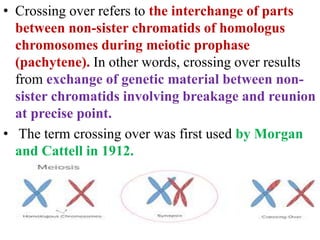
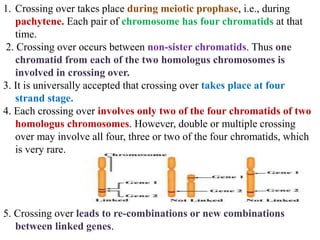
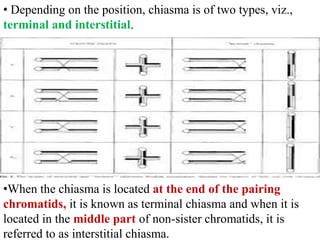
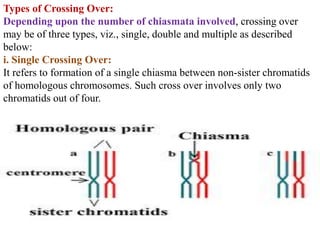
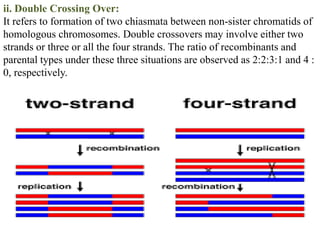
Crossing over refers to the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. It results in new combinations of genes and genetic variation. Crossing over occurs via the formation of chiasmata, where segments are exchanged between chromatids. It can involve two, three, or all four chromatids, and can be single, double, or multiple. Factors like temperature, radiation, age, and nutrition can influence the rate of crossing over. Its significance includes providing evidence for gene order and creating genetic variation important for breeding programs.