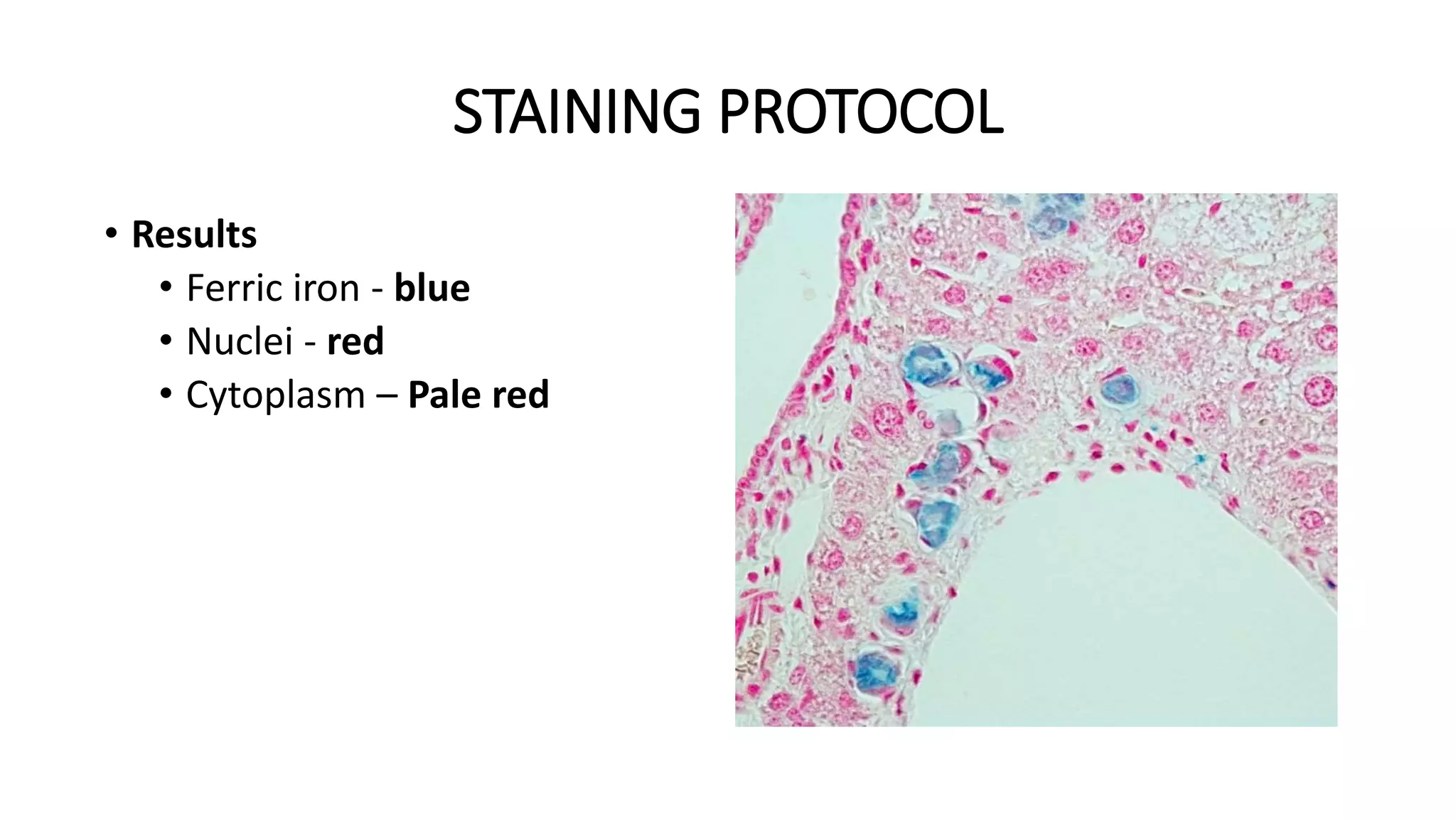
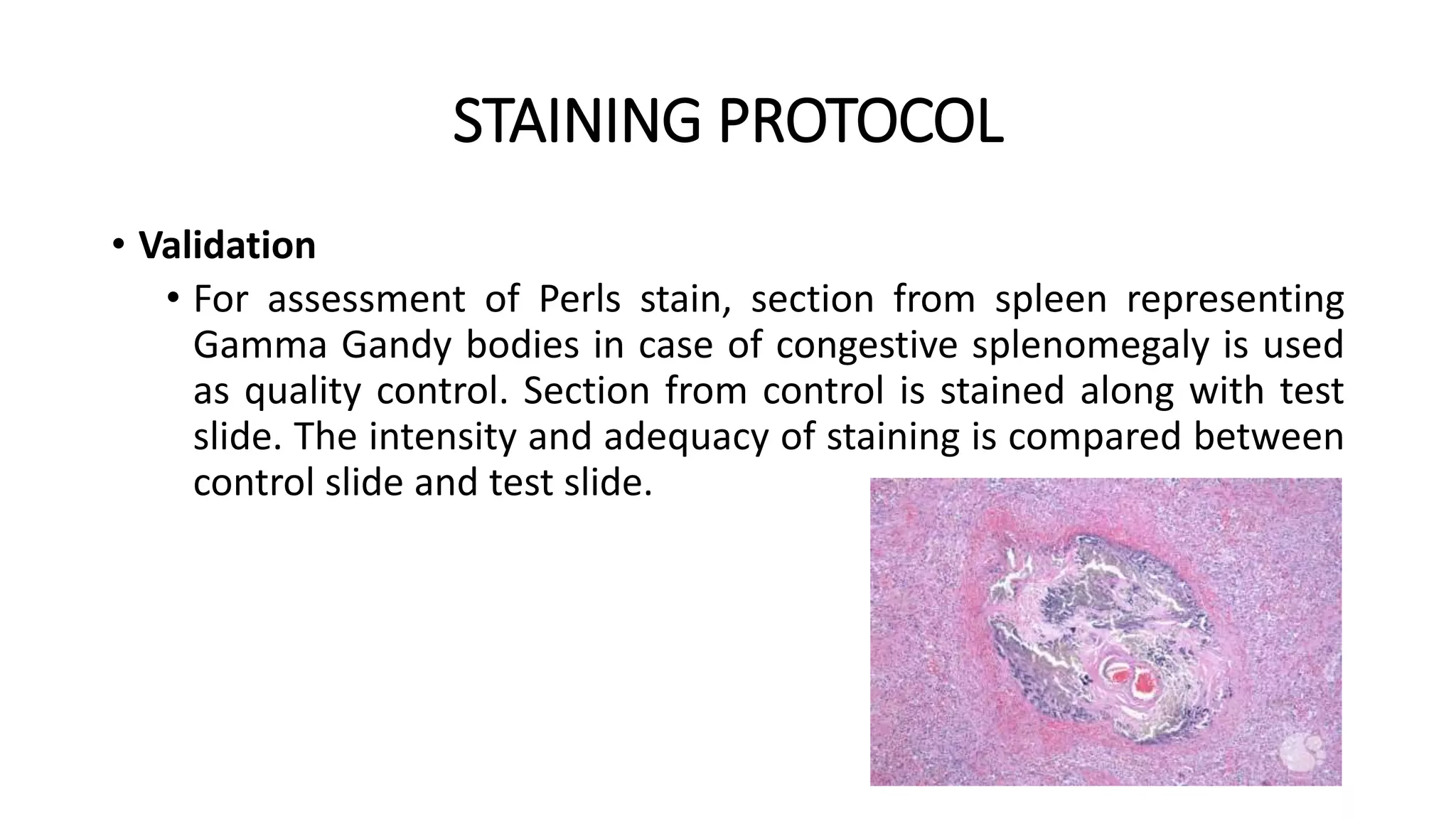
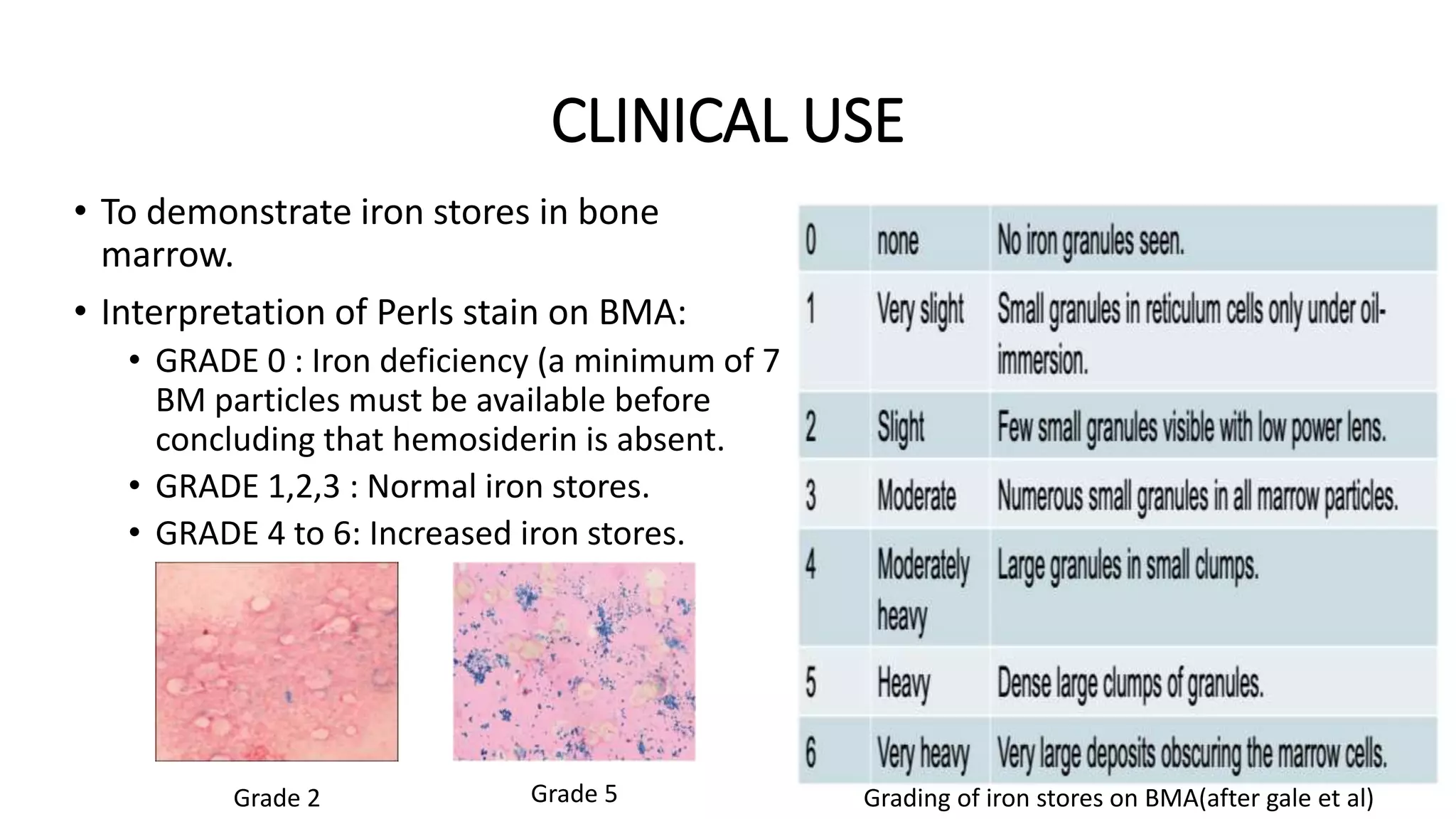
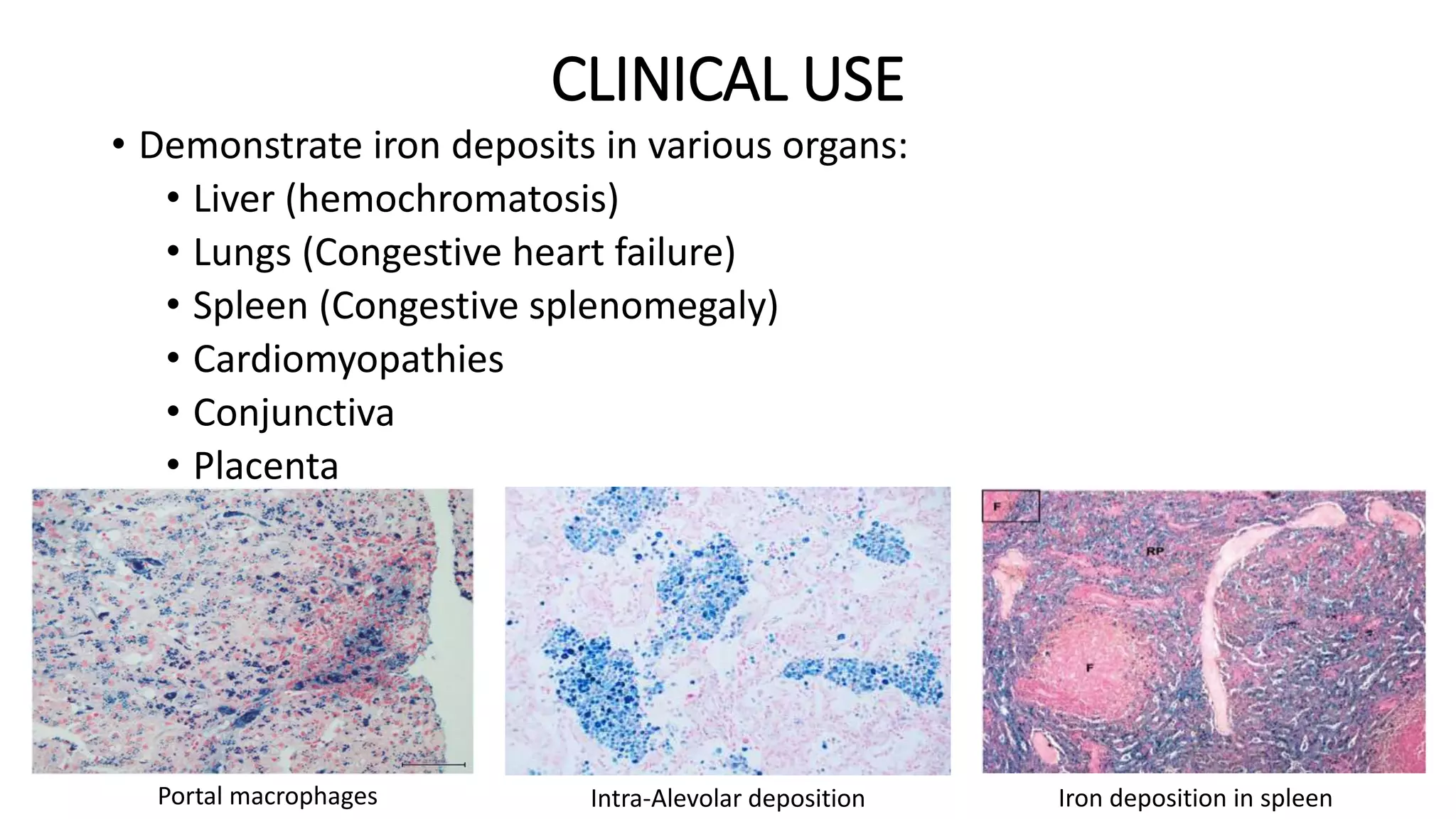
This document discusses Perls stain, which is used to identify iron deposits in tissue samples. It provides background on pigments in living tissue, including endogenous pigments like hemosiderin and hematogenous pigments. The history of Prussian blue and its use as Perls stain is described. The principle of the stain is that hydrochloric acid releases ferric ions from hemosiderin, which then react with potassium ferrocyanide to form insoluble Prussian blue pigment. Staining protocols, quality control, and clinical applications for identifying iron deposits in organs are covered.