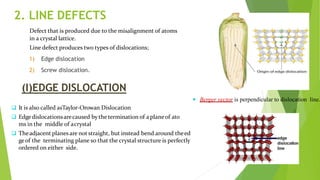
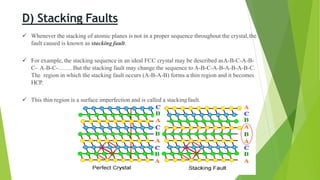
The document discusses crystal defects and their significance. It begins with an introduction to crystals and crystal defects. There are four main types of crystal defects discussed: point defects, line defects, surface defects, and volume defects. Point defects include vacancies, interstitials, and impurities. Line defects are dislocations like edge and screw dislocations. Surface defects include grain boundaries, twin boundaries, and stacking faults. Volume defects occur on a larger scale and include voids, porosity, and precipitates. In conclusion, the presence discusses how crystal defects can impact properties and significance like improving semiconductor performance or lowering melting points.