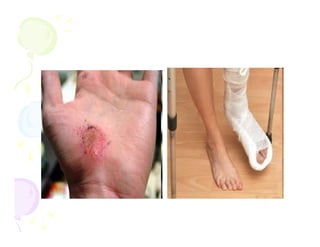
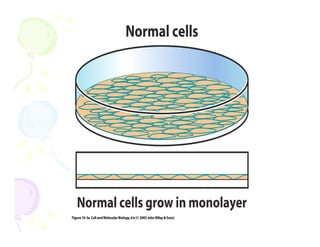
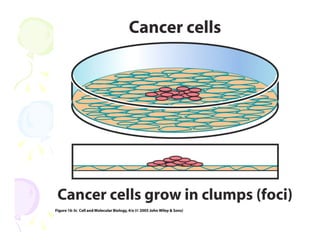
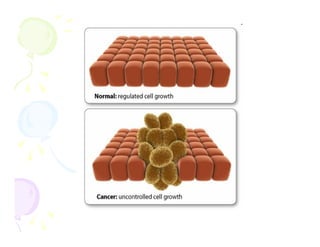
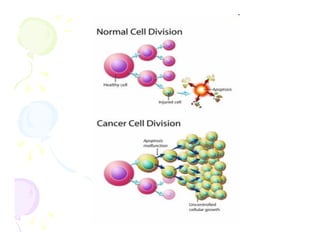
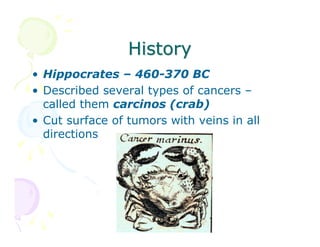
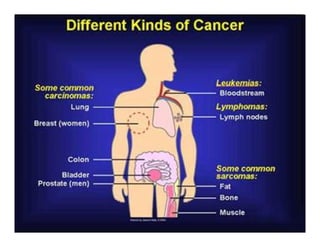
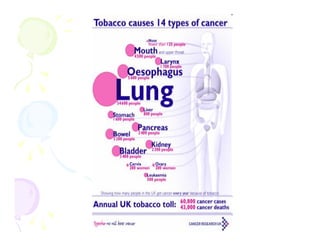
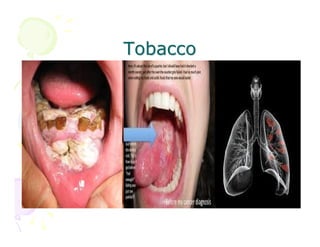
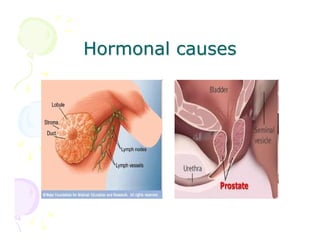
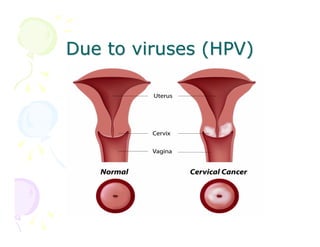
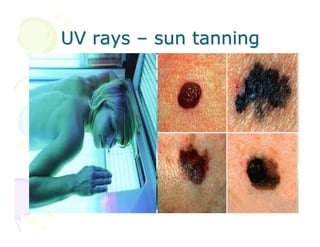
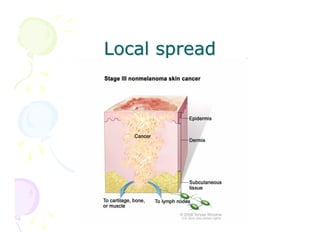
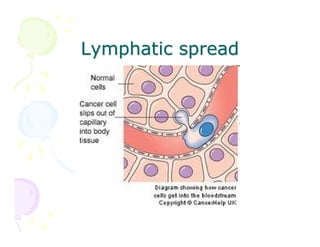
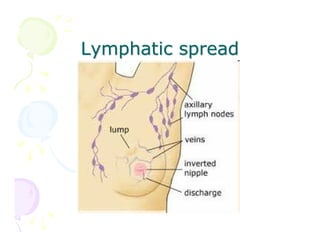
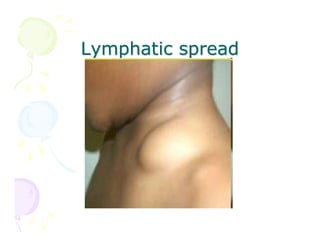
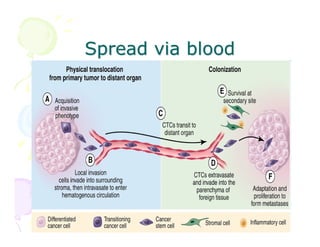
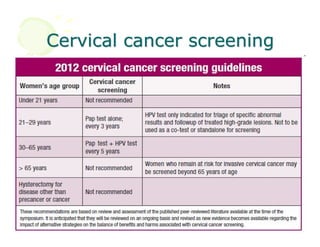
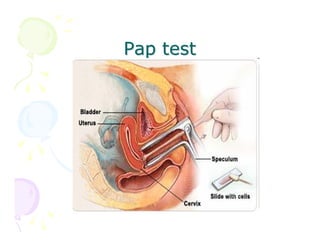
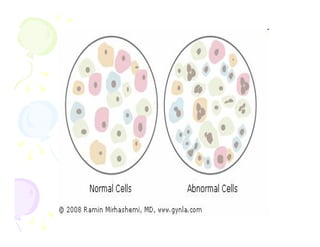
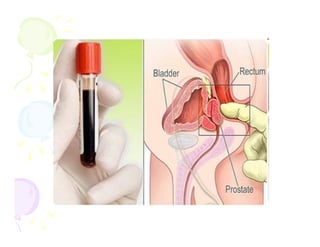
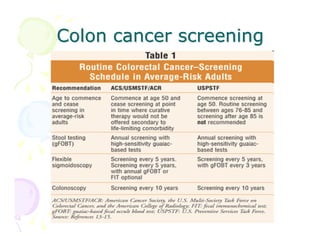
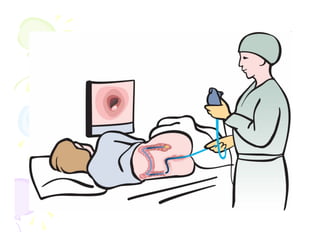
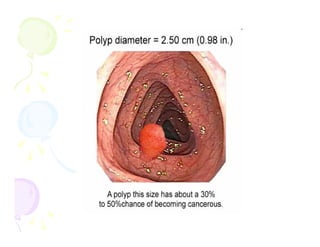
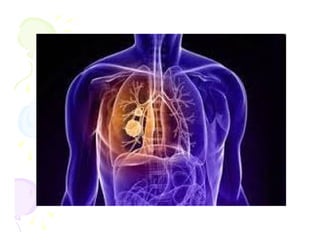
This document discusses the history and current state of cancer. It notes that cancer occurs when cells grow out of control and details some key events in cancer's history such as the first descriptions in ancient Egypt and Greece. The document outlines several causes of cancer like tobacco, viruses, and radiation. It discusses how cancer spreads and common screening tests for early detection of breast, cervical, prostate, colon, and lung cancers. The takeaway message is that cancer has affected humanity for millennia but screening and research into molecular mechanisms can help control and potentially cure cancer at early stages.