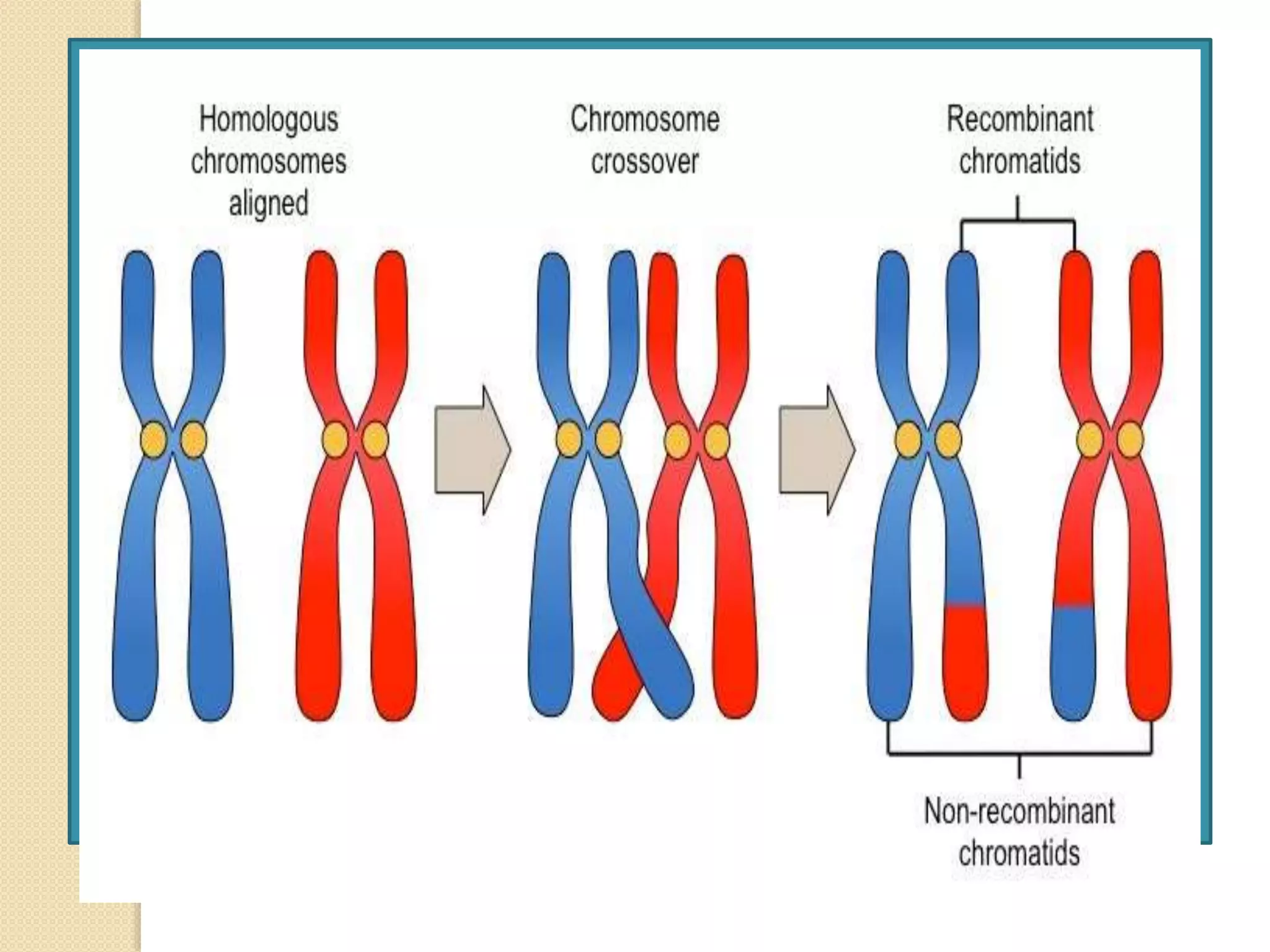
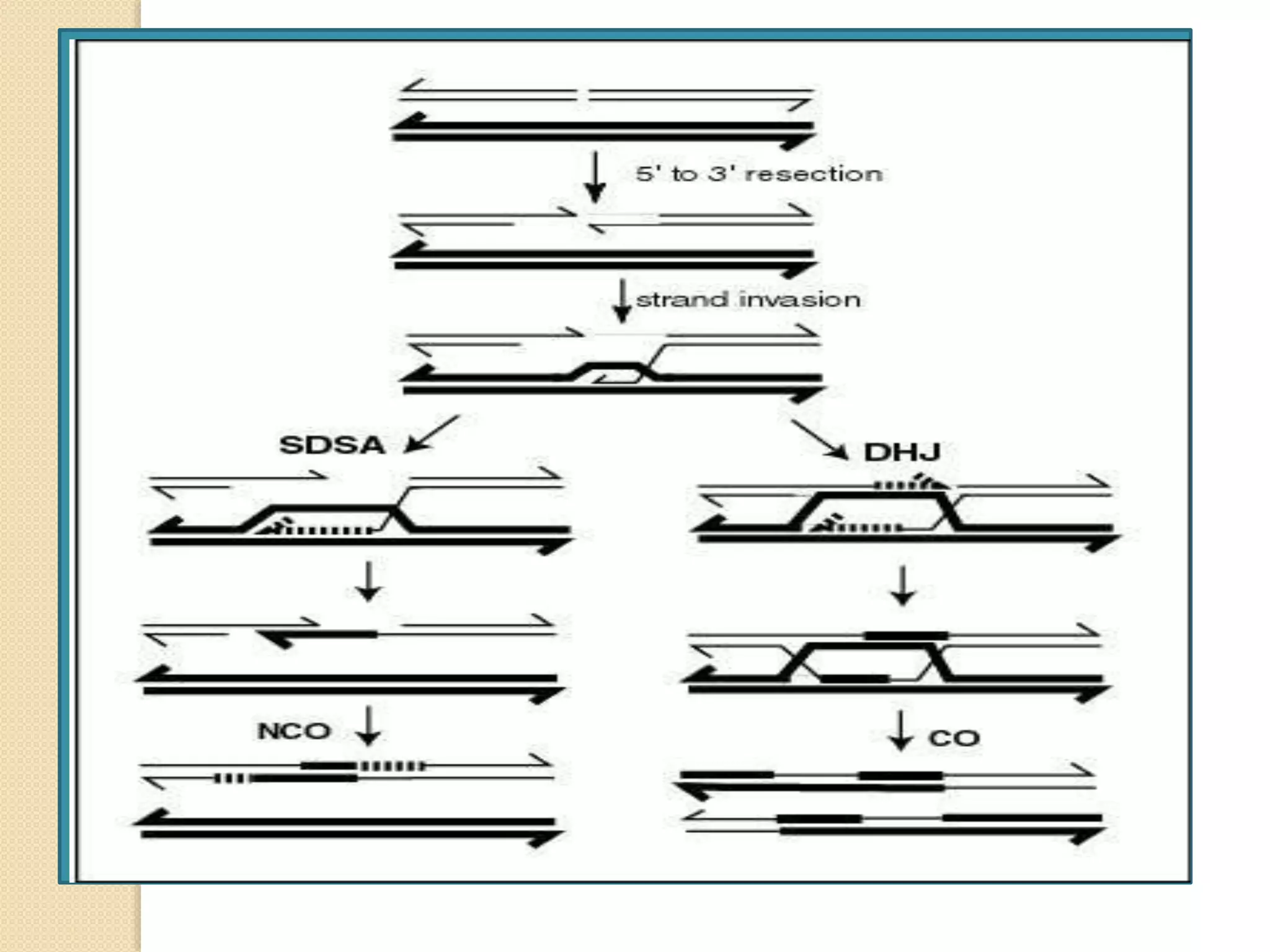
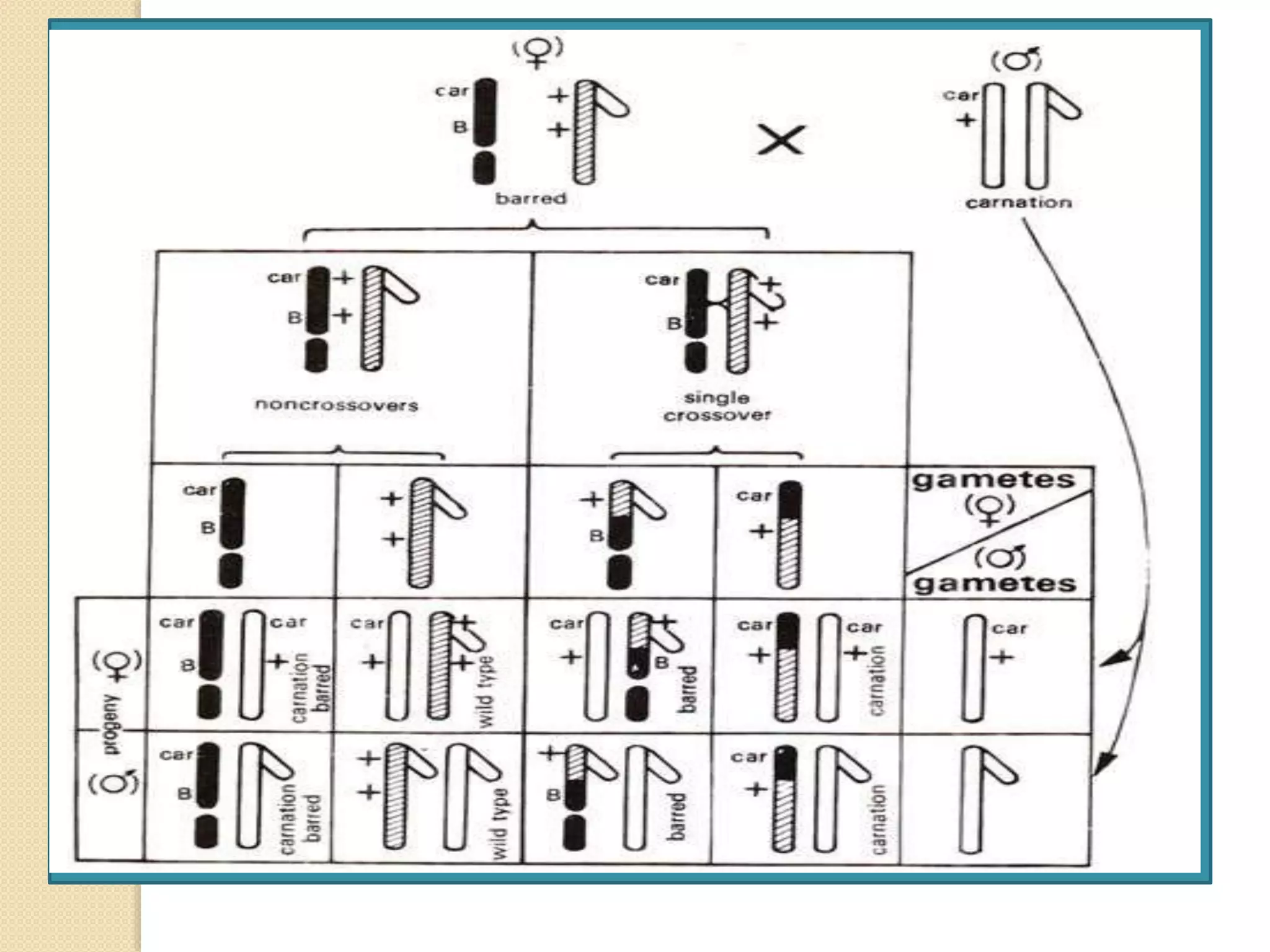
The document discusses the concept of crossing over in genetics, detailing its mechanisms, significance, and the factors influencing recombination frequency. Crossing over is a crucial process during meiosis that results in genetic diversity by exchanging segments between non-sister chromatids, leading to the formation of recombinant phenotypes. The text highlights various types of crossing over, including somatic and germinal crossing, and explores molecular mechanisms and experimental evidence supporting these concepts.