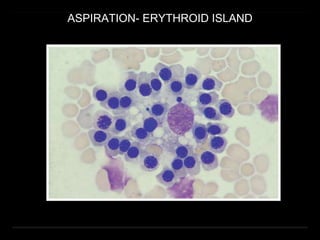
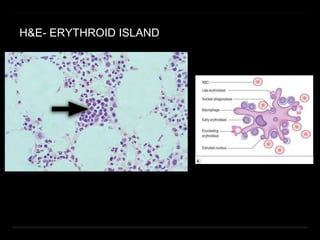
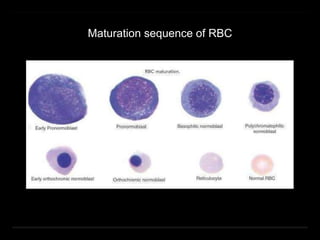
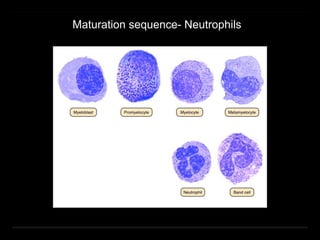
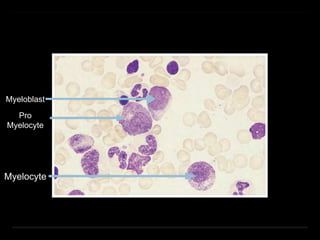
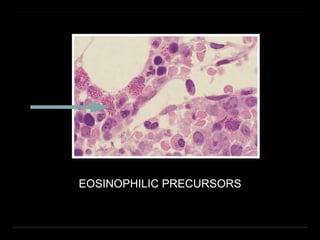
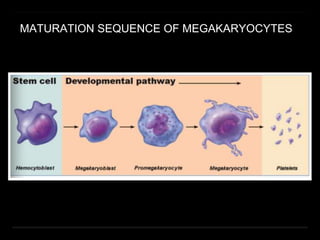
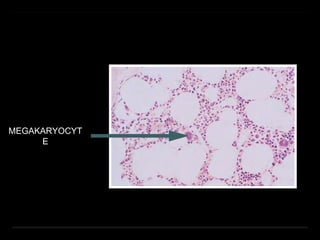
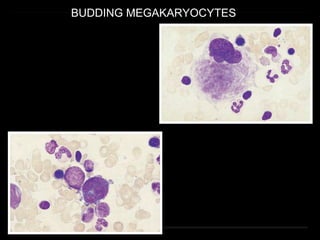
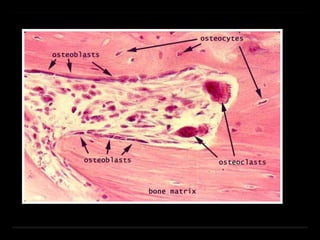
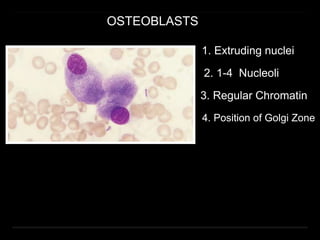
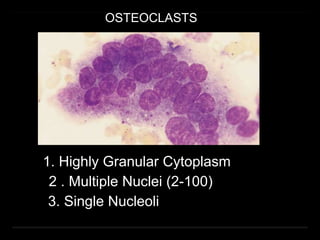
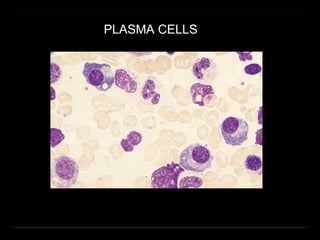
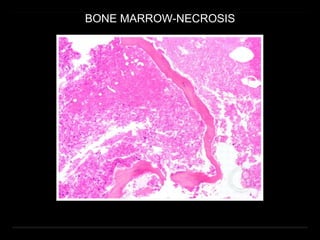
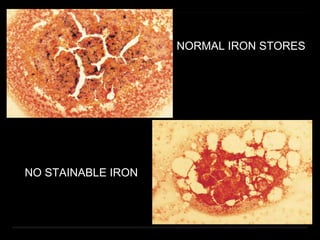
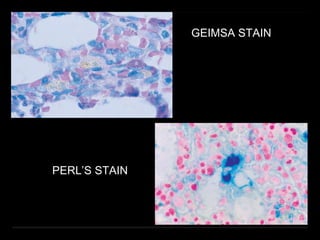
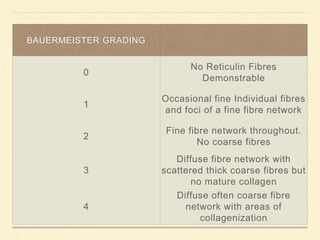
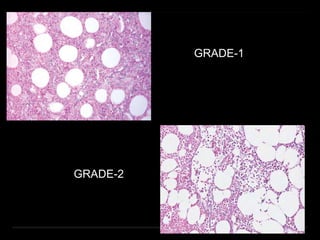
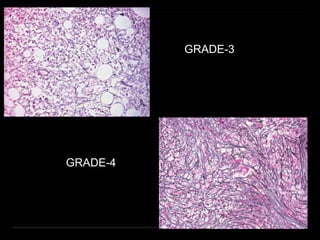
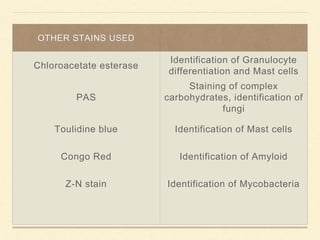
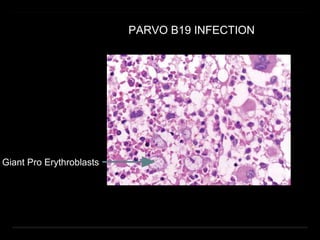
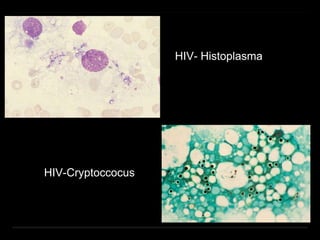
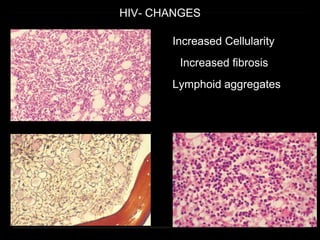
