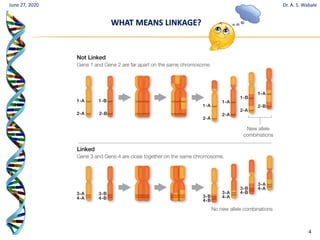
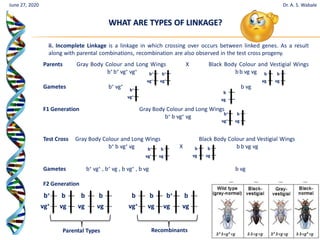
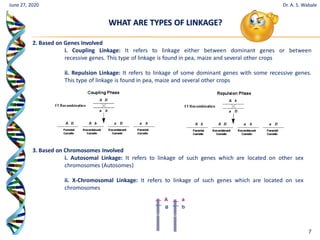
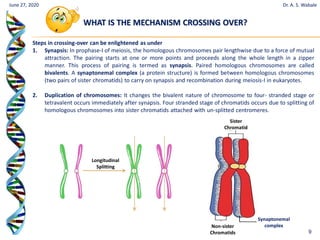
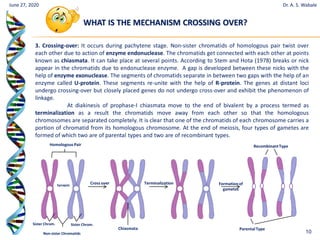
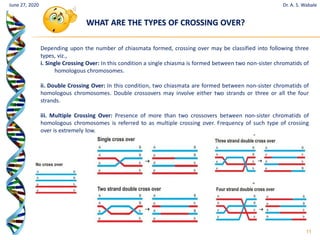
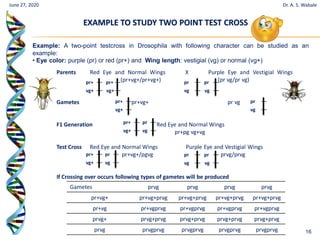
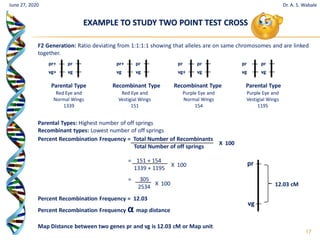
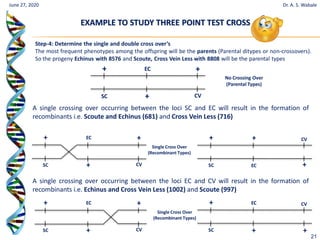
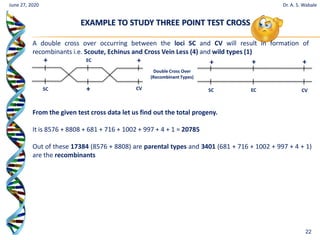
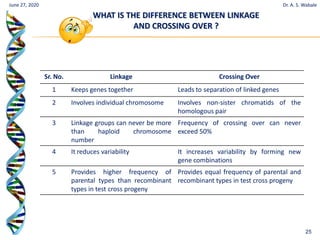
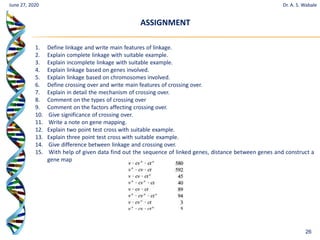
The document discusses linkage and crossing over in genetics. It defines linkage as two or more genes staying together on the same chromosome during inheritance. Crossing over refers to the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during meiosis. There are two main types of linkage - complete linkage where no crossing over occurs, and incomplete linkage where crossing over does occur, resulting in both parental and recombinant offspring types. The document also outlines the mechanism of crossing over and factors that can influence its frequency.