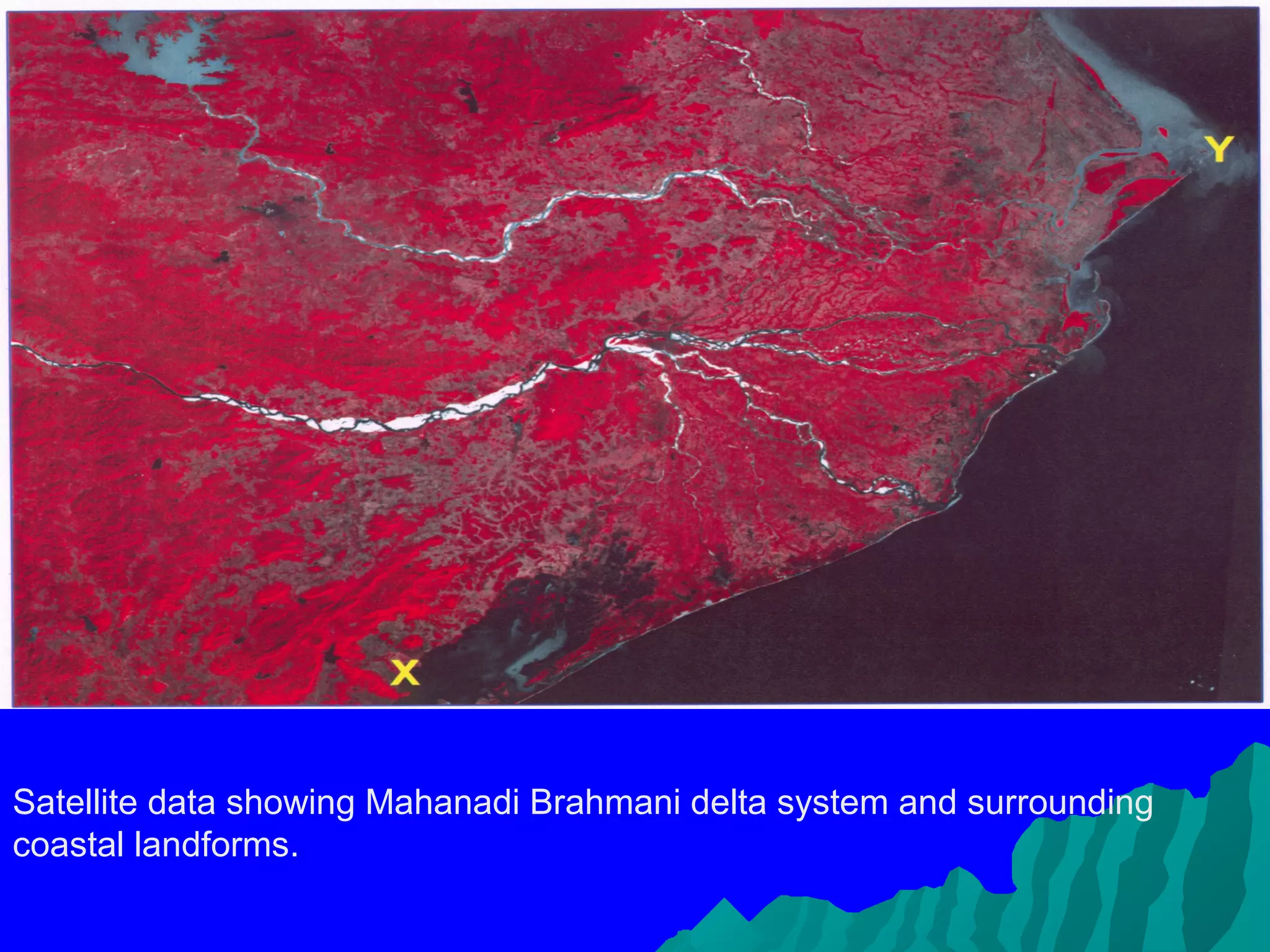
This document discusses the application of remote sensing in geomorphology. Remote sensing involves acquiring information about the Earth's surface from a distance, using sensors on aerial platforms or satellites. It has several advantages for geomorphological mapping and analysis, including multi-temporal coverage to detect changes over time and multi-spectral data to better identify landforms. Both aerial photos and satellite imagery can be interpreted to extract geomorphological information and understand landform genesis and evolution. Formal training is required to properly interpret remote sensing data and relate image elements to landforms and geological processes.