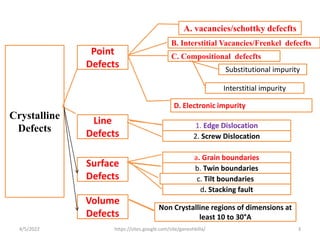
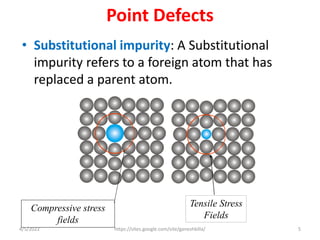
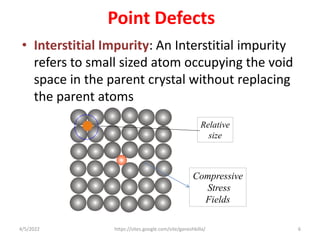
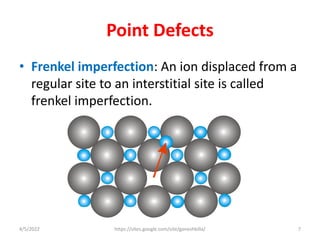
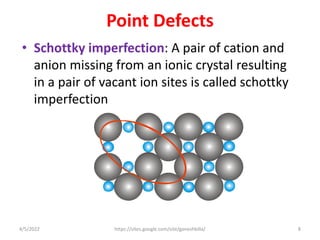
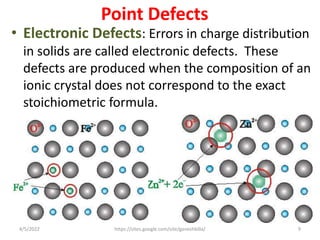
This document discusses various types of defects in crystals, including point defects like vacancies and interstitial atoms, line defects like edge and screw dislocations, surface defects such as grain boundaries and twin boundaries, and volume defects involving non-crystalline regions. Point defects involve missing or extra atoms, while line defects are one-dimensional imperfections described by Burgers vectors. Surface defects lie at crystal interfaces and boundaries. Volume defects involve large vacancies or non-crystalline regions within crystals.