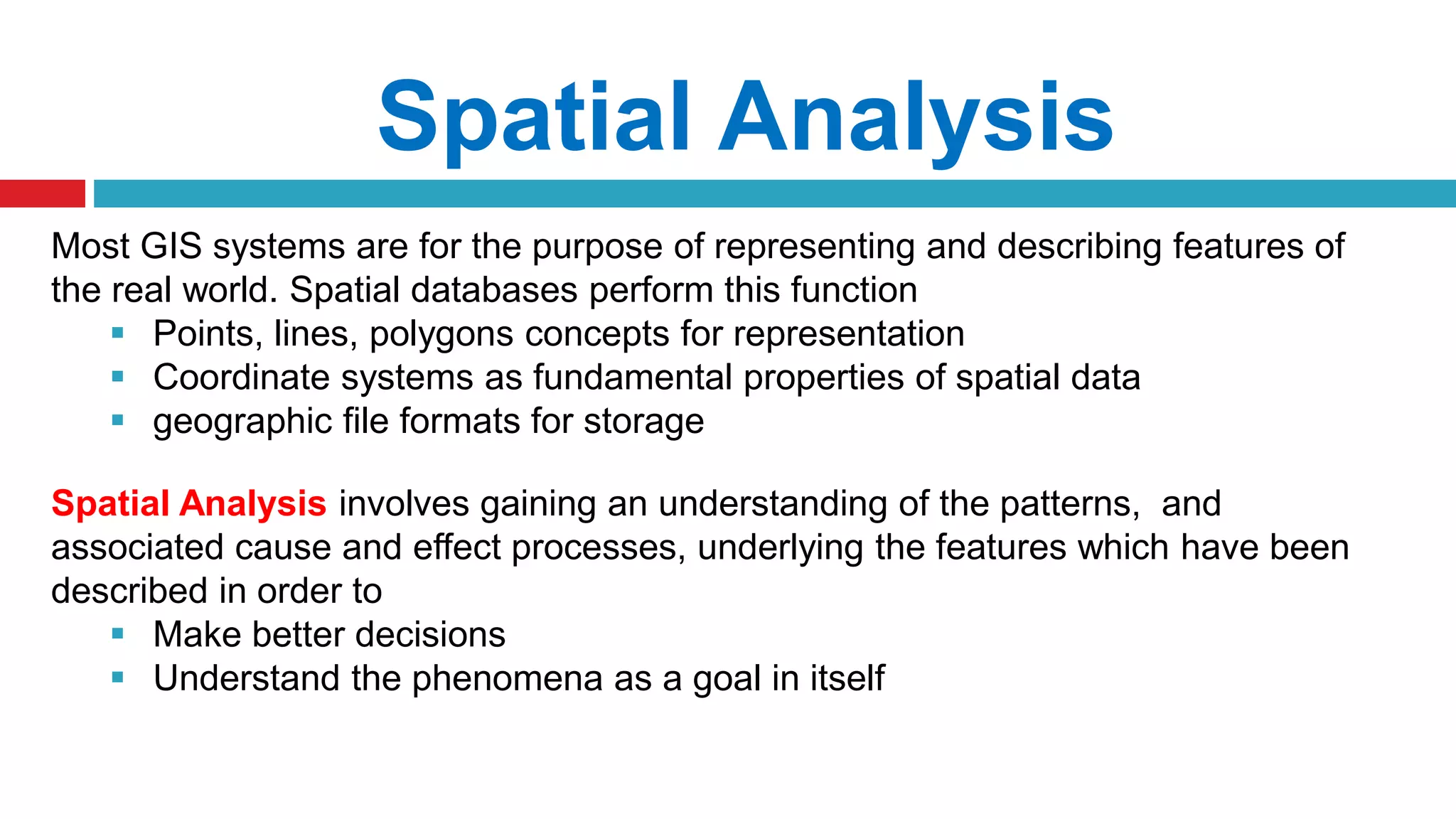
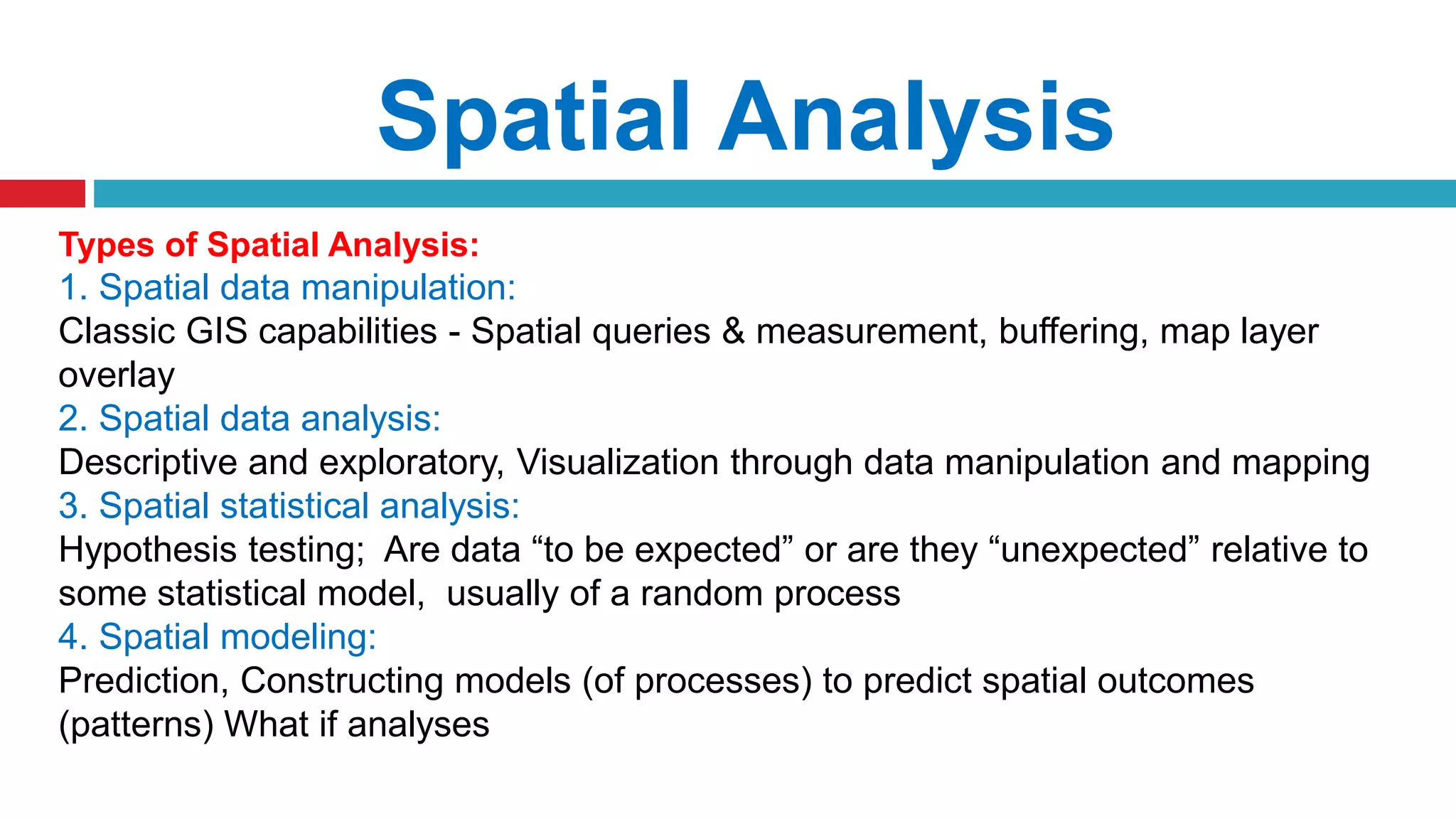
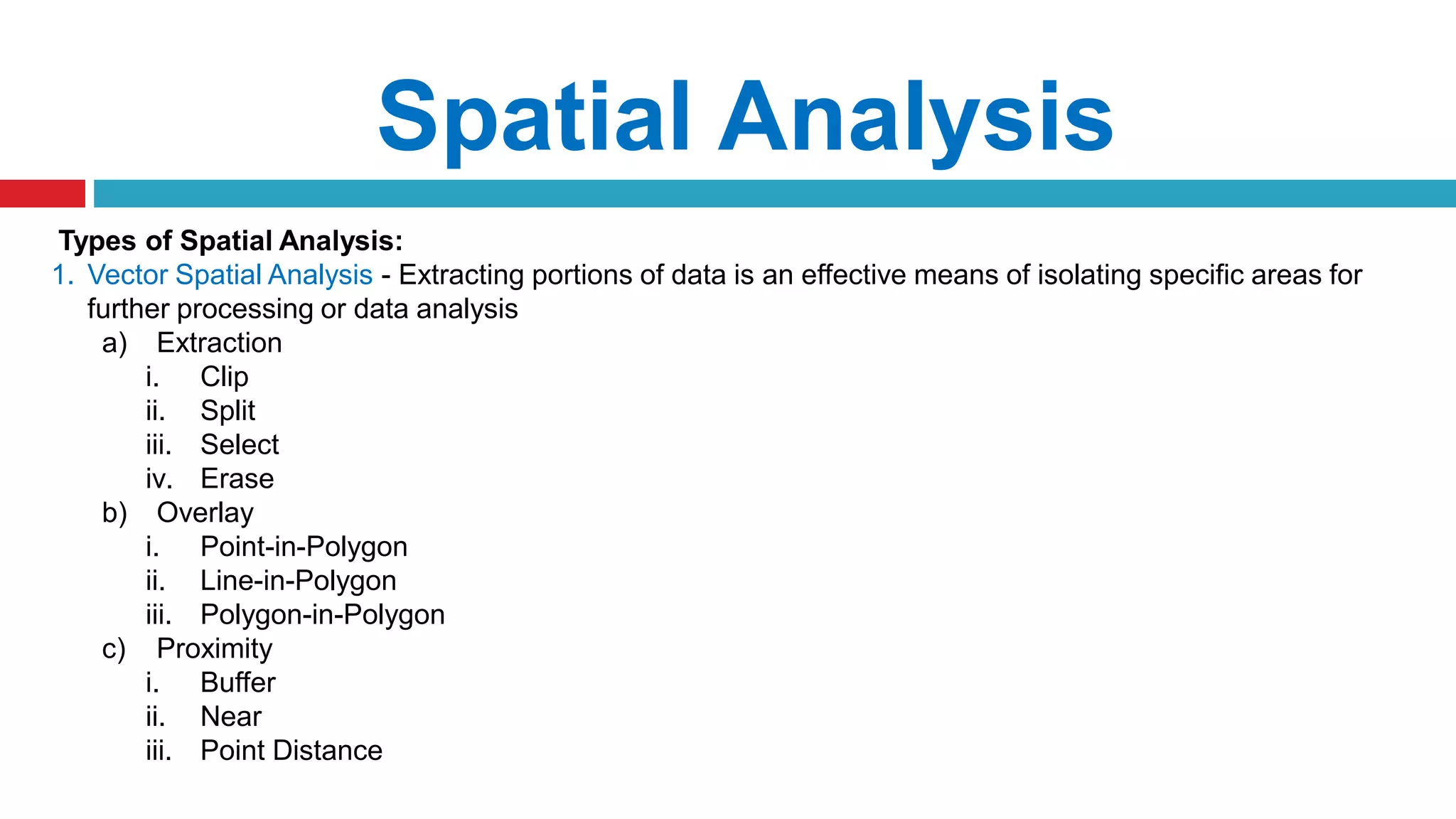
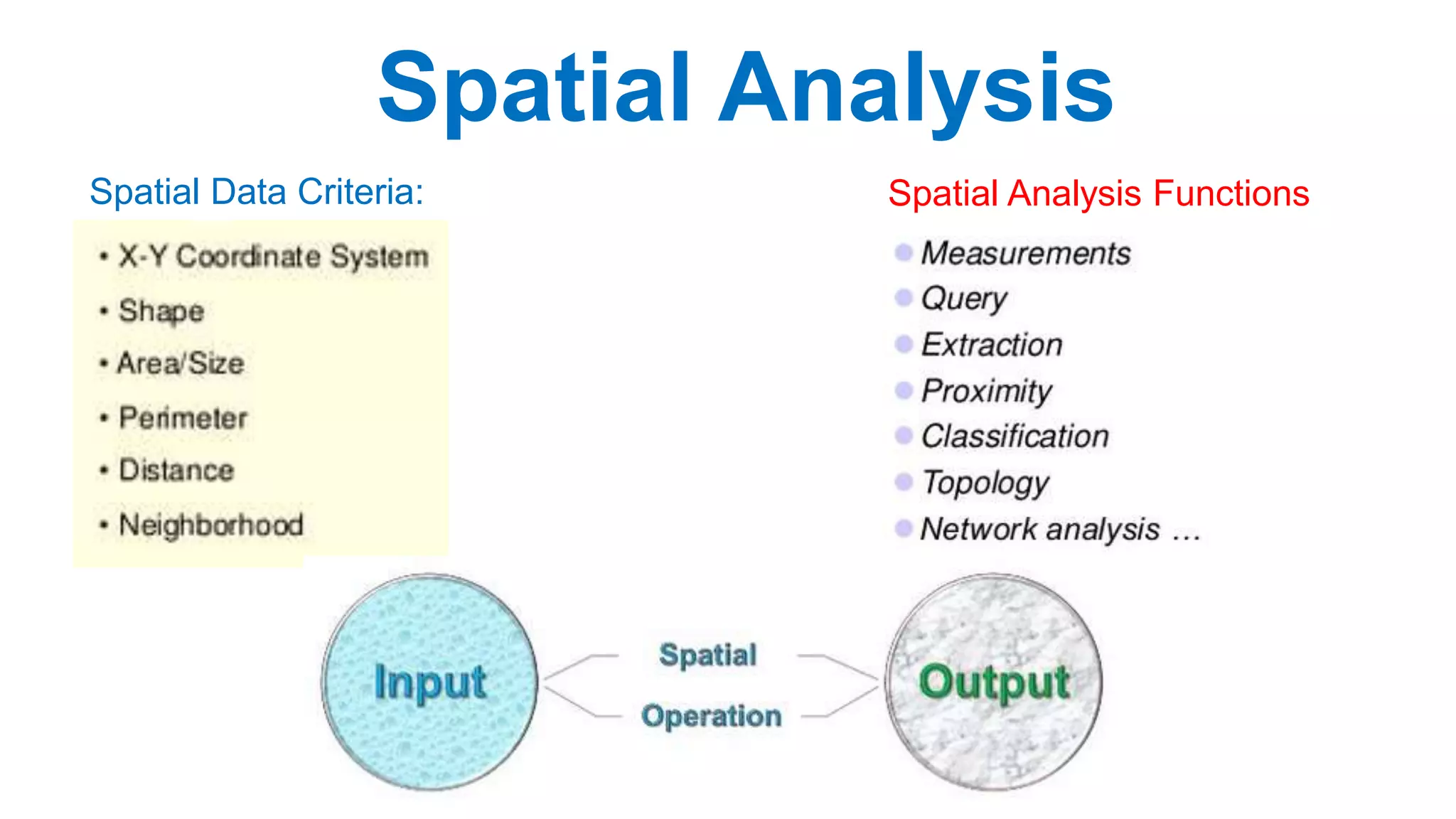
