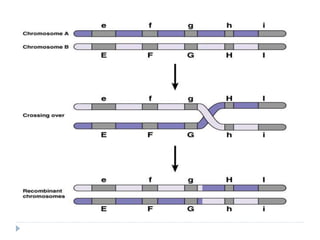
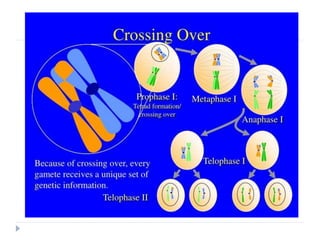
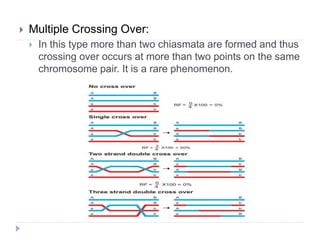
Crossing over is a genetic process involving the exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, resulting in new combinations of genes. It occurs during prophase-1 and metaphase-1, influenced by factors such as temperature and nutrition, and occurs more frequently in females. Different types of crossing over include single, double, and multiple crossing over, each varying by the number of chiasmata formed, ultimately contributing to genetic diversity in sexually reproducing species.