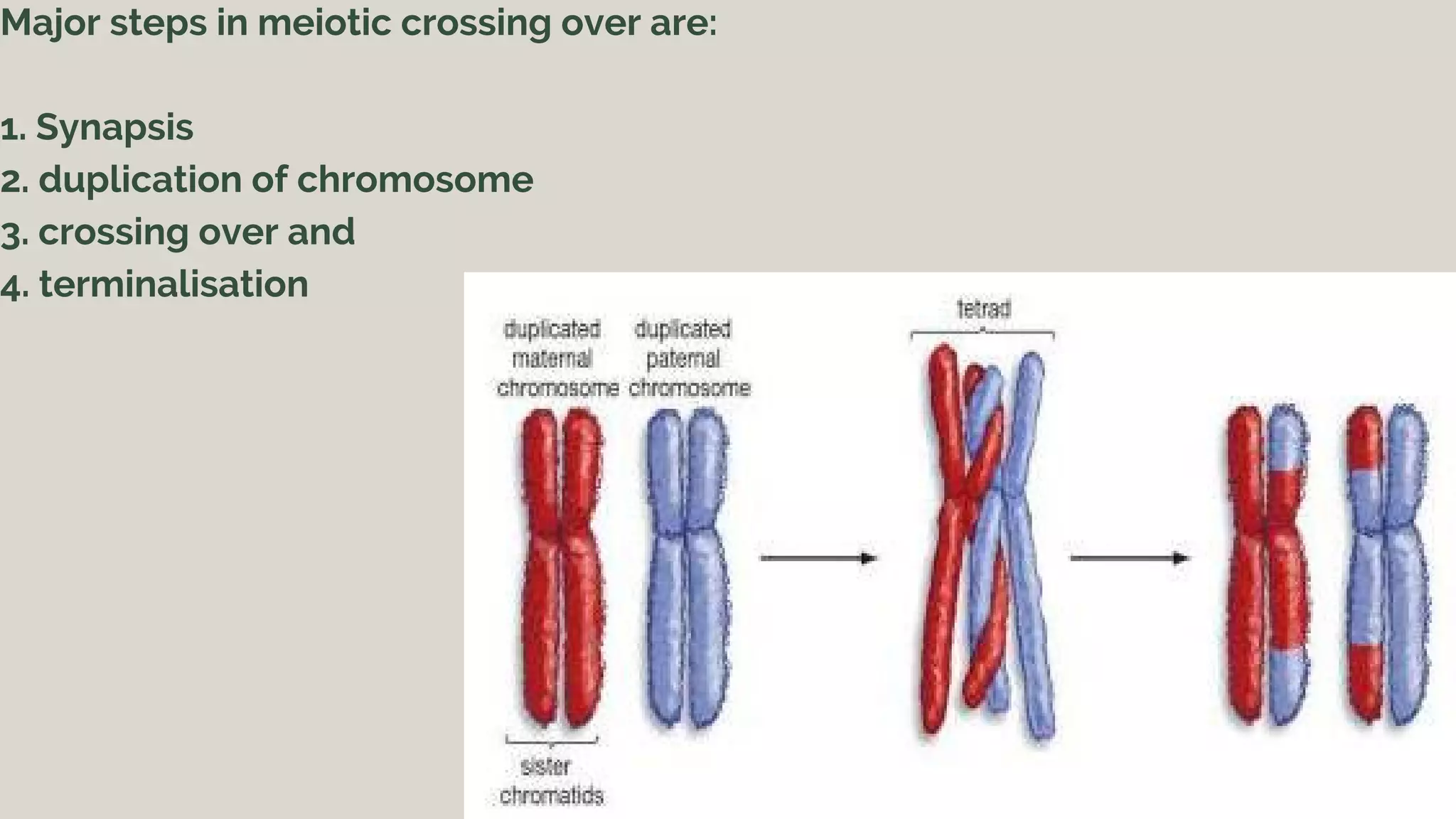
Crossing over occurs during meiosis when segments are exchanged between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, resulting in recombinant chromosomes. There are two main theories for the origin of crossing over: 1) it evolved as a method of DNA repair or 2) it evolved from bacterial transformation to propagate diversity. The major steps of meiotic crossing over are synapsis, chromosome duplication, crossing over itself, and terminalization. Crossing over increases genetic variation between offspring and parents, ensuring individuals do not look exactly alike.