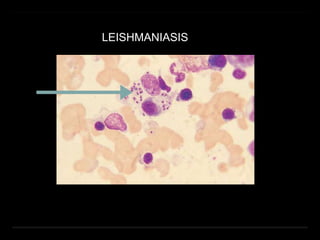
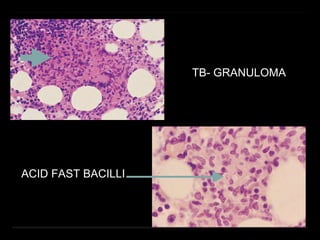
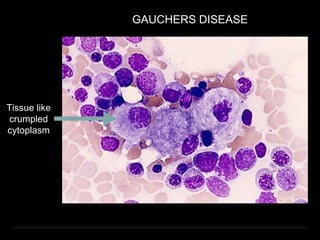
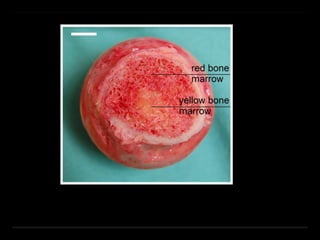
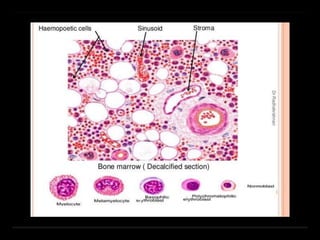
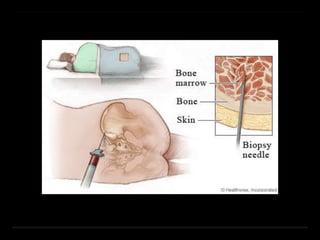
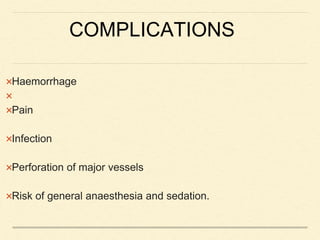
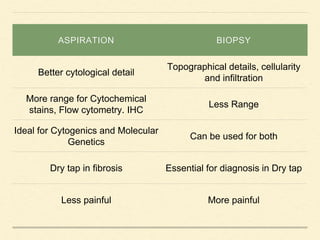
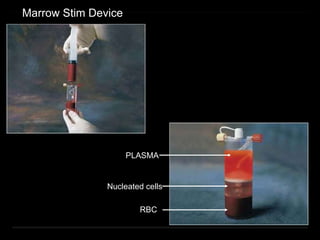
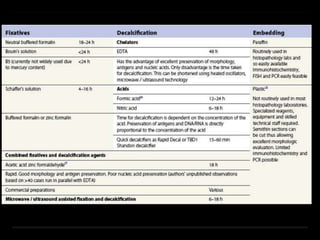
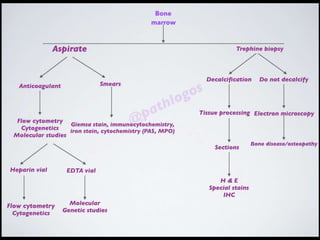
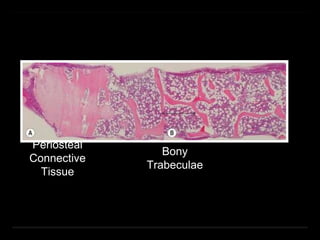
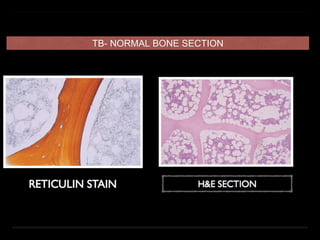
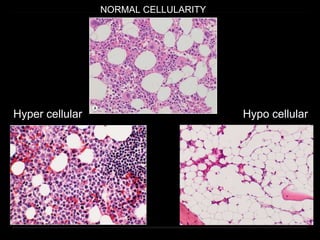
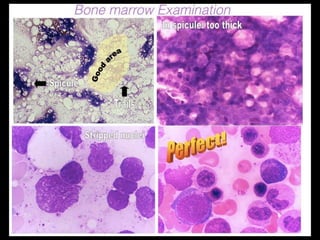
Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration provide qualitative and quantitative assessment of hematopoiesis. It can help make diagnoses of blood disorders like anemia and help stage diseases like lymphoma. The bone marrow has a structured organization with hematopoietic and stromal components. Biopsy and aspiration samples are analyzed microscopically after staining to evaluate cellularity, maturation of blood cell lineages, iron stores, and detect any abnormalities. This procedure helps diagnose conditions affecting the bone marrow including infections, storage diseases, and cancers.




























![95% RANGE MEAN[12] MEAN[11]
Myeloblasts 0–3 1.4 0.4
Promyelocytes 3–12 7.8 13.7[*]
Myelocytes (N) 2–13 7.6 –
Metamyelocytes 2–6 4.1 –
Neutrophils 22–46 32.1M; 37.4W 35.5
Myelocytes (E) 0–3 1.3 1.6
Eosinophils 0.3–4 2.2 1.7
Basophils 0–0.5 0.1 0.2
Lymphocytes 5–20 13.1 16.1
Monocytes 0–3 1.3 2.5
Plasma cells 0–3.5 0.6 1.9
Erythroblasts[†] 5–35 28.1M; 22.5W 23.5
Megakaryocytes 0–2 0.5
Macrophages 0–2 0.4 2.0
Normal ranges for differential counts on aspirated bone
marrow (500 cells should be counted)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bonemarrow-4-180106181202/85/Bone-marrow-biopsy-and-interpretation-55-320.jpg)