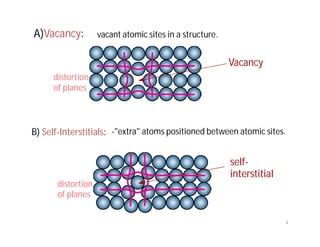
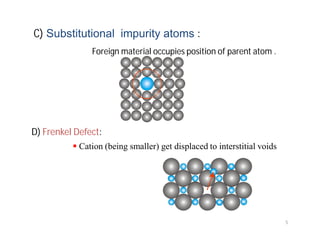
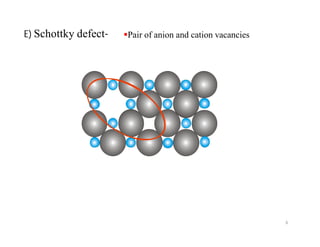
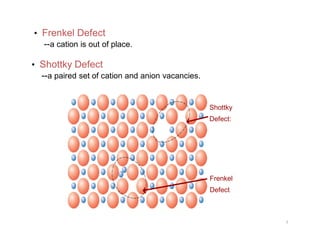
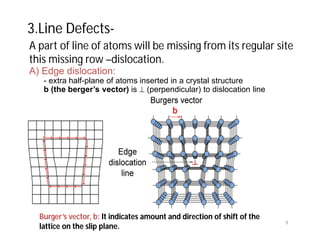
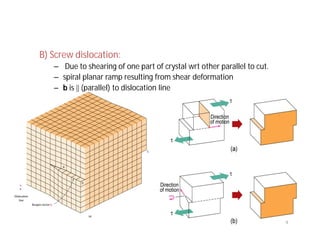
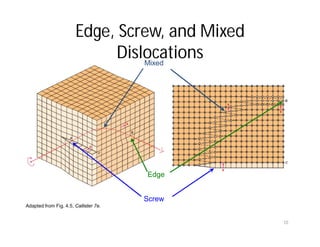
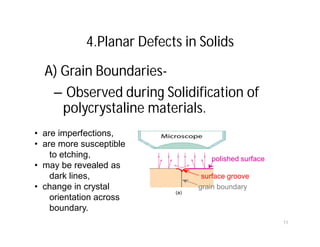
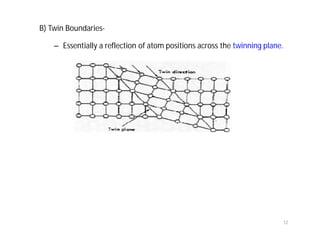
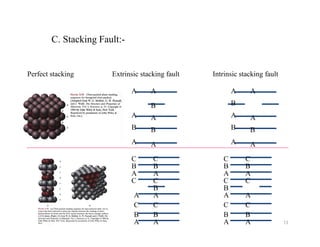
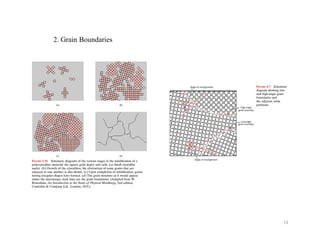
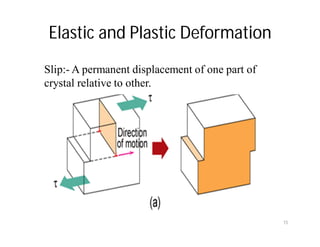
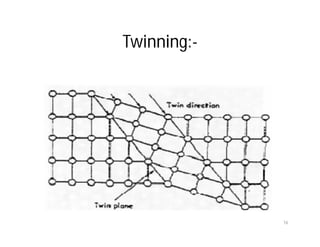
This document discusses various types of imperfections that can occur in crystal structures, including point defects (vacancies, self-interstitials, substitutional impurities), line defects (dislocations like edge and screw dislocations), and planar defects (grain boundaries, twin boundaries, stacking faults). It provides examples of each type of defect, diagrams to illustrate defects like vacancies, interstitials, and different types of dislocations, and brief explanations of defects like Frenkel defects and Schottky defects. The document also mentions defects leading to properties like specific heat and electrical resistance, and discusses concepts like slip and twinning during plastic deformation.