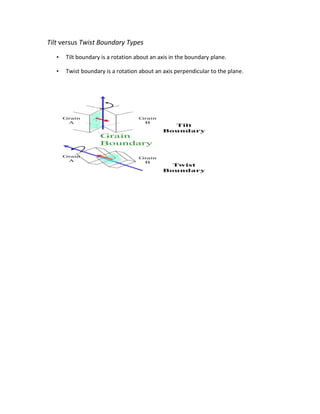
This document discusses types of grain boundaries in materials. It begins by explaining that grain boundaries can vary in their characteristics, such as energy and mobility, and that this affects the properties and evolution of materials. There are different ways to classify grain boundaries, including using tilt and twist descriptions. A tilt boundary involves a rotation about an axis within the boundary plane, while a twist boundary involves a rotation about an axis perpendicular to the plane. The document provides diagrams to further illustrate tilt and twist grain boundary types.


![9 Rotations at a Grain
Boundary
x
z
y
gA
-1
gB In terms of orientations:
rotate back from position A
to the reference position.
Then rotate to position B.
Compound (“compose”)
the two rotations to arrive
at the net rotation between
reference the two grains.
position:
(001)[100]
-1
Net rotation = gBgA
NB: these are passive rotations
10
Alternate Diagram
-1
gA
gB
gC
gD
TJABC
TJACB
gBgA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofgrainboundry-141203011854-conversion-gate02/85/Types-of-grain-boundry-4-320.jpg)