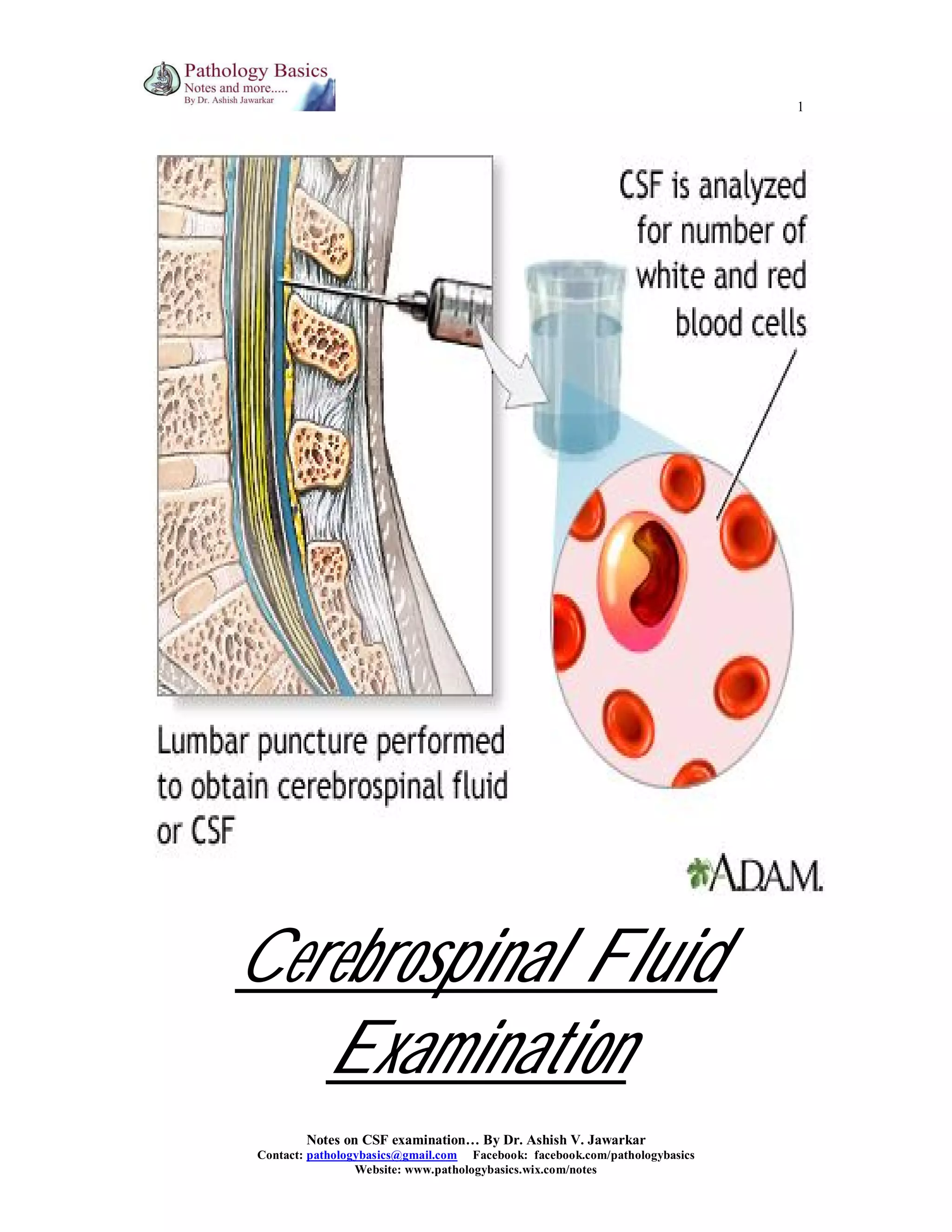
This document provides a comprehensive overview of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination, including its physiology, functions, and relevant laboratory tests. It details methods for specimen collection, pressure measurement, and examinations (gross, microscopic, chemical, and microbiological) alongside abnormal findings associated with various neurological conditions. Reference ranges and interpretative criteria for CSF components such as cell counts, proteins, and glucose levels are also outlined.