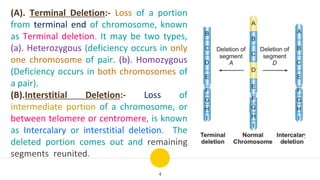
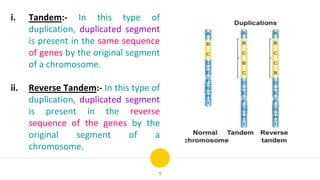
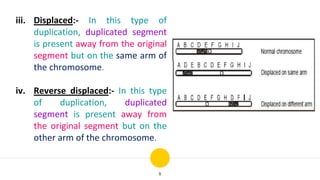
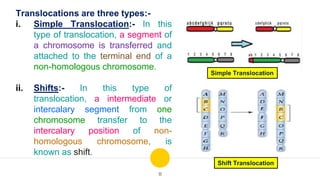
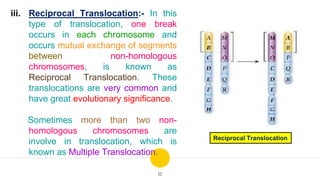
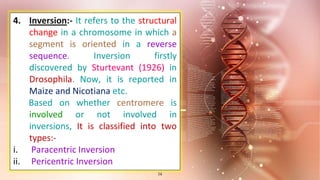
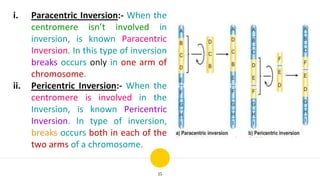
Structural chromosomal aberrations refer to changes in chromosome structure, such as deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions. Deletions involve the loss of a chromosome segment, duplications the presence of a segment twice, translocations the transfer of a segment between non-homologous chromosomes, and inversions the reversal of a chromosome segment. These changes can impact fertility, viability, phenotype, and karyotype by altering gene dosage, order, and position. Structural aberrations play an important role in evolution by creating genetic variability and changing karyotypes.