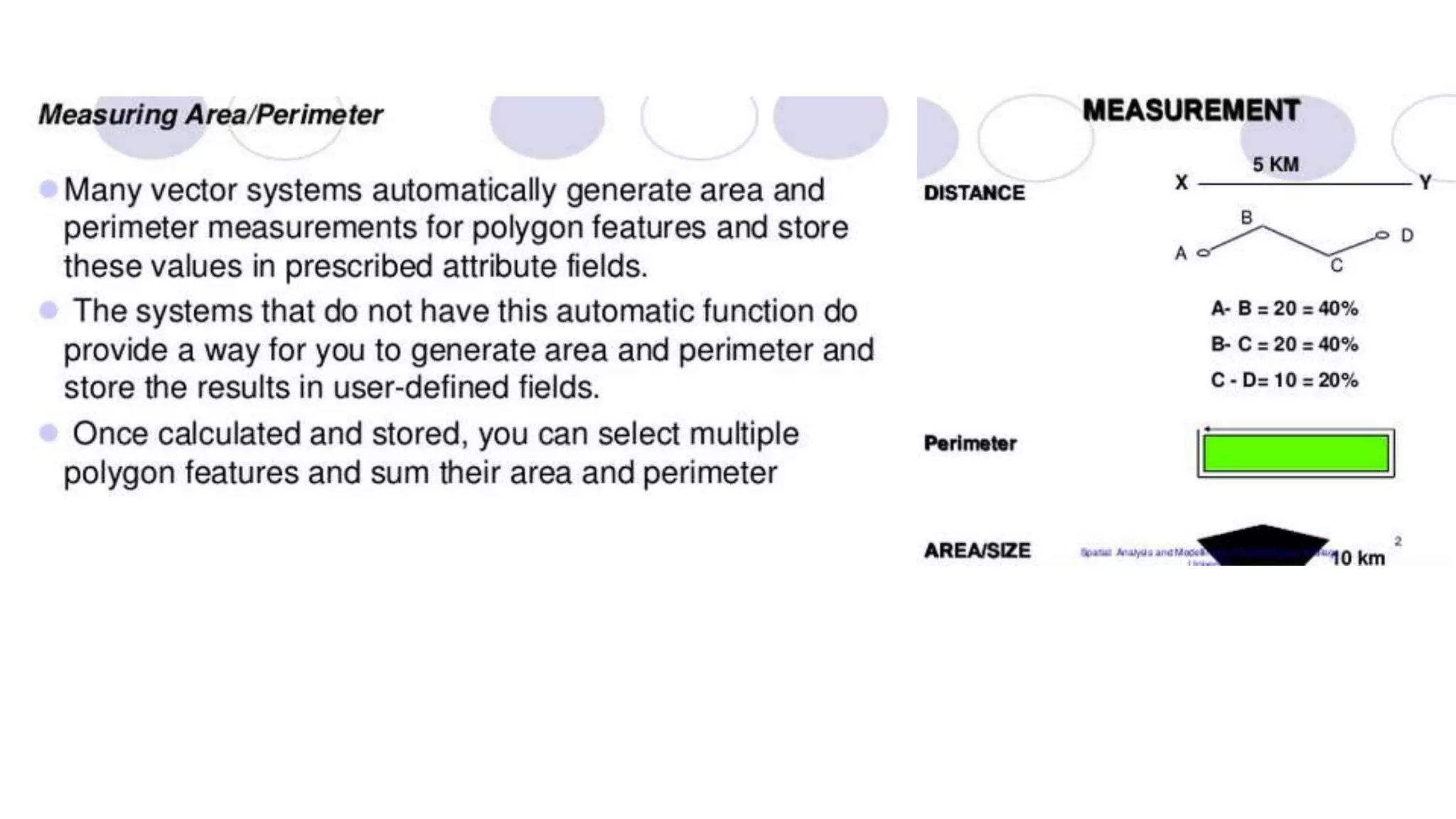
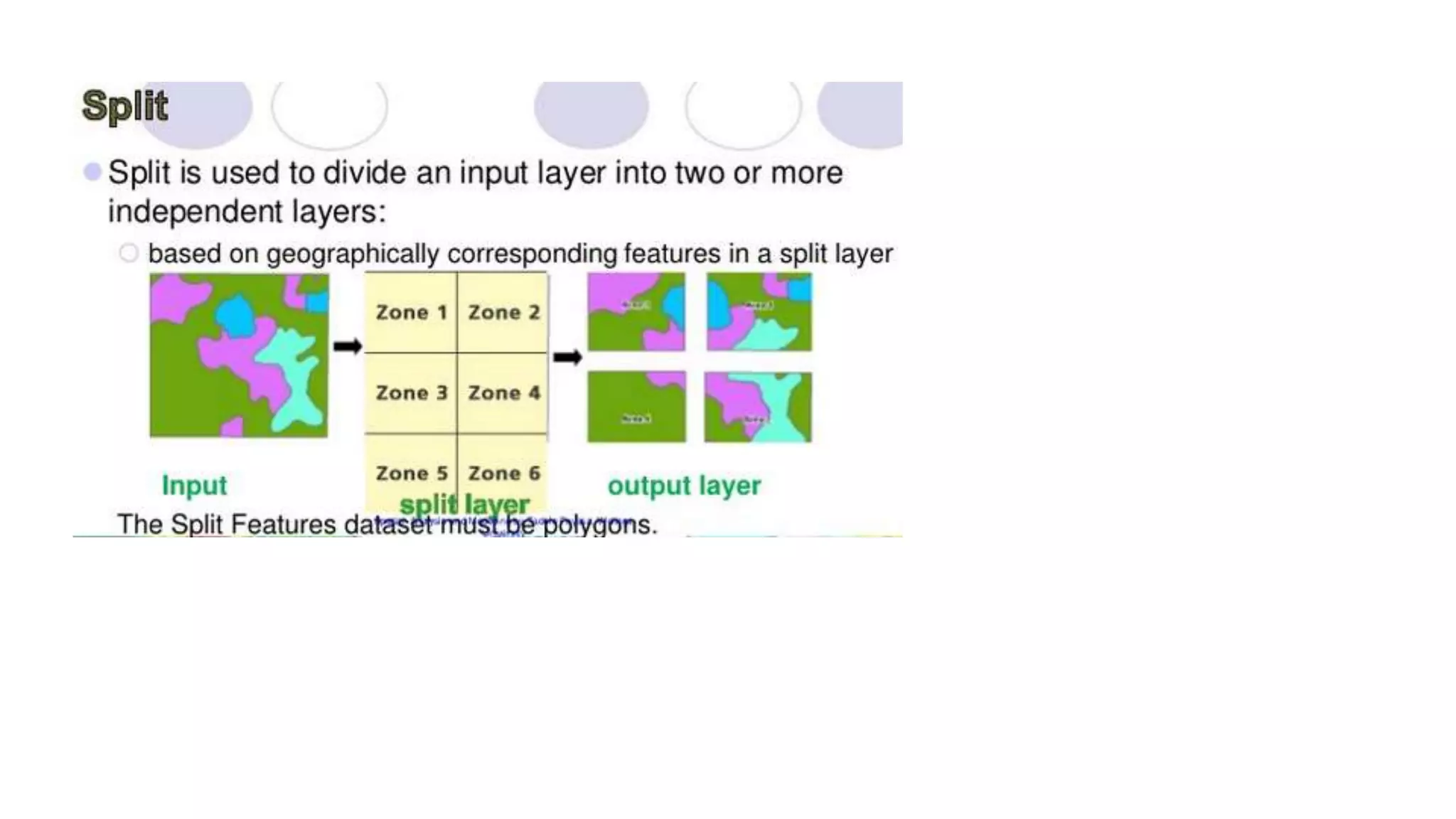
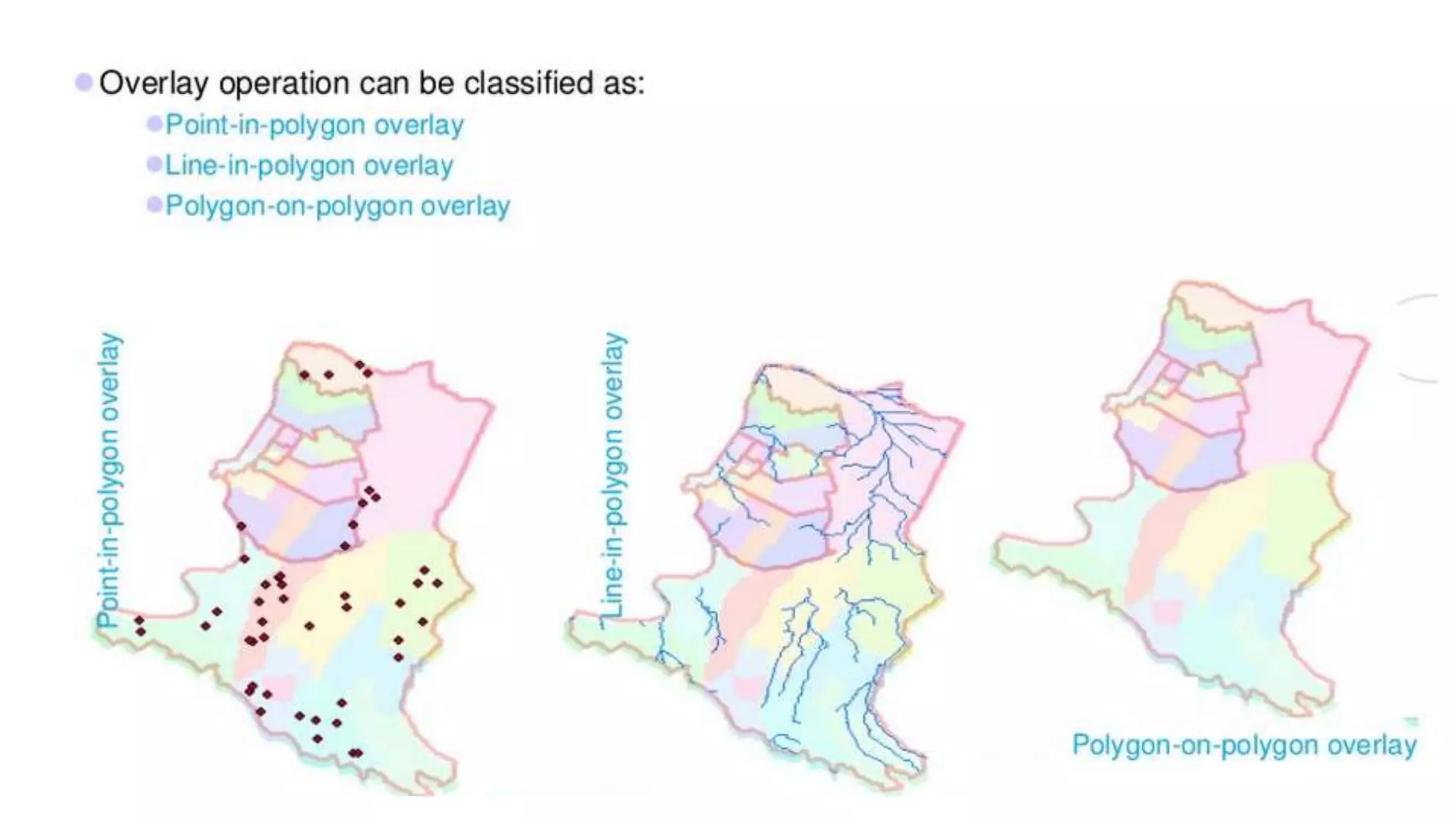
