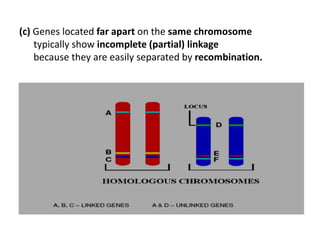
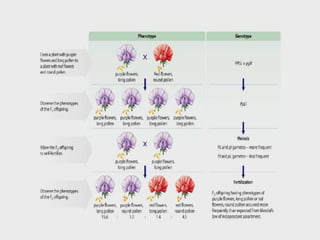
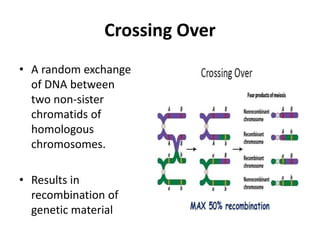
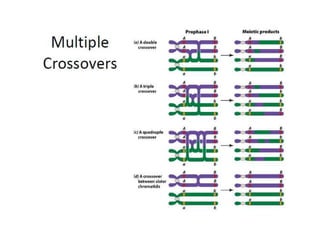
Genetic linkage refers to genes that are located close together on the same chromosome tending to be inherited together. Crossing over can break genetic linkage during meiosis by exchanging DNA between homologous chromosomes, producing recombinant gametes with new combinations of genes. The closer genes are on a chromosome, the less likely they are to be separated by crossing over. Crossing over increases genetic variation and plays an important role in plant and animal breeding.