Embed presentation
Downloaded 507 times

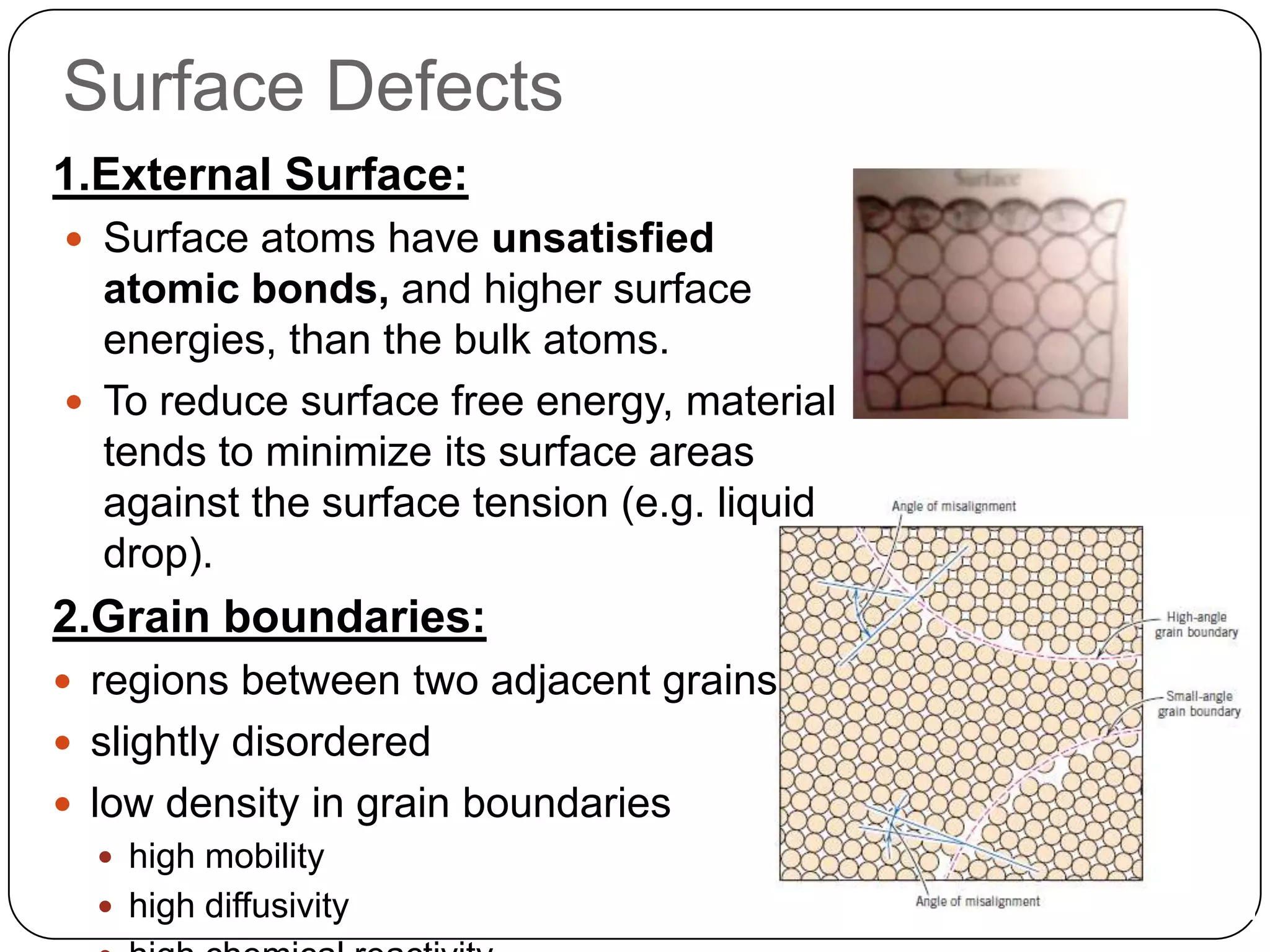
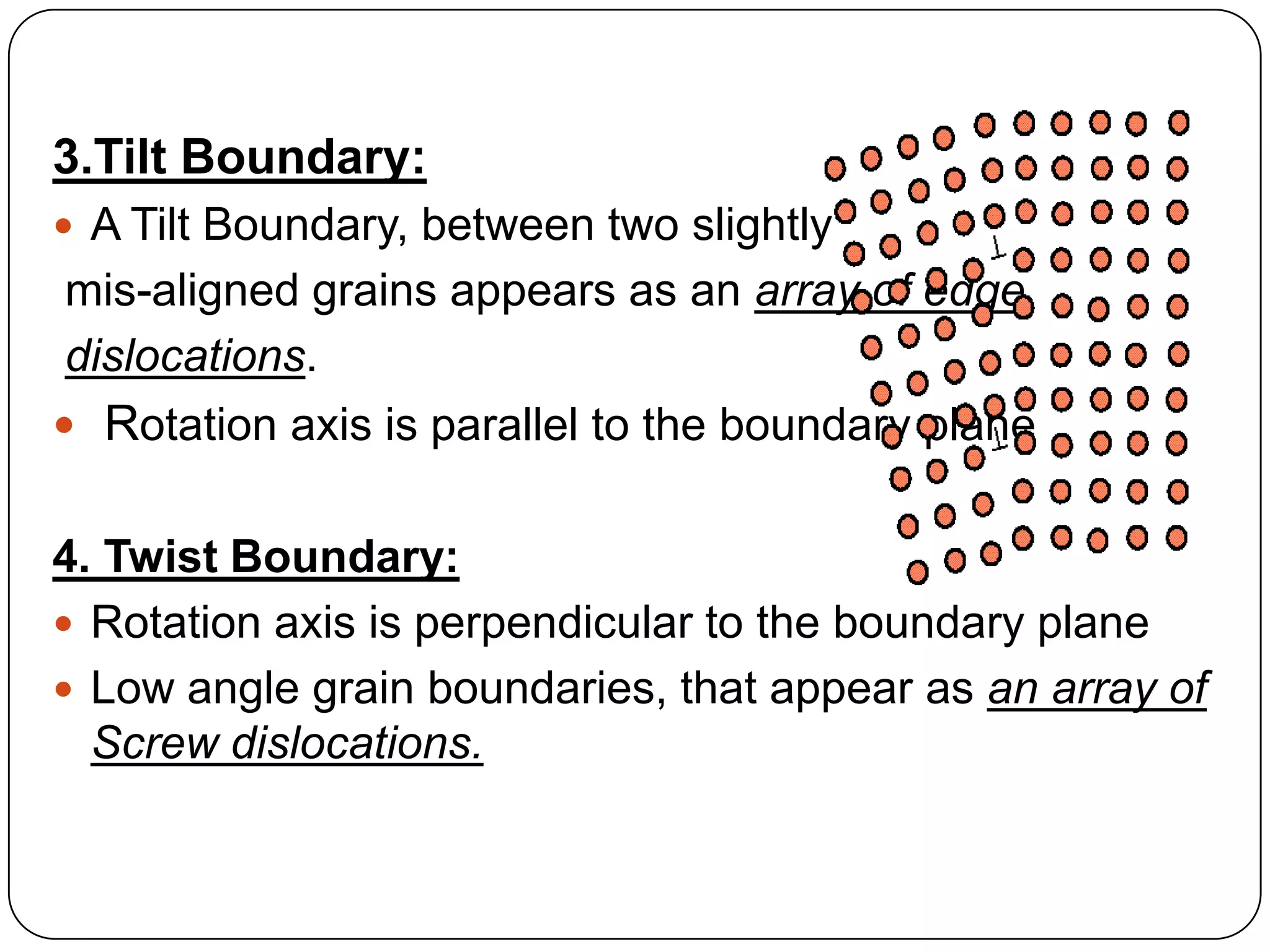
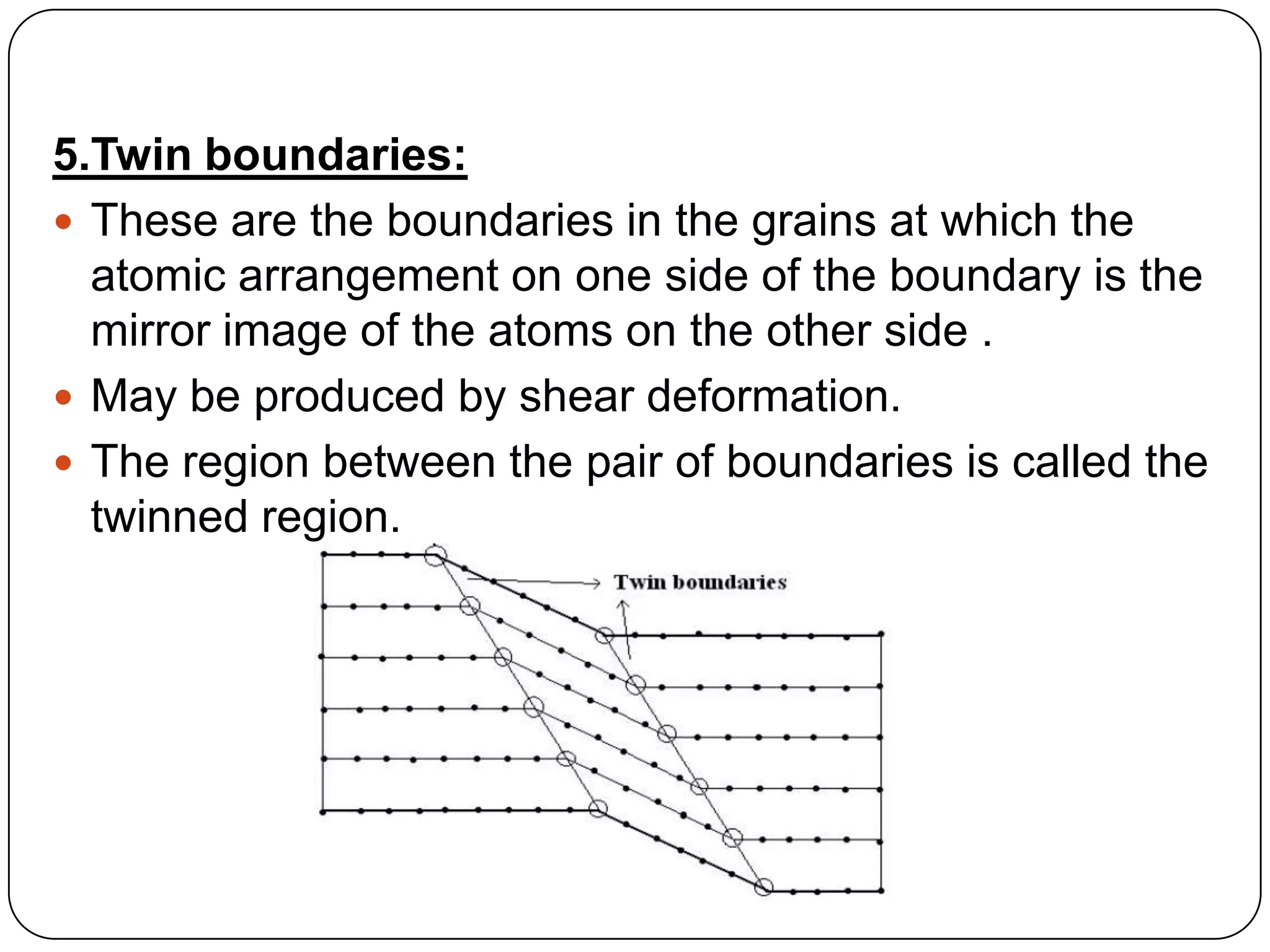
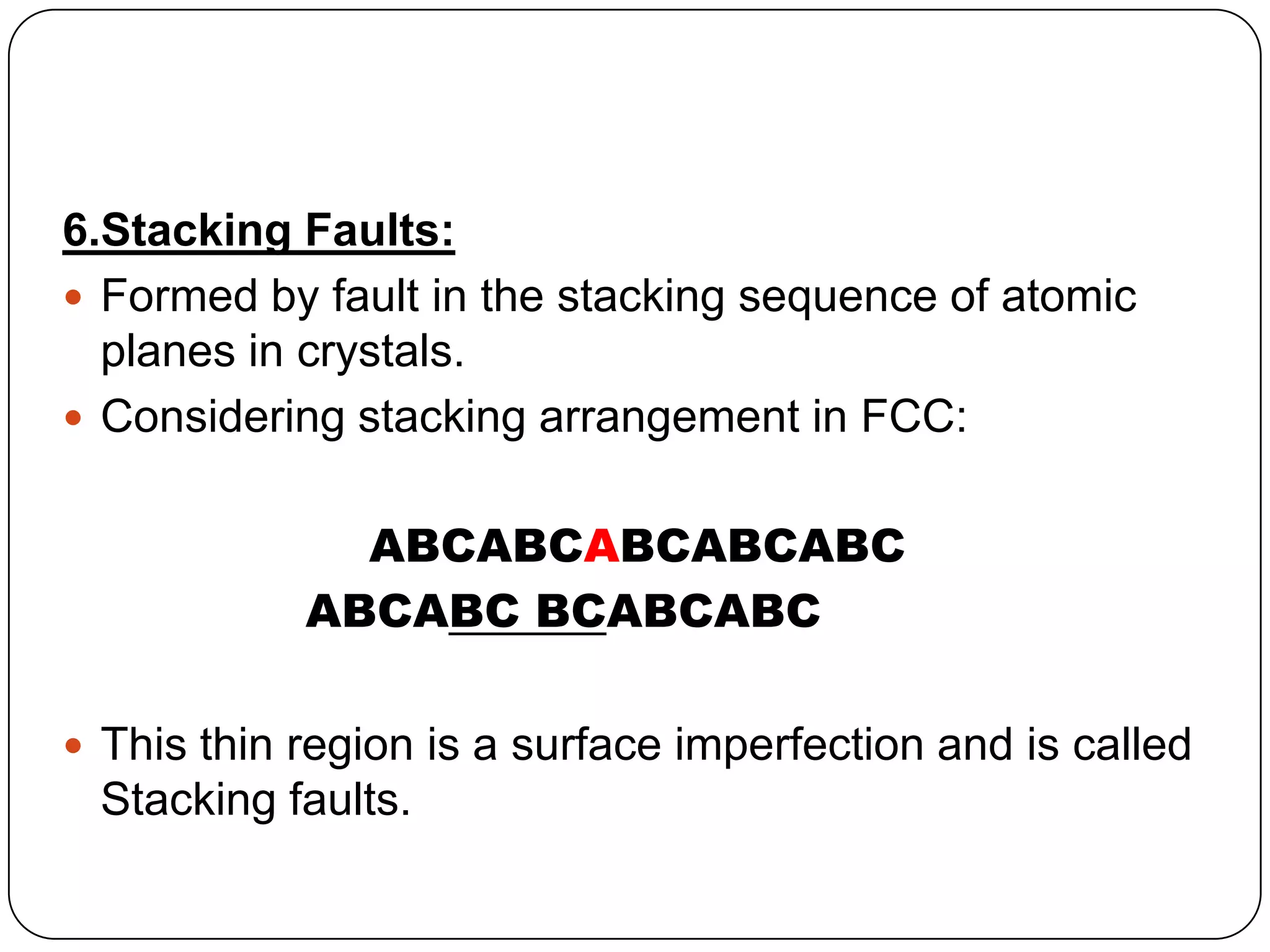


The document discusses various types of surface defects that can occur in crystals, including external surfaces, grain boundaries, tilt boundaries, twist boundaries, twin boundaries, and stacking faults. External surfaces have unsatisfied atomic bonds and higher surface energy than bulk atoms. Grain boundaries are regions between two adjacent grains that are slightly disordered with low density and high mobility. Tilt boundaries appear as arrays of edge dislocations when grains are misaligned with a parallel rotation axis. Twist boundaries have a perpendicular rotation axis and form as arrays of screw dislocations for low angle grain boundaries. Twin boundaries are mirror images of atomic arrangements across the boundary formed by shear deformation. Stacking faults are imperfections in the stacking sequence of atomic planes in crystals.