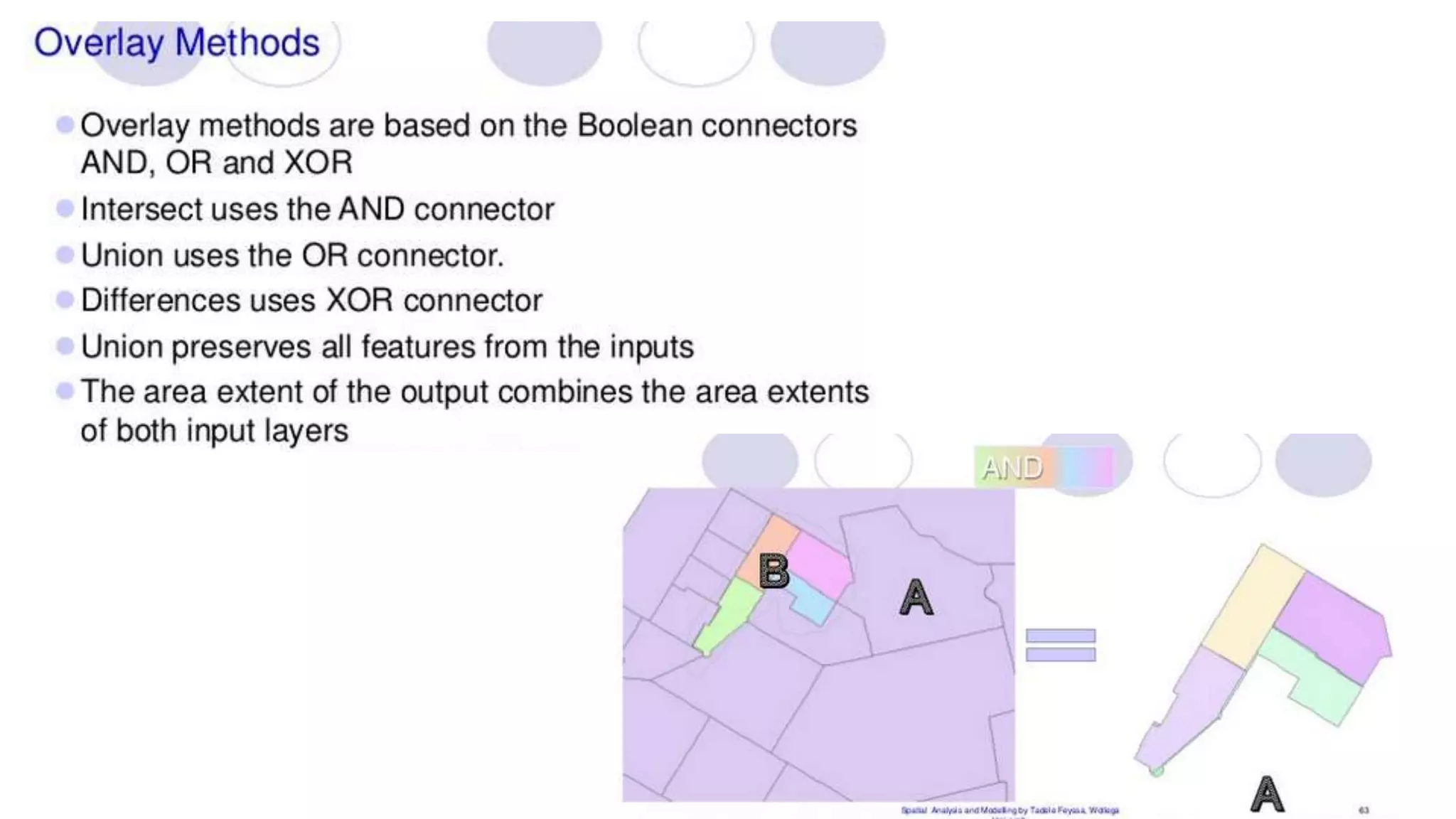
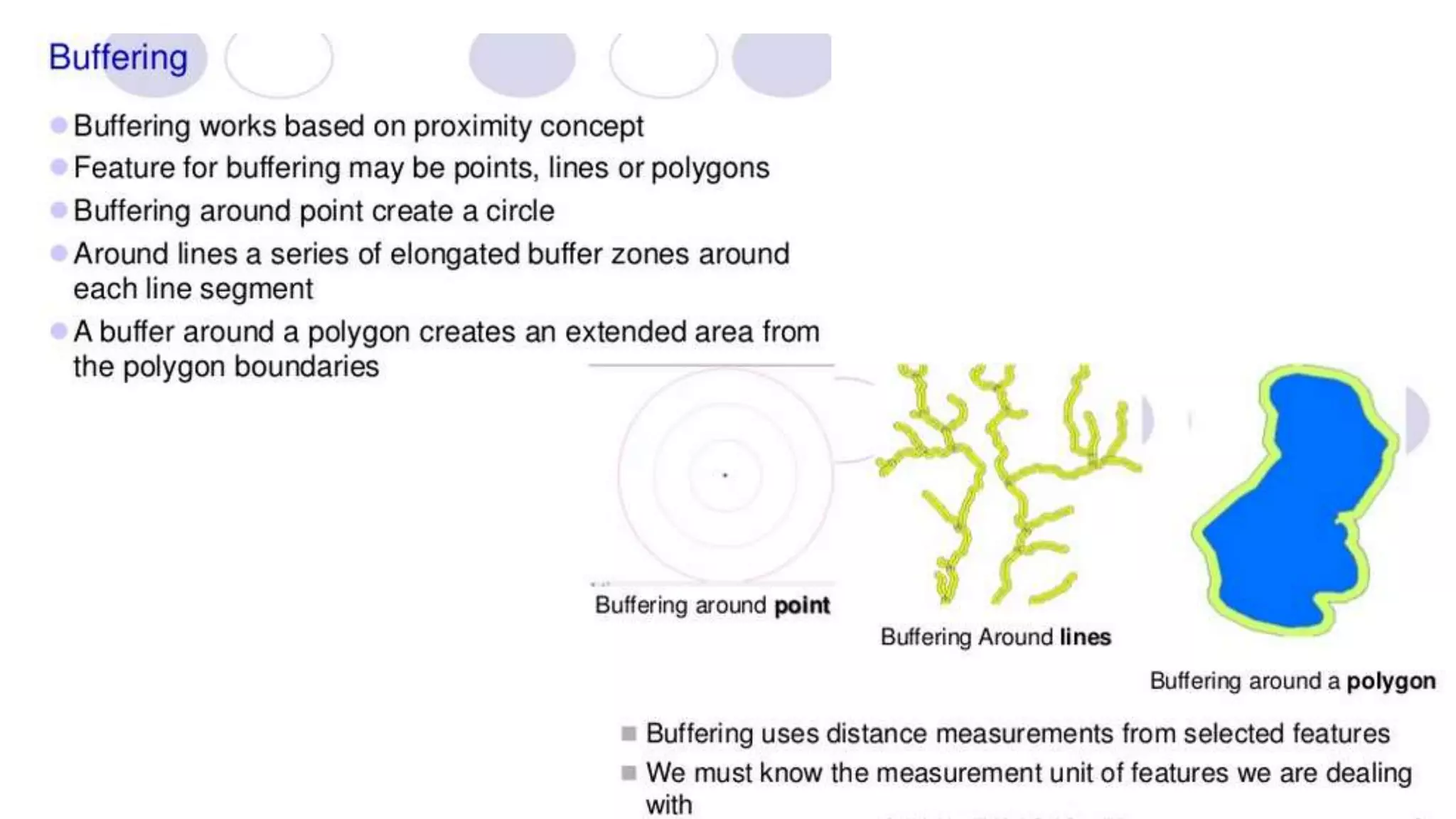
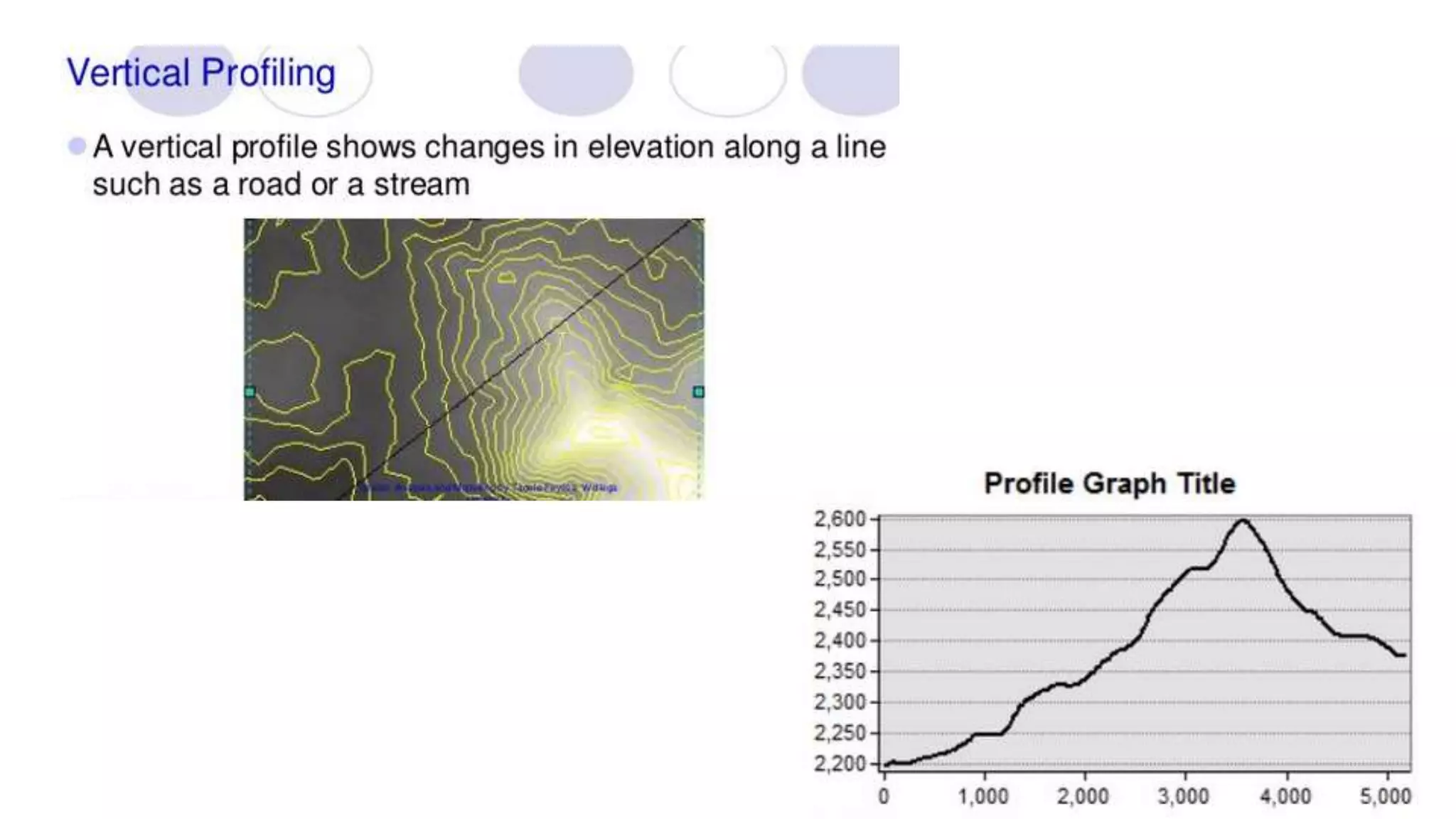
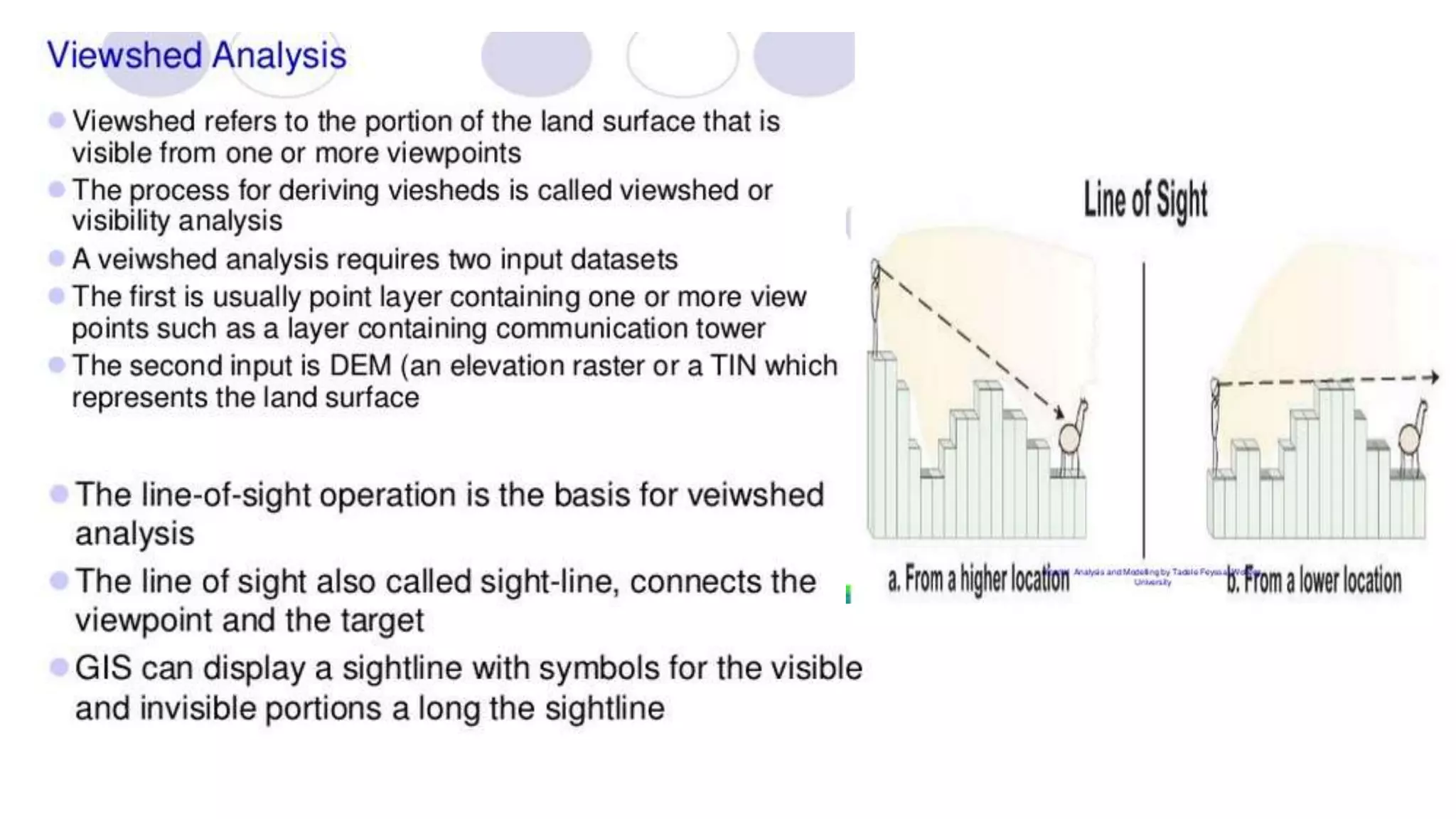
