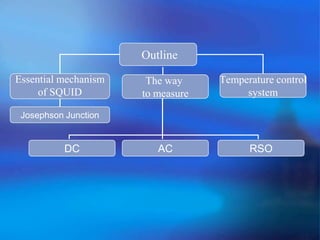
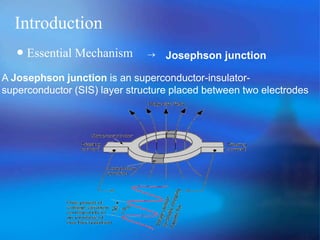
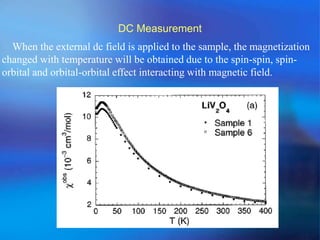
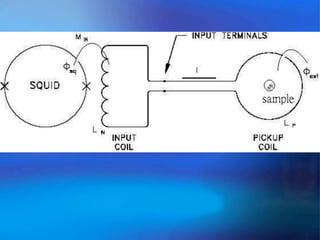
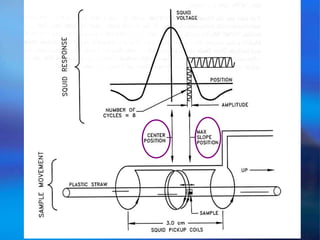
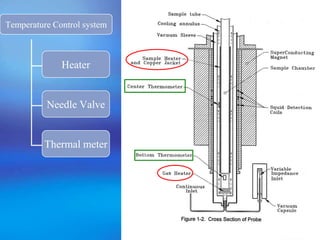
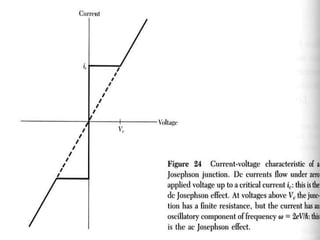
The document discusses the Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID), which uses the Josephson junction effect to achieve extremely sensitive magnetic flux-to-voltage conversion. SQUIDs can be used to precisely measure small magnetic fields and currents. The document outlines how SQUIDs work and their applications in measuring DC and AC magnetic fields. It also describes temperature control systems, reciprocating sample options (RSO), and considerations for optimizing RSO measurements.







![Conclusion
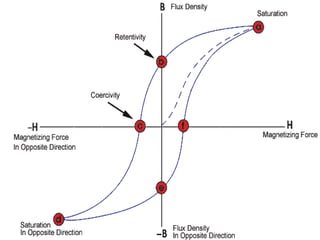
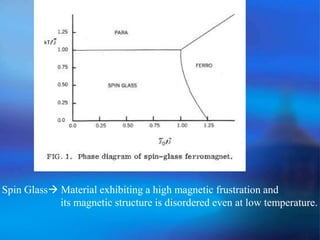
Tc [Curie Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic
and ferromagnetic behavior.
TN [Neel’ Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic
and Antiferromagnetic behavior.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/squid2-131003080324-phpapp01/85/Squid2-16-320.jpg)


![Tc [Curie Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic
and ferromagnetic behavior.
TN [Neel’ Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic
and Antiferromagnetic behavior.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/squid2-131003080324-phpapp01/85/Squid2-21-320.jpg)