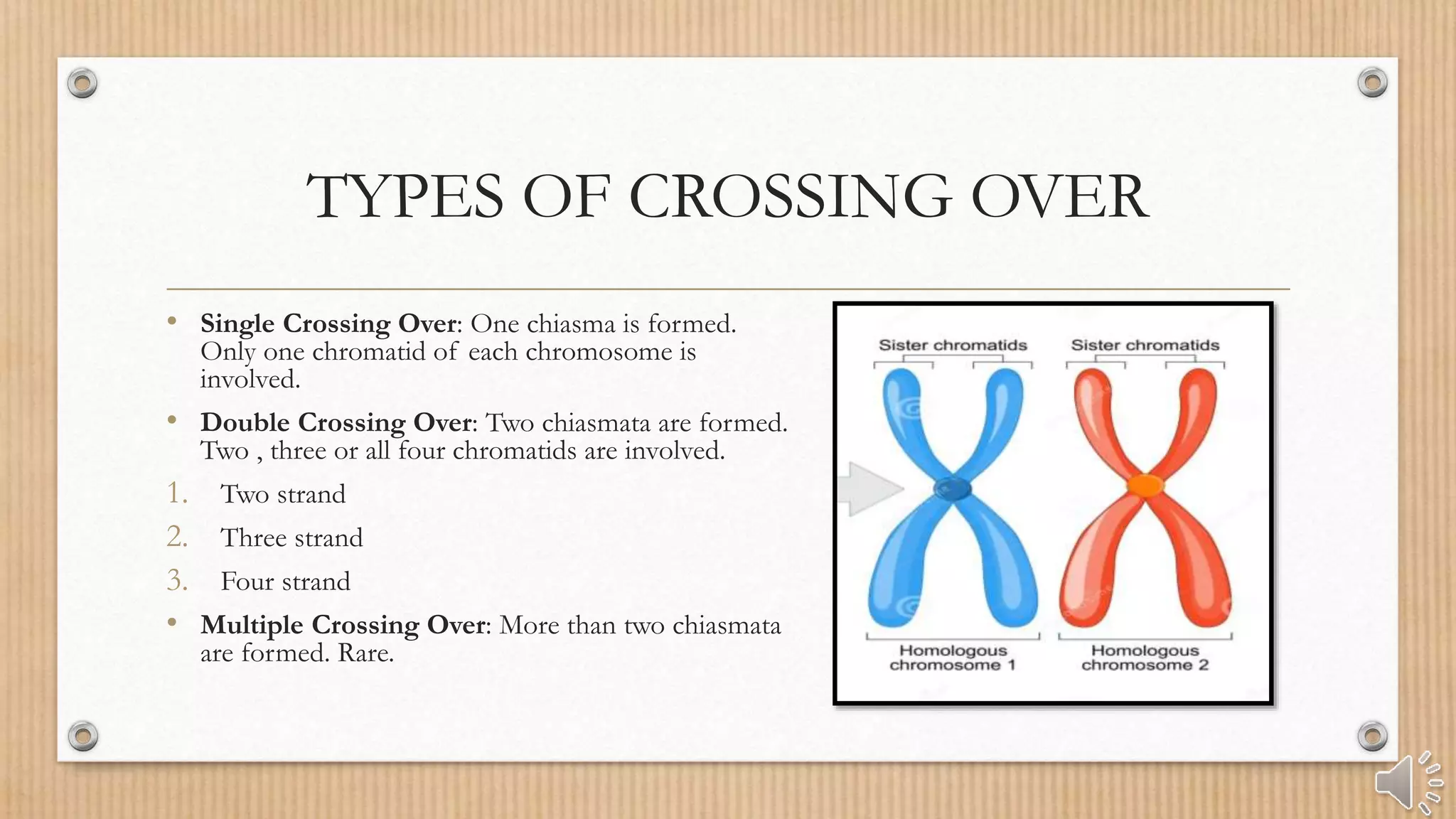
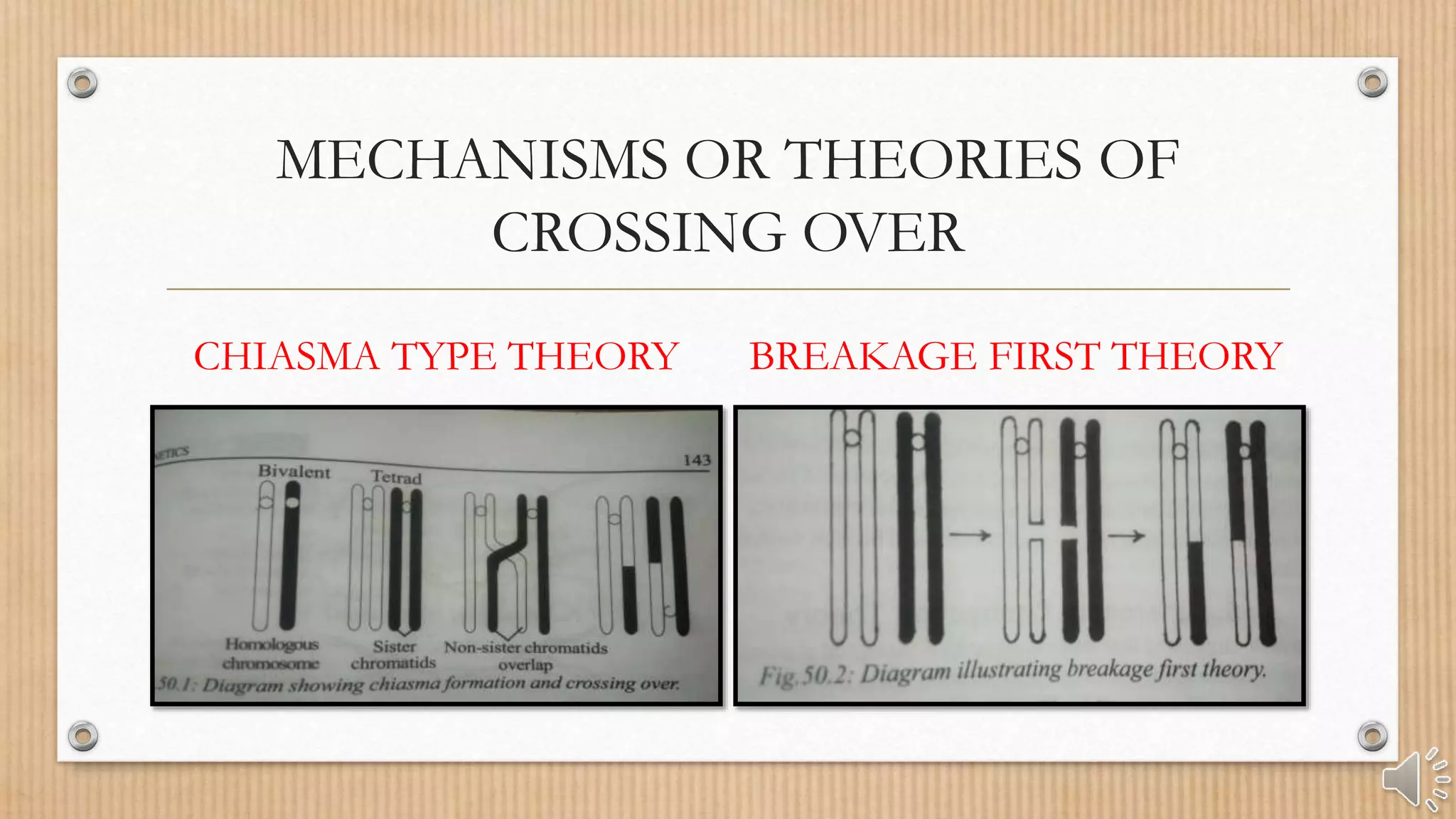
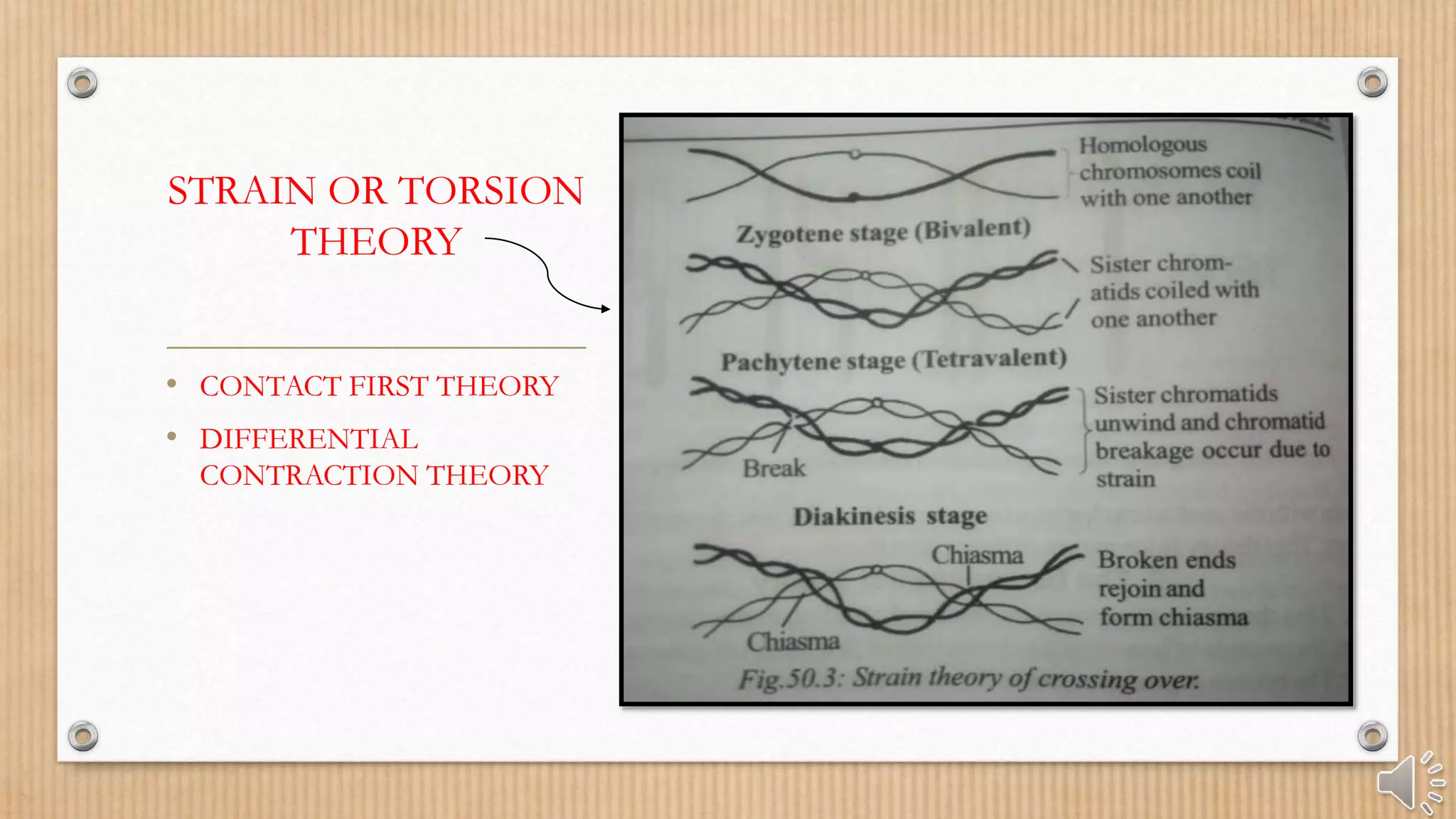
Crossing over is the interchange of chromosomal parts between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, occurring during meiosis. It results in genetic recombination and diversity through the formation of chiasmata, which are essential for proper chromosome segregation. Factors such as temperature, age, and chromosome location can affect the frequency of crossing over.