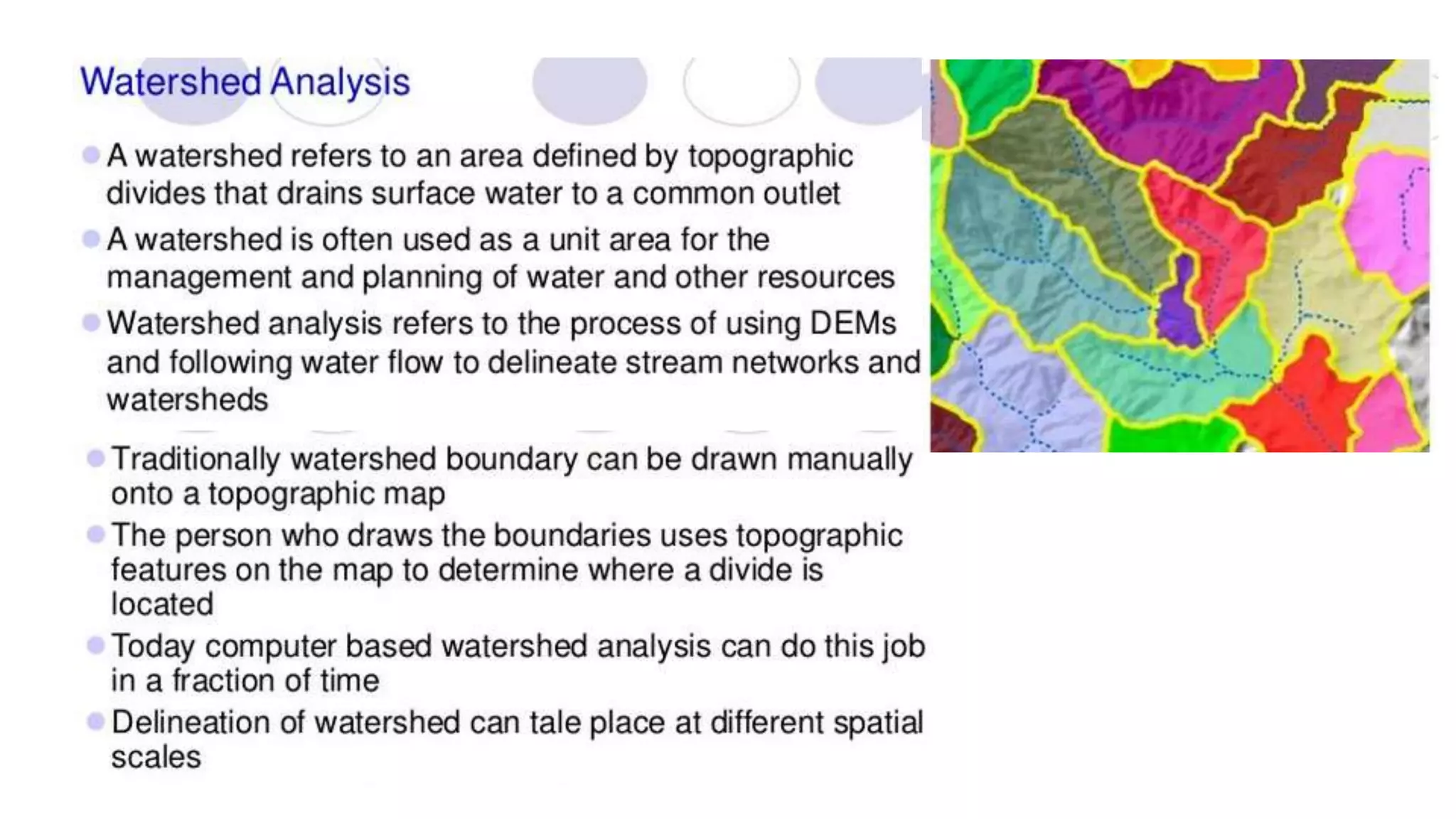
This document discusses spatial analysis and modeling in a geographical information system. It defines spatial analysis as gaining an understanding of patterns and processes underlying geographic features in order to make better decisions and understand phenomena. The document outlines four types of spatial analysis: spatial data manipulation, spatial data analysis, spatial statistical analysis, and spatial modeling. It also describes different vector and raster spatial analysis techniques, such as clipping, overlaying, buffering, and slope/aspect calculations. Spatial modeling is defined as using models to predict spatial outcomes and enable "what if" analyses.