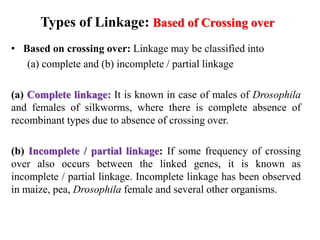
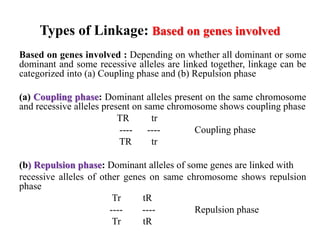
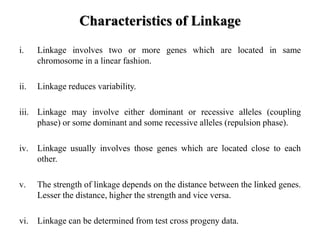
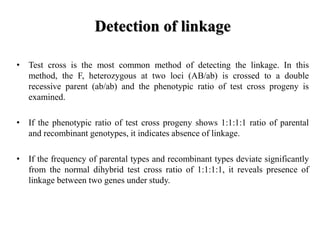
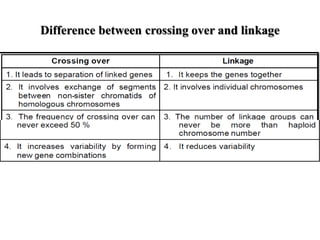
- Linkage refers to the tendency of genes located near each other on the same chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis. This is because genes located close together on a chromosome move together to the same pole during cell division.
- There are different types of linkage based on whether crossing over occurs, the genes involved, and the chromosomes. Linkage can be complete or incomplete depending on the presence or absence of crossing over. It can involve dominant or recessive alleles.
- Linkage is detected through test crosses, where deviations from expected Mendelian ratios indicate genes are linked. The strength of linkage depends on distance between genes, with closer genes showing stronger linkage.